* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Americans who supported the King Red Coats/ Lobsterbacks
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
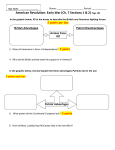
Written by: Greg Clevenger Choosing Sides • Patriots – Supported the Revolution • Loyalists – Americans who supported the King • Red Coats/ Lobsterbacks – British Army British Advantages • Well-equipped • Disciplined • Strongest navy American Advantages • Accuracy of the rifle • Knowledge of the land • Guerilla warfare tactics • Superb command British Leaders • General Charles Cornwallis • General John Burgoyne • Benedict Arnold • William Howe • All considered America one of the worst places to serve Military Leaders—American • George Washington: Commander of Americans Forces • Nathanael Greene: Top Strategist • Henry Knox: Artillery Expert • Benedict Arnold: Commander under Washington The War at Sea • Approximately 3,000 men enlisted—America made 13 Frigates • Most, if not all, were destroyed or captured • Colonial Navy authorized by Continental Congress October 13, 1775 Major Battles • Fort Ticonderoga • Bunker Hill • Trenton Battle of Trenton—1776 • Surprise attack the day after Christmas • Washington crossed the Delaware • Approximately 1000 German soldiers fighting for the British captured Trenton & Princeton • American casualties were four • German leader, Colonel Rall mortally wounded • Washington cleared British from central New Jersey More Significant Battles • Saratoga • Winter at Valley Forge • Yorktown • Were blend of successes and failures for American Army Battle of Saratoga – 1777 • The turning point of the war • The biggest American victory at the time • Approximately 5,000 British surrender to Washington • After the American victory France changed its policies. • Feb. 1778 France and American formed an alliance • France declared war on Britain the next month • Spain declared war in 1779 • Bernardo de Galvez chased British troops out of Louisiana and Florida. Battle of Saratoga – 1777 Valley Forge – 1777-1778 • American Army out of food and clothing • Valley Forge briefly a refuge • Supplies ran out and many died • Washington appeals to Congress for help • Low point for American Army • Any deserters are shot Valley Forge – 1777-1778 • Marquis de Lafayette joined Washington as an aide • Friedrich von Steuben drilled the troops teaching them military discipline Albigence Waldo “The army which has been surprisingly healthy hitherto, now begins to grow sickly…I am sick—discontented—and out of humor.” —Albigence Waldo (1777) Single click the speaker icon to hear the clip >>>> Battle of Yorktown—1781 • French blockade aided this final battle • Escape for the British was impossible • British General Cornwallis faced American forces approximately twice his size John Paul Jones Yorktown • Approximately 8,700 British troops surrendered • Pinned in by American and French Naval fleets • General Benjamin Lincoln accepted the surrender sword • British bands played “The World has Turned Upside Down” The Treaty of Paris—1783 • Officially ended the American Revolution • Set many geographic borders, including U.S. and Canada • Florida was returned to Spain • British merchants must be paid for lost items • Loyalists must be paid for lost property The Articles of Confederation • Written by John Dickson in 1777 • Ratified in 1781 • Governed Americans in 1781-1787 • Paved way for new Constitution Articles of Confederation • • • • NO President (Executive) NO Army NO Courts (Judicial) NO Taxing Power (monetary problems) • NO power to enforce laws (regulate trade) • States were sovereign The U.S. Constitution Constitution • Provided 3 Branches of Gov. – Executive – Legislative – Judicial • Pres. Commander in Chief of Military • Congress can levy tax and pass laws • Federal Gov. is sovereign but states have rights. Effects/Results/Outcomes Northwest Ordinance of 1787 – Set up rules for statehood once 60,000 people – Outlawed slavery in new states (Northwest territories) – Free education in new states – Allow for Westward Expansion Concluding Thoughts • Eight years • Timeless impact • Subject of countless plays and films • Maker of heroes • Birth of a nation