* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LIGHT: What is it?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
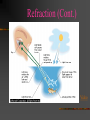
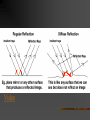
NATURE OF WAVES © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Waves (Def.) – A wave is a disturbance that transfers energy. Medium – Substance or region through which a wave is transmitted. Speed of Waves – Depends on the properties of the medium. LIGHT: What Is It? © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Video Light Energy Atoms As atoms absorb energy, electrons jump out to a higher energy level. Electrons release light when falling down to the lower energy level. Photons - bundles/packets of energy released when the electrons fall. Light: Stream of Photons © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Electromagnetic Waves Speed in Vacuum 300,000 km/sec 186,000 mi/sec Speed in Other Materials Slower in Air, Water, Glass Speed of Light Video © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Transverse Waves © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Energy is perpendicular to direction of motion Moving photon creates electric & magnetic field Light has BOTH Electric & Magnetic fields at right angles! Electromagnetic Spectrum © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Electromagnetic Spectrum Spectrum – Light we can see Roy G. Biv – Acronym for Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, & Violet. Largest to Smallest Wavelength. Visible Refraction of Light Refraction – Bending of light due to a change in speed. Occurs when the wave enters a new medium. Index of Refraction – Amount by which a material refracts light. Prisms – Glass that bends light. Different frequencies are bent different amounts & light is broken out into different colors. Refraction (Cont.) Video Reflection of Light Reflection – Bouncing back of light waves The Law of Reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection Regular reflection –smooth surfaces scatter light very little. Images are clear & exact. Ex: mirrors Diffuse reflection – reflected light is scattered due to an irregular surface. Ex: walls Video Diffraction The bending of waves around a barrier or through an opening. New waves are formed from the original Light waves diffract much less than sound waves. Wave Interference Two waves combining to form a new wave. Constructive Interference Occurs when waves combine to make a wave with a bigger amplitude. Occurs when the crests overlap, they make higher crests The new amplitude is equal to the net of the the amplitude of the two crests that combine. Destructive Interference Occurs when the waves combine to make a wave with a smaller amplitude. Occurs when the Crest of one wave overlaps With the trough of another wave. If the crest has a larger amplitude than the trough, the crest amplitude decreases and part of it will remain. If the original waves had equal amplitudes, then the crest and through completely cancel each other out.