* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sex-linked Inheritance - Chapman @ Norquay School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
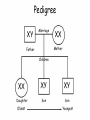
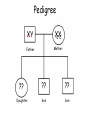
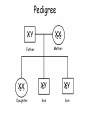
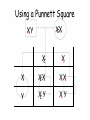
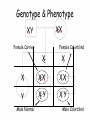
Sex-linked Inheritance Objectives • Know the difference between autosomal chromosomes and sex chromosomes. • Understand sex-linked inheritance. • Be able to create a family pedigree. • Solve sex-linked problems using a Punnett square Gender Determination in Humans • • • • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. 22 of them are called autosomal. The 23rd pair are the sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes determine whether an offspring will be male or female. • XX = Female • XY = Male Pedigree XY Marriage XX Mother Father Children XX XY XY Daughter Son Son Oldest Youngest Red/Green Colorblindness • The gene which allows us to distinguish between red and green is on the X chromosome. XC XC XC Xc Xc Xc = Female with normal vision = Female carrier = Female who is colorblind Red/Green Colorblindness • For males, it appears to be easier to inherit sex-linked traits. XC Y Xc Y = Male with normal vision = Male who is colorblind Pedigree XY c XX CC Father Mother ?? ?? ?? Daughter Son Son Pedigree XY c XX CC Father Mother XX C c XY C XY C Daughter Son Son Using a Punnett Square XX Cc XY c XC Xc Xc XC Xc Xc Xc Y XC Y Xc Y Genotype & Phenotype XX Cc XY c Female Carrier Female Colorblind XC Xc Xc XC Xc Xc Xc Y XC Y Xc Y Male Normal Male Colorblind Hemophilia A sex-linked bleeding disorder (dangerous) XX H H = Female normal XX H h = Female carrier XX h h = Female with hemophilia XY H = Male normal XY h = Male with hemophilia Review • What is the general format for a pedigree? • Why are Punnett Squares better to use sometimes? • Why do sex-linked traits affect males more frequently than females? Important Point • Some sex-linked traits are dominant. This means that even if the female is only a carrier of the illness, she will be affected with the disease. • The dominant gene dominates the gene pair. Practice Problems 1. Muscular dystrophy is a sex-linked illness. Draw a pedigree showing the sons and daughter of an affected father and a normal mother. 2. Draw a Punnett Square to show the same illness for an affected father and a carrier mother.