* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answers File
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
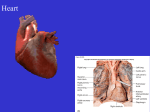
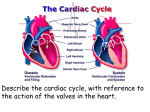
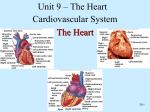
(((((((((((((( B ))))))))))))) Q1: Correct the following statements :(10 M.) 1. Low PH of the small intestine activates digestive enzymes. 2. Final destinations of starch and fat digestion is blood stream. 3. In saltatory conduction the impulse jumps over areas of Purkinje`s fibers. 4. Starling`s law of the heart mean: The greater the initial length of cardiac muscle fiber , the lesser the force of contraction. 5. Rhythmicity of heart is a neurogenic in origin , because cardiac muscles are automatically excited muscles and does not depend on the nervous stimulus. ******************************************************* Q2: A// Speak about types and subtypes of skeletal muscles and their function. (6 M.) B// (Neurons with myelin (or myelinated neurons) conduct impulses much faster than those without myelin) discussed this statement.(4 M.) ********************************************************* Q3: What are the differences between the following: (10 M.) 1. S1, lub & S2 dub 2. Chemical digestion in stomach & small intestine 3. Absolute & Relative Refractory periods 4. Smooth muscles & Skeletal muscles *********************************************************** Q4: What are the cardiac cycle , and what are its phases. (10 M.) 1 Q1: Correct 1. Low PH of the stomach activates enzymes. 2. Final destinations of starch and protein digestion is blood stream. 3. In saltatory conduction the impulse jumps over areas of nodes of Ranvier. 4. Starling`s law of the heart: The greater the initial length of cardiac muscle fiber , the greater the force of contraction . 5. Rhythmicity of heart is a myogenic in origin , because cardiac muscles are automatically excited muscles and does not depend on the nervous stimulus ******************************************************* Q2: A// Speak about types and subtypes of skeletal muscles and their function. (6 M.) • Type I, slow oxidative, slow twitch, or "red" muscle is dense with capillaries and is rich in mitochondria and myoglobin, giving the muscle tissue its characteristic red color. It can carry more oxygen and sustain aerobic activity. • Type II, fast twitch, muscle has three major kinds that are, in order of increasing contractile speed: • a) Type IIa, which, like slow muscle, is aerobic, rich in mitochondria and capillaries and appears red. • b) Type IIx (also known as type IId), which is less dense in mitochondria and myoglobin. This is the fastest muscle type in humans. It can contract more quickly and with a greater amount of force than oxidative muscle, but can sustain only short, anaerobic bursts of activity before muscle contraction becomes painful (often attributed to a build-up of lactic acid). N.B. in some books and articles this muscle in humans was, confusingly, called type IIB 2 • c) Type IIb, which is anaerobic, glycolytic, "white" muscle that is even less dense in mitochondria and myoglobin. In small animals like rodents or rabbits this is the major fast muscle type, explaining the pale color of their meat. B// (Neurons with myelin (or myelinated neurons) conduct impulses much faster than those without myelin) discussed this statement.(4 M.) Because fat (myelin) acts as an insulator, membrane coated with myelin will not conduct an impulse. So, in a myelinated neuron, action potentials only occur along the nodes and, therefore, impulses 'jump' over the areas of myelin - going from node to node in a process called saltatory conduction (with the word saltatory meaning 'jumping'), Because the impulse 'jumps' over areas of myelin, an impulse travels much faster along a myelinated neuron than along a non-myelinated neuron. ********************************************************* Q3: What are the differences between the following: (10 M.) 1. S1, lub & S2 dub (S1 , lub ) a First heart sound , soft and low pitch sound, caused by closure of AV valves. ( S2 , dub) Second heart sound sharp and high pitch sound . caused by closure of semilunar valves 2. Chemical digestion in stomach & small intestine In Stomach:Digestive chemicals•HCL: activates enzymes, breaks up foods •Pepsin: digests proteins •Renin: digests milk In Small Intestine Two sources of enzymes •Liver and Gall bladder (secret Bile: aids in fat digestion and absorption) •Pancreas secretes pancreatic juice (1.Amylase: breaks down starch 3 2.Lipase: breaks down fats 3.Ribonuclease (RNAase): breaks down RNA 4.Deoxyribonuclease (DNAase): breaks down DNA 