* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transport and Circulation - Jamestown Public Schools
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
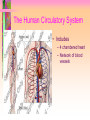
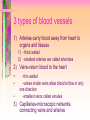
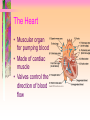
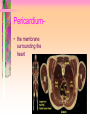
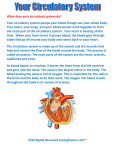
Transport and Circulation Ch 37 Transport • The process by which substances move into or out of cells. Review-Transport Across a Cell Membrane • This is essential for homeostasis. • Remember, the cell membrane is selectively permeable. Getting across the cell membrane 1) diffusion-movement from high to low concentration 2) osmosis-diffusion of water 3) active transport-using energy to move materials across membrane When does this occur? Review-Transport in Protists • Materials diffuse in or out of cells based on concentration differences. • Or, active transport is used to keep internal concentrations higher than external environment. Review-Transport in Plants • Plants have specialized tissues – Xylem-transports water up – Phloem-transports food (glucose) and nutrients up and down Transport in Animals • Hydra-substances diffuse into and out of organism by active and passive transport • Earthworm-closed circulatory system • Insects-open circulatory system • Mammals-closed circulatory system The Human Circulatory System • Includes – 4 chambered heart – Network of blood vessels 3 types of blood vessels 1) Arteries-carry blood away from heart to organs and tissues 1) -thick walled 2) -smallest arteries are called arterioles 2) Veins-return blood to the heart • -thin walled • • -valves inside veins allow blood to flow in only one direction -smallest veins called venules 3) Capillaries-microscopic networks connecting veins and arteries QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture. The Heart • Muscular organ for pumping blood • Made of cardiac muscle • Valves control the direction of blood flow Heartbeat • Caused by the alternating relaxation and contraction of heart – Diastole=relaxation – Heart fills with blood – Systole=contraction – Blood flows out of the heart into the 2 largest arteries » Aorta-carries blood to body tissues » Pulmonary arteries-carries blood to lungs Pericardium• the membrane surrounding the heart Structure of heart • -4 chambers – 2 atria-the upper chambers – 2 ventricles-the lower chambers • Oxygen poor blood is on the right side • Oxygen rich blood is on the left side Diagram of Heart Ideal Blood Pressure Systole 120/80 Diastole High blood pressure is known as Hypertension Pulse-expansion and relaxation of arteries that can be felt at certain pressure points QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture. Prevention of Heart Disease • • • • • • Don’t smoke Reduce foods high in cholesterol Monitor blood pressure Limit your salt intake Exercise regularly/avoid obesity Manage stress Systems related to circulation • • • • Lymphatic Excretory (renal circulation) Respiration (pulmonary circulation) Digestive (hepatic circulation) QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture.