* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
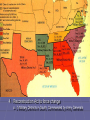
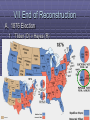
Reconstruction Incl. Review of the Civil War Photos from: http://www.civilwarphotos.net/ Lets start with looking back at the civil war… A. Look at these quote and tell me about the difference in their expectations for the war: B. “ We shall crush out this rebellion as an elephant would trample on a mouse” – words from one confident Union Supporter. C. “Just throw three or four [bomb] shells among those blue-bellied Yankees and they’ll scatter like sheep” – a prediction from a confederate in North Carolina. Lincoln’s 1st inaugural Address (Lincoln elected President 1860) …Apprehension seems to exist among the people of the Southern States that by the accession [rise] of a Republican Administration their property and their peace and personal security are to be endangered … I have no purpose, directly or indirectly, to interfere with the institution of slavery in the States where it exists. I believe I have no lawful right to do so, and I have no inclination to do so. … It follows from these views that no State upon its own mere motion can lawfully get out of the Union;… and that acts of violence within any State or States against the authority of the United States are insurrectionary or revolutionary,… I. Causes for the Civil War A. Economic Differences 1. 2. North Industrial South Agricultural B. Societal Differences 1. 2. North –Abolitionists South – Pro Slavery C. Sectionalism 1. States Rights v. Spread of Slavery D. Spark 1. 2. Election of 1860 Fort Sumter Seating Chart Period 5 Window Door Nick Max Laura Daniel Michael T Julia Mike M. Lauren Vanessa Samrah Angel Brittany Constance Brian Gretchen Matt C Diana Peter Stephen Jenna Shawn Jane Rene Josh Jake Jefferson Davis President of Confederacy I. Timeline – Civil War Civil War begin 1860 Lincoln elected Feb 1861 Southern states secede April 11 1861 Spark: Fort Sumter Civil War ends Jan 1863 The Emancipation Proclamation North Advantages: Productive Power Economic Power South Advantages: Home Court Military Leaders Disadvantages: Conquer unknown territory Disadvantages: Export Economy April 9 1865 General Lee surrenders 620,000 Casualties = Most US deaths in war EVER. “We are here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain – that this nation under God, shall have a new birth of freedom – and that government of the people, by the people, shall not perish from the earth. Gettysburg Address, Nov 19 1863 After 4 years of war, could Northerners and Southerners forgive each other? Could they become unified as citizens of the same country? How to bring former Confederate States back into the United States? What should be done to southern state governments that fought against the United States? Should people who fought against the United State be allowed to become American citizens? Should they be punished? WHAT DO YOU THINK While the Civil War was raging A. The national debate centered on these questions: B. Under what terms should the defeated Confederacy be reunited with the union? C. Who should establish these terms – the President or Congress D. What should be the place of the former slaves in the political life in the South? III. Reconstruction Plans They killed Lincoln! How should we punish the South? A. B. It is April 15, 1865. You are an American in a northern state. Someone has just assassinated President Lincoln! Government soldiers have hunted down the murderer, John Wilkes Booth. He was part of a group of assassins. They also tried to kill Secretary of State William Seward, but he will probably live. Booth and his group hated Lincoln and the Union. We Northerners are sad about the president’s death. We were angry at the South for starting the war and killing so many of our soldiers, but now we are furious! Lincoln wanted to make peace with the South. He wanted to unite the states again quickly. Now Lincoln is dead. It is time to punish the South for what they have done to our country and to our president. C. Comprehension Questions: C. D. E. F. Who are you in the decision? Why are the northern states angry? What part of the country do you think Booth is from? What did Lincoln want to do after the War? A. Decision – How should we punish the South? Choose one or more of the following options: B. Make the southern states pay for the damages caused in the war Make Southerners work for us as slaves Abolish slavery Keep our soldiers in the South Don’t let whites in the South vote Give Blacks the right to vote The US Congress should choose the new southern leaders Redistribute southern property Do not punish the South C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. Timeline – Reconstruction Plans 1863 Lincoln 10 % Plan July 1864 Wade- Davis Bill Civil WarApril ends April 9th 1865 14 1865 Feb 1865 Amendment 13th Iron Clad oath = majority swear allegiance =>Lincoln Pocket-veto Lincoln Assassinated April 1865 Johnson’s Plan Too Lenient: swear loyalty – in return for amnesty = approval of state govt Allowed loyal pardoned whites to vote state must ratify 13th amendment Pro’s: Faster reunion = faster rebuilding Slavery must be abolished Con’s: too lenient terms for the return of the south didn’t change the societal structure of the south Granted pardon to confederate leaders in return for support in upcoming election (1866) A life in Politics A. Results: 1. South Quickly met Johnson’s Conditions a. b. 2. Johnson approved new state govt Southern voters elect Representatives to Congress Rebellion in Congress a. b. c. Standoff betw Radical Republicans and President Radical Republicans refused to let Southern Representatives into Congress Instead Radicals formed a new plan for the South IV. Changes in the South Amendments & Govt Intervention A. Constitutional Amendments 1. 