* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dielectric Properties of Materials
Viscoelasticity wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Colloidal crystal wikipedia , lookup
Optical tweezers wikipedia , lookup
Density of states wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Acoustic metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Piezoelectricity wikipedia , lookup
Crystal structure wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Negative-index metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Metamaterial antenna wikipedia , lookup
Metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Tunable metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
History of metamaterials wikipedia , lookup
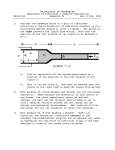
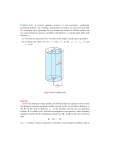
Physics Tutorial Sheet Dielectric Properties of Materials 1) Explain the behavior of dielectrics under static electric fields. Derive a Physics Tutorial Sheet Dielectric Properties of Materials 1) Explain the behavior of dielectrics under static electric fields. Derive a relation between P and E . 2) Explain the different types of polarization mechanism in dielectrics. 3) What is local field? Obtain an expression for Lorentz equation for local field and hence deduce Clausius-Mossotti relation. 4) Give the relationship between i) E , D and P vectors ii) dielectric 4) Give the relationship between i) 6) 7) 8) iii) dielectric constant and dielectric susceptibility. What is the significance of each of these factors? Derive a relation between dielectric constant and refractive index of the dielectric. Explain the phenomenon of spontaneous polarization in ferroelectric materials. Give important applications of ferroelectricity. What is piezoelectricity? Discuss direct and inverse piezoelectric effects. Explain their importance and applications. What is dielectric loss? Show that dielectric loss is given by the 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) n r 5) 6) 7) 8) constant and vector P iii) dielectric constant and dielectric susceptibility. What is the significance of each of these factors? Derive a relation between dielectric constant and refractive index of the dielectric. Explain the phenomenon of spontaneous polarization in ferroelectric materials. Give important applications of ferroelectricity. What is piezoelectricity? Discuss direct and inverse piezoelectric effects. Explain their importance and applications. What is dielectric loss? Show that dielectric loss is given by the rn r . relation, tan = Explain frequency dependence of dielectric constant. Find polarization (P) in dielectric material with dielectric constant, r = 2.8, when D = 3 × 10-8C/m2. An electric field of 6 × 104 volt/meter is applied on a sample of Neon gas at N.T.P. Calculate the dipole moment induced if the dielectric constant of Neon at N.T.P. is 1.000134. Also find out the atomic polarizability of Neon. The permittivity of diamond is 1.46 × 10-10 N-1m-2. Determine its dielectric constant and electrical susceptibility. (Given 0 = 8.86 × 1012 C2N-1m-2). The number of atoms in volume of one cubic meter of hydrogen gas is 9.8 × 1026. The radius of the hydrogen atom is 0.53 Å. Calculate the polarizability and relative permittivity. The following data refers to a dielectric material; r = 4.94 and n2 = 2.69, where n is the index of refraction, calculate the ratio between electronic and ionic polarizability for this material. Calculate the frequency of the fundamental note emitted by a quartz crystal. Given thickness of quartz crystal plate = 5.5 × 10-3m, Young’s modulus of Quartz = 8 × 10-10m-2 and density of the crystal = 2.65 × 103 kg m-3. For ice, relaxation time is given as 18 × 10-6 sec at 22°C. Calculate the frequency when the real and imaginary parts of the complex dielectric constant will become equal. What will be the phase difference between the current and voltage at this frequency? Which of the two will be leading in phase? E , D and P vectors ii) dielectric constant and vector P 5) relation between P and E . 2) Explain the different types of polarization mechanism in dielectrics. 3) What is local field? Obtain an expression for Lorentz equation for local field and hence deduce Clausius-Mossotti relation. 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) r . relation, tan = Explain frequency dependence of dielectric constant. Find polarization (P) in dielectric material with dielectric constant, r = 2.8, when D = 3 × 10-8C/m2. An electric field of 6 × 104 volt/meter is applied on a sample of Neon gas at N.T.P. Calculate the dipole moment induced if the dielectric constant of Neon at N.T.P. is 1.000134. Also find out the atomic polarizability of Neon. The permittivity of diamond is 1.46 × 10-10 N-1m-2. Determine its dielectric constant and electrical susceptibility. (Given 0 = 8.86 × 1012 C2N-1m-2). The number of atoms in volume of one cubic meter of hydrogen gas is 9.8 × 1026. The radius of the hydrogen atom is 0.53 Å. Calculate the polarizability and relative permittivity. The following data refers to a dielectric material; r = 4.94 and n2 = 2.69, where n is the index of refraction, calculate the ratio between electronic and ionic polarizability for this material. Calculate the frequency of the fundamental note emitted by a quartz crystal. Given thickness of quartz crystal plate = 5.5 × 10-3m, Young’s modulus of Quartz = 8 × 10-10m-2 and density of the crystal = 2.65 × 103 kg m-3. For ice, relaxation time is given as 18 × 10-6 sec at 22°C. Calculate the frequency when the real and imaginary parts of the complex dielectric constant will become equal. What will be the phase difference between the current and voltage at this frequency? Which of the two will be leading in phase?