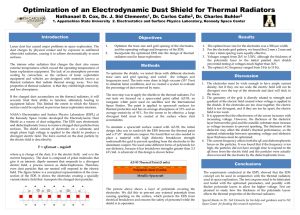
Detection Techniques for Electrical Wires Hidden
... current will enter to capacitor and the capacitor will be charged and produce voltage to coil of inductor. When the coil of inductor receives voltage supply to it and it will have current on it. So the coil of inductor produces magnetic flux around it. When any metal object bring close to the coil o ...
... current will enter to capacitor and the capacitor will be charged and produce voltage to coil of inductor. When the coil of inductor receives voltage supply to it and it will have current on it. So the coil of inductor produces magnetic flux around it. When any metal object bring close to the coil o ...
Accuracy of numerical methods by calculating static and quasistatic
... been calculated from the skull/brain resistivity ratio of 15 [16]. The source current was fixed at 1A in all cases. 2.2. Analytical formulation The analytical model we used to compare our results with has been defined by Rush and Drisscoll [14]. It is capable of calculating potential distribution in ...
... been calculated from the skull/brain resistivity ratio of 15 [16]. The source current was fixed at 1A in all cases. 2.2. Analytical formulation The analytical model we used to compare our results with has been defined by Rush and Drisscoll [14]. It is capable of calculating potential distribution in ...
Influence of the Tool Geometry on the Machining of
... machining for decades as they have no binding phase in their microstructure. Unlike tungsten carbide, the hardness of the ceramics is less decreasing with increasing temperature. Due to this fact, cutting ceramics have a very good wear resistance, even at high cutting speeds [2] compared to other cu ...
... machining for decades as they have no binding phase in their microstructure. Unlike tungsten carbide, the hardness of the ceramics is less decreasing with increasing temperature. Due to this fact, cutting ceramics have a very good wear resistance, even at high cutting speeds [2] compared to other cu ...
Electrical Effects and Devices/Dielectrics and Insulators
... resonance that arises from a displacement and vibration of atoms relative to each other, while an electronic resonance absorption effect occurs over the ultraviolet frequencies as a consequence of the electrons being forced to execute vibrations at the frequency of the external field. The characteri ...
... resonance that arises from a displacement and vibration of atoms relative to each other, while an electronic resonance absorption effect occurs over the ultraviolet frequencies as a consequence of the electrons being forced to execute vibrations at the frequency of the external field. The characteri ...
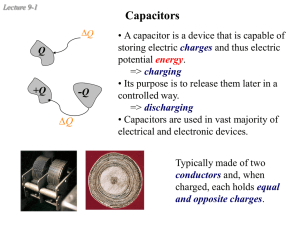
+Q - Purdue Physics
... => charging • Its purpose is to release them later in a controlled way. => discharging • Capacitors are used in vast majority of electrical and electronic devices. Typically made of two conductors and, when charged, each holds equal and opposite charges. ...
... => charging • Its purpose is to release them later in a controlled way. => discharging • Capacitors are used in vast majority of electrical and electronic devices. Typically made of two conductors and, when charged, each holds equal and opposite charges. ...
Dielectric
... reduces the amount of energy stored in the field. The easiest way to think about this is that the capacitance is increased while the charge remains the same so ...
... reduces the amount of energy stored in the field. The easiest way to think about this is that the capacitance is increased while the charge remains the same so ...
"Bioimpedance". In: Encyclopedia of Biomedical Engineering
... introduced, which, however, can be reduced by introducing 3- or 4-electrode systems (Fig. 1). Accordingly, in dielectric theory, the dielectric is considered as an insulator with dielectric losses; in bioimpedance theory, the material is considered as a conductor with capacitive properties. Dry samp ...
... introduced, which, however, can be reduced by introducing 3- or 4-electrode systems (Fig. 1). Accordingly, in dielectric theory, the dielectric is considered as an insulator with dielectric losses; in bioimpedance theory, the material is considered as a conductor with capacitive properties. Dry samp ...
RM4LA32MW
... 2 A at 24 V DC-13 70 °C conforming to IEC 60947-5-1/1991 2 A at 24 V DC-13 70 °C conforming to VDE 0660 3 A at 115 V AC-15 70 °C conforming to IEC 60947-5-1/1991 3 A at 115 V AC-15 70 °C conforming to VDE 0660 3 A at 24 V AC-15 70 °C conforming to IEC 60947-5-1/1991 3 A at 24 V AC-15 70 °C conformin ...
... 2 A at 24 V DC-13 70 °C conforming to IEC 60947-5-1/1991 2 A at 24 V DC-13 70 °C conforming to VDE 0660 3 A at 115 V AC-15 70 °C conforming to IEC 60947-5-1/1991 3 A at 115 V AC-15 70 °C conforming to VDE 0660 3 A at 24 V AC-15 70 °C conforming to IEC 60947-5-1/1991 3 A at 24 V AC-15 70 °C conformin ...
Chapter 24 = Capacitors and Dielectrics Lecture
... • Capacitance (C) is equal to the Charge (Q ) between two charges or charged “regions” divided by the Voltage (V) in those regions. • Here we assume equal and opposite charges (Q) • Thus C = Q/V or Q = CV or V=Q/C • The units of Capacitance are “Farads” after Faraday denoted F or f • One Farad is on ...