5.Zymogens: inactive enzymes that activate in the small intestine 3. Absolute & Relative Refractory periods ABSOLUTE - During an action potential, a second stimulus will not produce a second action potential (no matter how strong that stimulus is) corresponds to the period when the sodium channels are open (typically just a millisecond or less) RELATIVE - Another action potential can be produced, but only if the stimulus is greater than the threshold stimulus corresponds to the period when the potassium channels are open (several milliseconds) the nerve cell membrane becomes progressively more 'sensitive' (easier to stimulate) as the relative refractory period proceeds. So, it takes a very strong stimulus to cause an action potential at the beginning of the relative refractory period, but only a slightly above threshold stimulus to cause an action potential near the end of the relative refractory period 4. Smooth muscles & Skeletal muscles Smooth muscle or "involuntary muscle" consists of spindle shaped muscle cells found within the walls of organs and structures such as the esophagus, stomach, intestines, bronchi, uterus, ureters, bladder, and blood vessels.Smooth muscle cells contain only one nucleus and no striations Skeletal muscle or "voluntary muscle" is anchored by tendons to the bone and is used to effect skeletal movement such as locomotion. Skeletal muscle cells are multinucleated with the nuclei peripherally located.Skeletal muscle is called 'striated' because of the longitudinally striped appearance under light microscopy. *********************************************************** 4 Q4: What are the cardiac cycle , and what are its phases. (10 M.) The mechanical events , occurring in the heart within one beat ( from the beginning of a heart beat the next beat ). Cardiac cycle involves five stages . The first two of five are responsible for filling the ventricles. During these two stages , the blood moves from the atria to fill the ventricles. The other three stages are responsible for emptying the ventricles and ejecting blood into the arterial system. To understand the events of the cardiac cycle lets imagine that we are describing events occurring with one half of the heart ( right or left) because the same events occur simultaneously in the other one. Phases of cardiac cycle : 1. Early diastole ( also called the atrial diastole , or complete heart diastole) : During this phase : * Atria are relaxed * Ventricles are relaxed * Semilunar valves are closed * Atrioventricular valves are open During this phase the blood moves passively from the venous system into the ventricles ( about 80 % of blood fills the ventricles during this phase. 2. Atrial systole : During this phase : * Atria are contracting * Ventricles are relaxed * AV valves are open * Semilunar valves are closed * Atrial pressure increases.the a wave of atrial pressure appears here. * intraventricular pressure increases due to the rush of blood then decrease due to continuous relaxation of ventricles. The remaining 20% of blood is moved to fill the ventricles during this phase , due to atrial contraction. 3. Isovolumetric contraction : During this phase : * Atria are relaxed * Ventricles are contracting * AV valves are closed * Semilunar valves are closed * First heart sound The ventricular fibers start to contract during this phase , and the intraventricular pressure increases. This result in closing the AV valves , but the pressure is not yet enough to open the semilunar valves , so the blood volume remain unchanged , and the muscle fibers length also remain unchanged , so we call this phase as isovolumetric contraction ( iso : the same , volu= volume , metric= length). 4. Ejection phase : Blood is ejected from the ventricles into the aorta and pulmonary artery During this phase : * Ventricles are contracting * Atria are relaxed * AV valves are closed * Semilunar valves are open * First heart sound * Intraventricular pressure is increased , due to continuous contraction * increased aortic pressure . 5. Isovolumetric relaxation: This phase due to backflow of blood in aorta and pulmonary system after the ventricular 5 contraction is up and the ventricles relax . This backflow closes the semilunar valves . During this phase : * Ventricles are relaxed * Atrial are relaxed * Semilunar valves are closed . * AV valves are closed. * Ventricular pressure fails rapidly * Atrial pressure increases due to to continuous venous return. the v wave appears here. * Aortic pressure : initial sharp decrease due to sudden closure of the semilunar valve , followed by secondary rise in pressure , due to elastic recoil of the aorta . 6