* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The French Revolution
Arnaud II de La Porte wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the French Revolution wikipedia , lookup
Reign of Terror wikipedia , lookup
Vincent-Marie Viénot, Count of Vaublanc wikipedia , lookup
Louis XVI and the Legislative Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Demonstration of 20 June 1792 wikipedia , lookup
Insurrection of 10 August 1792 wikipedia , lookup
Storming of the Bastille wikipedia , lookup
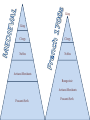
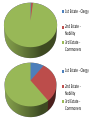
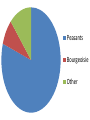
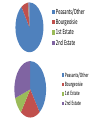
The French Revolution King King Clergy Clergy Nobles Nobles Artisans/Merchants Bourgeoisie Artisans/Merchants Peasants/Serfs Peasants/Serfs ESTATES One of the three classes into which French society was divided before the Revolution. King Clergy Nobles Bourgeoisie Artisans/Merchants Peasants/Serfs 1st estate: Clergy – 130,000 out of 27 million people = .5% Land: Owned 10% Taxes: Paid 0% 2nd estate: Nobility 350,000 out of 27 million people = 1.3% Land: Owned 25-30% Taxes: Paid 0% Held Government, Military, religious, and legal positions 3rd estate: “Commoners: EVERYONE ELSE – 98% Land: Varied among groups Taxes: Paid 100% 1st Estate - Clergy 2nd Estate Nobility 3rd Estate Commoners 1st Estate - Clergy 2nd Estate Nobility 3rd Estate Commoners TAILLE An annual direct tax, usually on land or property, that provided a regular source of income for the French monarchy • Peasants The Third Estate – 75-80% – 35-40% of land • Middle Class “Bourgeoisie” owned the rest • Many peasants had little or no land to own/live on • Also, crafts people, shopkeepers, workers – Struggling b/c price of consumer goods increased faster than wages Peasants Bourgeoisie Other Peasants/Other Bourgeoisie 1st Estate 2nd Estate Peasants/Other Bourgeoisie 1st Estate 2nd Estate Serfdom continues • Ex: Peasants have to pay fees to grind flour/press grapes because lord controlled flour mill/wine press • Harvest time: peasants had to work to harvest noble’s crops Bourgeoisie The middle class, including merchants, industrialists, and professional people Bourgeoisie • 8% of the 3rd Estate population • Owned 20-25% of the land – – – – Merchants Bankers Industrialists Lawyers, doctors, writers • Unhappy with noble’s privileges – Did not want to abolish nobility • About 6500 new nobles had been created by appointment throughout the 1700s – Shared the goals of trying to employ Enlightenment ideas – Both groups increasingly upset with monarchical system Louis XVI LOUIE 16th King of France during the late 1700s, king prior to/during the French Revolution Financial Crisis • Issue #1: Long standing social imbalance • Issue #2: Near collapse of French Budget – Bad harvests – Slowdown in manufacturing • Led to food shortages • Rising prices for food • Unemployment • King and Advisers continued to spend the money! – Wars – Court Luxuries • Esp. Marie Antoinette Estates-General • B/c of budget crisis – Louis XVI forced to call meeting of Estates-General • A meeting of representatives from all 3 estates – Had not met since 1614 • b/c French kings held ALL power • May 5, 1789 – 1st and 2nd estates had 300 reps each – 3rd estate had 600! • Wanted to set up a constitutional government that would make clergy/nobility pay taxes too Meeting with the E-G • Arguments about voting – Tradition • Each estate had 1 vote – SO… 1st+2nd estate could outvote 3rd (even though combined they only represented 2% of the population) • 3rd estate wanted each deputy have one vote – Would eventually give them the majority vote • King said he like things the way they were • 3rd estate had had ENOUGH – Declared themselves the “National Assembly” – Arrived at their meeting chambers to find the doors locked – Moved to an indoor tennis court • Tennis court oath Tennis Court Oath The National Assembly met on an indoor tennis court and vowed to continue meeting until they had formed/adopted a new constitution. Prepping for War • Louis prepared to use force against 3rd estate • July 14, 1789 – 900 Parisians (someone from Paris) gathered at Bastille (BASTEEL) • A prison/armory (Former fortress) – Price of bread record high • Crowd starving and agitated – Rumor said King’s troops were coming • There was supposed to be ammunition in the Bastille – The Parisians stormed the Bastille and after hours of fighting eventually took it • Released 7 prisoners (murderers… yay!) • Beheaded prison warden • Found no munitions – Tore down Bastille brick by brick Revolt Revolution • Louis mistakenly thought the Bastille was just a “Revolt” – Revolution • Could no longer trust royal troops to shoot at mobs • King’s authority had collapsed in Paris • Revolts were breaking out all over France – Enough was enough! • “Great Fear” – Panic sparked by peasant rebellions – Peasants afraid the work of the National Assembly would be stopped by foreign armies – Rumors spread that foreign troops were on their way – Reaction: breaking into houses of lords to destroy records of their obligations Out with the old, in with the new • Aug 4, 1789 – N.A. gets rid of legal privileges of clergy and nobility • Aug 26 – Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen • Inspired by English Bill of Rights & American Declaration of Independence/Constitution • Charter of basic liberties • “liberty, property, security, and resistance to oppression” • All men are equal under the law • Appointment to public office based on talent • No group is exempt from taxes Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen The declaration of guaranteed equal rights drawn up by the National Assembly during the French Revolution. Olympe de Gouges When men made claims that women were not equal under the law because they “do not hope to exercise political rights and functions” she refused to accept their opinions and spoke out in favor of women’s rights. King goes to Paris • Louis refused to accept the National Assembly’s decrees • October 5 – Women’s March – Thousands of Parisian women marched on Versailles – Met with the king • Told him their children were starving because there was no bread • Forced him to accept it • Forced to go to Paris with son and wife as prisoners New Constitution • Limited monarchy – Only “active” citizens could vote • Men over 25 who paid a certain amount of taxes – Really, only wealthy reps. would be chosen • Change spread – Some still wanted more radical changes • Poor • Louis hated the regulation of the church & limited power of the monarchy – Tried to flee with family – Almost made it • Caught and brought back • Assembly met and made a law that allowed to try the king if he turned against the country It gets worse • Other nations feared what the revolution would mean, talked of using force to restore Louis XVI – Assembly struck first – Declared war on Austria • 1792 – Protests – bread shortages • Defeats in the war • Paris radicals declared themselves a commune – Organized mob attack on royal palace and assembly Sans-Culottes “without breeches” Members of the Paris Commune who considered themselves ordinary patriots (they wore long trousers instead of fine knee length breeches of the nobles. Radicals • • • • More radical/violent stage Calling for universal male suffrage Birth of the sans-culottes REALLY starting from the ground up