... • Capacitance (C) is equal to the Charge (Q ) between two charges or charged “regions” divided by the Voltage (V) in those regions. • Here we assume equal and opposite charges (Q) • Thus C = Q/V or Q = CV or V=Q/C • The units of Capacitance are “Farads” after Faraday denoted F or f • One Farad is on ...
Full paper - International Journal on Smart Sensing and
... insulators [3-6]. Transformers, which are built with tight insulation tolerances, are subject to various aging stresses. While the aging of the insulation material becomes gradually more severe, the leakage current generally tends to increase and arcing discharge may occur [7]. The proof tracking in ...
... insulators [3-6]. Transformers, which are built with tight insulation tolerances, are subject to various aging stresses. While the aging of the insulation material becomes gradually more severe, the leakage current generally tends to increase and arcing discharge may occur [7]. The proof tracking in ...
- University of Bath Opus
... Two machining trials under cryogenic and dry conditions with similar cutting parameters have been conducted. From these machining trials, the machined surfaces have been evaluated for arithmic surface roughness (Ra). Comparison of surface rougness, illustrated in figure 3, suggests that cryogenic co ...
... Two machining trials under cryogenic and dry conditions with similar cutting parameters have been conducted. From these machining trials, the machined surfaces have been evaluated for arithmic surface roughness (Ra). Comparison of surface rougness, illustrated in figure 3, suggests that cryogenic co ...
Dielectric Properties of Materials
... The permittivity of diamond is 1.46 × 10-10 N-1m-2. Determine its dielectric constant and electrical susceptibility. (Given 0 = 8.86 × 1012 C2N-1m-2). The number of atoms in volume of one cubic meter of hydrogen gas is 9.8 × 1026. The radius of the hydrogen atom is 0.53 Å. Calculate the polarizabil ...
... The permittivity of diamond is 1.46 × 10-10 N-1m-2. Determine its dielectric constant and electrical susceptibility. (Given 0 = 8.86 × 1012 C2N-1m-2). The number of atoms in volume of one cubic meter of hydrogen gas is 9.8 × 1026. The radius of the hydrogen atom is 0.53 Å. Calculate the polarizabil ...
Laser Beam Machining
... referred to as the heat-affected zone or HAZ. The heating (and subsequent cooling) waves propagating through the HAZ cause mechanical stress and may create micro cracks (or in some cases, macro cracks) in the surrounding material. These defects are "frozen" in the structure when the material cools, ...
... referred to as the heat-affected zone or HAZ. The heating (and subsequent cooling) waves propagating through the HAZ cause mechanical stress and may create micro cracks (or in some cases, macro cracks) in the surrounding material. These defects are "frozen" in the structure when the material cools, ...
Electrical Discharge Machining- EDM
... referred to as the heat-affected zone or HAZ. The heating (and subsequent cooling) waves propagating through the HAZ cause mechanical stress and may create micro cracks (or in some cases, macro cracks) in the surrounding material. These defects are "frozen" in the structure when the material cools, ...
... referred to as the heat-affected zone or HAZ. The heating (and subsequent cooling) waves propagating through the HAZ cause mechanical stress and may create micro cracks (or in some cases, macro cracks) in the surrounding material. These defects are "frozen" in the structure when the material cools, ...
First Measurement of the Atomic Electric Dipole
... to image no. 2 and background subtraction. Similarly, yparallel;antiparallel is derived from image no. 3. An EDM would cause a polarity-dependent phase shift Δϕ, with the EDM given by d ¼ ℏΔϕ=ð4EτÞ (here τ is the spin precession time with the E field applied). An effect common to both E-field polari ...
... to image no. 2 and background subtraction. Similarly, yparallel;antiparallel is derived from image no. 3. An EDM would cause a polarity-dependent phase shift Δϕ, with the EDM given by d ¼ ℏΔϕ=ð4EτÞ (here τ is the spin precession time with the E field applied). An effect common to both E-field polari ...
ENG165-265.2017 .4
... referred to as the heat-affected zone or HAZ. The heating (and subsequent cooling) waves propagating through the HAZ cause mechanical stress and may create micro cracks (or in some cases, macro cracks) in the surrounding material. These defects are "frozen" in the structure when the material cools, ...
... referred to as the heat-affected zone or HAZ. The heating (and subsequent cooling) waves propagating through the HAZ cause mechanical stress and may create micro cracks (or in some cases, macro cracks) in the surrounding material. These defects are "frozen" in the structure when the material cools, ...
Document
... referred to as the heat-affected zone or HAZ. The heating (and subsequent cooling) waves propagating through the HAZ cause mechanical stress and may create micro cracks (or in some cases, macro cracks) in the surrounding material. These defects are "frozen" in the structure when the material cools, ...
... referred to as the heat-affected zone or HAZ. The heating (and subsequent cooling) waves propagating through the HAZ cause mechanical stress and may create micro cracks (or in some cases, macro cracks) in the surrounding material. These defects are "frozen" in the structure when the material cools, ...
