* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 15 - People @ EECS at UC Berkeley
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electrical discharge machining wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Polymer capacitor wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
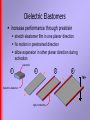
Design Realization lecture 15 John Canny / Jeremy Risner 10/9/03 Last Time Composites: Fiberglass, carbon fiber and kevlar. Hierarchical materials. Cellular materials, honeycomb and foam. This time Polymers for actuation “Wet” versus “Dry” actuation “Wet” – Ionic actuators. Utilize mobility or diffusion of ions. polymer-metal composites conductive polymers others . . . “Dry” – Electronic actuators. Utilize Coulomb forces. dielectric elastomers electrostrictive polymers others . . . Polymer-Metal Composites Ionic Polymer Metal Composites (IPMC) ion exchange polymer membrane – selectively pass ions of a single charge - Dupont Nafion gold plated electrodes on either side applied voltage induces movement of ions and water – causes expansion on one side bending movement Polymer-Metal Composites performance of IPMC strain: 3% energy density: 0.01-0.1 J/cm3 speed: 100 Hz output pressure: 10-30 MPa drive voltage: 1-2 V Polymer-Metal Composites work best in aqueous environments robot fish in tank EAMEX, Japan Conductive Polymers Polypyrrole (PPy)– conductive polymer oxidation-reduction reaction when voltage is applied redox induces ion flow into or out of polymer flow in = expansion requires electrolyte Conductive Polymers performance for PPy bilayer actuator strain: 12.4% energy density: 0.040 J/g speed: <1Hz output pressure: 22 MPa drive voltage: +/- 1V Conductive Polymers attach polymer to a unstretchable film (gold) to create unimorph actuator Electrostricted Polymers Electrostricted graft elastomers motion achieved through electrostriction applied electric field induces a change from one polarized direction to another, or one phase to another. flexible backbone polarized chain Electrostricted Polymers performance strain: 4% energy density: 0.245 J/g speed: 10 kHz output pressure: 22 MPa drive voltage: 2 – 3 KV Dielectric Elastomers elastomer film is sandwiched between compliant electrodes apply electric field: E = V/m Maxwell pressure: p = ee0E2 electrodes squeeze elastomer in thickness apply voltage V+ Dielectric Elastomers materials available off-the-shelf 3M VHB acrylic tape various silicone elastomers desired features high dielectric constant and breakdown strength low elastic modulus – high % elongation thin film Dielectric Elastomers increase performance through prestrain stretch elastomer film in one planar direction fix motion in prestrained direction allow expansion in other planar direction during activation electrode 1 2 3 4 V+ dielectric elastomer rigid constraints Dielectric Elastomers performance strain: >200% energy density: 0.75 – 3.4 J/cm3 speed: 10Hz - 20kHz output pressure: 3.0 – 7.2 MPa drive voltage: 5kV Dielectric Elastomers morphologies planar actuators • butterfly/bowtie unimorphs/bimorphs rolls bellows/speakers Actuator Comparison Actuator Work Actuator Power