13th Amendment a. 2. 3. abolish slavery 14th Amendments a. b. Passed by Congress: 13 June 1866 Ratified: 9 July 1868 Equal protection & due process of the laws Citizenship 15th a. Passed by Congress: 31 January 1865 Ratified: 6 December 1865 Amendments Passed by Congress: 26 February 1869 Ratified: 3 February 1870 Vote cannot be denied (due to race, color or previous condition of servitude) b. Left states with right to deny suffrage on other grounds B. Result of Amend 13th Black Codes instituted which 1. Restricted rights of Freedmen C. Freedman Bureau Provide Aid to 4 mill freed blacks 1. Establish Hospitals ; Schools; Institutions of higher Ed; Provide Food and Housing D. Sharecropping = rented land pay landowner a share of crop grown on land. E. Derogatory terms 1. 2. Carpetbagger - reformer traveling to South to help fx. in the Freedmans Bureau Scalawags = white southerner who support the Republicans. Term used by Former Confederates Problems to be dealt with 1) Dislike and fighting between the President Johnson and Congress dominated by Radical Republicans 2) Distrust and anger between Freedmen (African Americans) and Southern Whites 3) Anger toward the north – arrival of carpetbaggers (many of them Freedman Bureau employees) 4) Anger towards white southerners backing the Republican Party – scalawags V. Radical Republicans A. Radical Reconstruction 1. Election 1866 = Radicals won control of both houses 2. For states to rejoin = new state constitution + ratify 14th Amendment 3. outraged by rpts of violence against freedmen = seek protection by military 4. Reconstruction Act to force change a. 5 Military Districts in South; Commanded by Army Generals The First Vote appeared on the cover of Harper’s Weekly on Nov 16 1867 A. B. C. D. When was this illustration published Describe the African American in the center? What is he doing? Can you tell what he does for a living? How is the second man different from the first? VI. Constitutional Crisis A. Impeachment - to accuse 1. House vote to impeach (Feb 24 1868) 2. Charge: High crimes and misdemeanors 3. Senate vote to remove 4. Not Convicted/ Political motivated 5. Vote – 1 shy of 2/3 The Presidency of Ulysses. S.Grant By the 1870’s Republicans were losing power. People in the north were growing tired of trying to help the south, and were willing to let the south run their own governments, even if it meant AfricanAmericans losing their rights. Corruption in Grant’s presidency also contributed to the downfall of Republicans. Grant gave many of his friends important jobs, many of which stole money. Grant won reelection in 1872, but many northerners lost faith in reconstruction and democrats won valuable seats in government. The amnesty act of 1872 restored the right to vote to nearly all white southerners who voted for many democrats. Many other issues in the south kept blacks from voting, allowing a great deal of control to move into the hands of democrats. 26 Who elects the President of the U.S? Name our two major political parties? How does a presidential candidate get nominated? Who nominates him/her? A. The citizens of the United States do not elect their president directly. When Americans cast their vote for a presidential candidate, they are really voting for an elector--a delegate pledged to vote for that same candidate. There are 538 such electors chosen in every presidential election. As a group they are known as the electoral college. B. A Candidate must win 270 electoral votes nationwide in order to become president VII End of Reconstruction A. 1876 Election 1. Tilden (D) v Hayes (R) a. Too close to call – electoral votes in dispute b. Deal – Reps promise to end reconstruction S. Dems let Rutherford become President A cartoon threatening that the KKK would lynch carpetbaggers, Tuscaloosa, Alabama, Independent Monitor, 1868. B. Jim Crow Laws/ Segregation http://www.martinfrost.ws/htmlfiles/kkk1.html 1. Voting Restrictions a. Paying to vote = Poll Taxes b. Ability to read = Literacy Tests c. Grandfather must have voted prior to Jan 1868 = Grandfather Clause http://www.martinfrost.ws/htmlfiles/kkk1.ht ml d. Intimidation by KKK 2. Plessy v Ferguson (1896) a. legalize segregation by declaring: “separate but equal facilities” Who is the man on the left? Who is the man on the Right? What are the couple within the shield doing? Explain the drawing to the left of the couple? Explain the drawing to the right of the couple What is the coat of arms for the shield? What is “worse than slavery”? What does it say on top by the eagle? What is “the lost cause”? Does this cartoon in any way illustrate the failure of Reconstruction? Look at the words below; use the words to compose 3 sentences that correctly describe important initiatives of or events during the period of Reconstruction. Freedmen’s Bureau 14th Amendment Education Sharecropping Reconstruction Voting 40 Acres and a Mule Rebuilding Below are some choices of how to deal with the South in our effort to rejoin the Confederacy and the Union; Which would you pick? A. B. C. D. E. Should the south be shown leniency? (10% swear loyalty to union) Should Southern plantations be broken up and given to freed slaves? No involvement in politics of former Confederate Leaders (should not be allowed to vote or hold office) Should the federal government provide food, clothing, jobs and educational opportunities to the Freemen? Should the south be controlled by Congress through deployment of Soldiers to the South?