Lecture 4
... referred to as the heat-affected zone or HAZ. The heating (and subsequent cooling) waves propagating through the HAZ cause mechanical stress and may create micro cracks (or in some cases, macro cracks) in the surrounding material. These defects are "frozen" in the structure when the material cools, ...
... referred to as the heat-affected zone or HAZ. The heating (and subsequent cooling) waves propagating through the HAZ cause mechanical stress and may create micro cracks (or in some cases, macro cracks) in the surrounding material. These defects are "frozen" in the structure when the material cools, ...
The Mechanism of Electrode Erosion in Electrical Discharges
... this order must now be considered. A certain (microscopic)volume of metal lying under this area will be suddenly heated, and part of this heat must be dissipated by thermal conduction through the bulk of the metal; the rate at which this can occur has been given previously (8). Heat will also be los ...
... this order must now be considered. A certain (microscopic)volume of metal lying under this area will be suddenly heated, and part of this heat must be dissipated by thermal conduction through the bulk of the metal; the rate at which this can occur has been given previously (8). Heat will also be los ...
EXAM 2
... then opened, and charged capacitor is connected to the uncharged capacitor C2 = 5nC by closing switch S2. The final charge on C2 is A. 10 nC B. 20 nC C. 30 nC D. 40 nC E. 50 nC 6. What maximum potential difference (before it breaks down) can be applied to an air filled parallel-plate capacitor C = 2 ...
... then opened, and charged capacitor is connected to the uncharged capacitor C2 = 5nC by closing switch S2. The final charge on C2 is A. 10 nC B. 20 nC C. 30 nC D. 40 nC E. 50 nC 6. What maximum potential difference (before it breaks down) can be applied to an air filled parallel-plate capacitor C = 2 ...
Capacitance
... boxes except Electric Field Detector. Move the red voltmeter wire to the top plate and the black wire to the bottom plate. 2. Increase the battery voltage between 0 and 1.5V. Record observations for changes in each of the following as you increase the voltage. a. Capacitance ...
... boxes except Electric Field Detector. Move the red voltmeter wire to the top plate and the black wire to the bottom plate. 2. Increase the battery voltage between 0 and 1.5V. Record observations for changes in each of the following as you increase the voltage. a. Capacitance ...
Powerpoint - Appalachian State University
... 1. The electrodes must be wide enough to have ample current density, but if they are too wide the electric field will not be divergent over the top of the electrode and dust will stick to the traces. 2. The geometry of the grid is directly related to strength and gradient of the electric field creat ...
... 1. The electrodes must be wide enough to have ample current density, but if they are too wide the electric field will not be divergent over the top of the electrode and dust will stick to the traces. 2. The geometry of the grid is directly related to strength and gradient of the electric field creat ...
Dielectric
... (I used 1 V=1 J/C: check for yourself that that nasty combination of units simplifies like I claimed, to Coulombs) How much energy is stored in the capacitor now? U=Q*V/2 = 32E-9 C * 12V / 2 = 0.2 micro Joules. Aside: Where exactly is the energy stored, in a capacitor? The answer is that it's stored ...
... (I used 1 V=1 J/C: check for yourself that that nasty combination of units simplifies like I claimed, to Coulombs) How much energy is stored in the capacitor now? U=Q*V/2 = 32E-9 C * 12V / 2 = 0.2 micro Joules. Aside: Where exactly is the energy stored, in a capacitor? The answer is that it's stored ...
Lecture 15 - People @ EECS at UC Berkeley
... Electrostricted graft elastomers motion achieved through electrostriction applied electric field induces a change from one polarized direction to another, or one phase to another. flexible backbone ...
... Electrostricted graft elastomers motion achieved through electrostriction applied electric field induces a change from one polarized direction to another, or one phase to another. flexible backbone ...
Electrical discharge machining

Electrical discharge machining (EDM), sometimes colloquially also referred to as spark machining, spark eroding, burning, die sinking, wire burning or wire erosion, is a manufacturing process whereby a desired shape is obtained using electrical discharges (sparks). Material is removed from the workpiece by a series of rapidly recurring current discharges between two electrodes, separated by a dielectric liquid and subject to an electric voltage. One of the electrodes is called the tool-electrode, or simply the ""tool"" or ""electrode"", while the other is called the workpiece-electrode, or ""workpiece"".When the distance between the two electrodes is reduced, the intensity of the electric field in the volume between the electrodes becomes greater than the strength of the dielectric (at least in some point(s)), which breaks, allowing current to flow between the two electrodes. This phenomenon is the same as the breakdown of a capacitor (condenser) (see also breakdown voltage). As a result, material is removed from both electrodes. Once the current stops (or is stopped, depending on the type of generator), new liquid dielectric is usually conveyed into the inter-electrode volume, enabling the solid particles (debris) to be carried away and the insulating properties of the dielectric to be restored. Adding new liquid dielectric in the inter-electrode volume is commonly referred to as ""flushing"". Also, after a current flow, the difference of potential between the electrodes is restored to what it was before the breakdown, so that a new liquid dielectric breakdown can occur.