* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anterior muscles
Survey
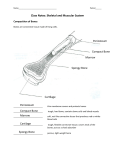
Document related concepts
Transcript
ANATOMY Human anatomy:-is the study of the structure of the body. The body consist of :1. Head &neck. 2. The trunk: 1)thorax contain lung &heart. 2)abdomen upper part(liver, spleen, digestive system.) lower part(pelvis: rectum, bladder& reproductive system.) 3. Four limps: upper limp:1)arm. 2)forearm. 3)hand. 4)finger. Lower limp:1)thigh. 2)leg. 3)foot. 4)finger. Anatomical position:Consider the body at standing position with the arms handing by the side & the palm of the hand facing forward. Terms used to describe anatomical position:1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Anterior. Posterior. Inferior. Medial. Lateral. Proximal. Distal. External. Upper. Surface of the body Plane. Line. (imagine line). A. Vertical planes:1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Median plane. Anterior median line. Posterior median line. Mid clavicular line. Median line of arm. 1 6. Median line of lower limp. 7. Axillary lines:- a)anterior. b)posterior. c)mid axillary line. B. 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Horizontal plane:Transpyloric plane. Sub costal plane Inter tubercular plane. -:تقاطع الخطوط العمودية الترقوية مع األفقية يقسم البطن إلى ست مناطق هي Right &left hypochondrial region. Epi gastric region. Right &left lumber region. Umbilical region. Right &left iliac region. Supra pubic region. 2 Bones and skeleton Skeleton:it’s consist of a group of different bones attached to each other to formed &keep the body on standing position on his feet. Types of bones:1. Long bone. 2. Short bone. 3. Flat bone. 4. Irregular bone. 5. Pneumatic bone. 1. Long bone:-are found in the limps, this bone composed of a tubular shaft of compact &spongy bone with a central medullary cavity contain bone marrow the ends of this bones is spongy. Found in i. Femur ii. Radius iii. Metatarsal 2. Short bone:- it’s consist of thin cortical layer surrounding the spongy bone. It’s found in carpal &tarsal bone. 3. Flat bones:- it’s consist of two layer of compact bone between layer of spongy bone. It’s found in skull &scapula. 4. Irregular bone:- consist of thin compact layer surrounding spongy bone. It’s found in vertebrae &some skull bones. 5. Pneumatic bones:- In skull bone have cavities contain air called sinus. The function of skeleton:1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Keeping the body straight up ward. Carrying the body weight. Source the ca++. Formation of the blood cell in the bone marrow. Protect the internal organ. It’s provide attachments for muscle &ligaments. 3 Skeleton of the upper limp Skeleton of the upper limp: It’s consist of 4types of skeleton:1. Skeleton of shoulder girdle. 2. Skeleton of upper arm. 3. Skeleton of forearm. 4. Skeleton of hand. 1.skeleton of shoulder girdle:A. Clavicle:- two bones, left &right present at the upper part of the chest at the root of the neck. It consist of body &two ends. The body is curved in shape. The two ends: 1)lateral end articulate with scapula. 2)medial end articulate with sternum. B. Scapula:- is large flattened triangular bone lying on the postero-lateral aspect of the chest &extend from 2nd to 7th ribs. The spine of scapula divide the posterior surface into two Supra spinous fossa Infra spinous fossa The lateral end of spine is extend &flattened to form acromial process The scapula has three border: Superior Medial Lateral The scapula has three angle: Superior lateral inferior glenoid cavity at the lateral angle articulate with the head of humerus. 2.skeleton of upper arm:humerus:- longest- strongest &biggest of upper arm consist of : I. II. III. Upper end which is rounded &articulated with glenoid fossa forming shoulder joint. Shaft extend between the upper & lower ends the upper part of the shaft is cylindrical &the lower part is triangular in shape. Lower end articular ulna Radius non articular 4 3.skeleton of forearm:1. radius bone :- is the lateral of two forearm has upper &lower end styloid process 2. Ulna:- longer than radius &lies medial to it. Upper end 1.coronoid process Between trochlear notch 2.olecranon process Trochlea of humerus articulate Lateral of the coronoid process there’s radial notch radio – ulnar joint. Lower end – small than separated by shallow groove. Shaft – extend between upper &lower ends. 4.skeleton of hand:I. The Carpal bones(wrist):- 8 bones in two rows proximal & distal from the lateral. Proximal: scaphoid The lunate triquetrum pisiform Distal: trapezium trapezoid capitate hamate II. The Metacarpal bone:- 5bones , 1stone articulate with thumb. III. The phalanges:- short long bone 3phalages for finger &two for the thumb. 5 Skeleton of lower limp A-The hip bones:Each hip bone is composed of three bones. 1. The Ilium 2. The pubic 3. The ischium The two hip bones together with sacrum make up the pelvic girdle, which connect lower extremities with the trunk. 1.the Ilium:it’s the biggest bone of the hip bones, it’s have two ends &three surfaces. the upper end extend to form a border “called iliac crest”. The lower end formed the upper part of acetabulum ,for the hip joint. *The three surfaces are: gLuteal surface Iliac fossa Sacro- pelvic surface 2.The pubic:has a body& two ramus. The body lies anteriorly &articulate with that of the opposite side at the pubic symphasis .the superior ramus run laterally from the body to take a part in the formation of the acetabulum &the inferior ramus runs down ward to meet inferior ramus of ischium. 3.the ischium:is the lowest portion of the pelvis. It’s have a body which joints the lower part of acetabulum. The superior ramus project down ward on the body to form ischial tuberosity on which the weight of the body is born when sitting. Inferior ramus of ischiam raise for ward to meet the inferior ramus of pubic enclosed a large opening called obturater foramen which is covered during life by membrane. Acetabulum:It’s deep-cup shaped articulate with head of femur &it’s composed of parts of three bones & it’s have acetabular notch. *pelvis in female is heart in shape to facilitate a born B-bones of thigh:The femur: it’s the longest bone of the skeleton; it has upper &lower end & cylindrical shaft. 6 The upper end consist of:I. II. head spherical, covered with cartilage extend upper medial ward. neck connect the head with shaft the neck make an angle of about 1250 with the shaft . III. Greater trochanter it’s a process extend upper to the shaft end & laterally to the neck. Trochantric fossa it’s a fossa between the neck &greater trochanter. IV. Lesser trochanter it’s found postero-medial posteriorly between the trochaters is a intra trochanteric crest. The shaft:- it’s cylindrical in shape in posterior aspect, there’s line aspira these line are divided at the lower oart of the body to form two border Medial supra- condylar ridge lateral supra- condylar ridge lower end:- consist of two process called medial & lateral condyle these two process connect together to form inter-condylar notch. the patella:- it is a sesamoid bone in the tendon وترof quadriceps femurs muscle, it’s triangular in shape articulate posteriorly with patellar surface of the femur . the muscular tendon extend to the tibial tuberosity known patellar ligament. C-Bones of leg:1.Tibia:- it’s long bone it’s consist of upper &lower ends with shaft. A-The upper end articulate with femur to from knee joint, it’s have two process called medial &lateral condyle, the upper surface of these two process are covered by cartilage, these two condyle articulate with condyle of femur, between these articulated surface there is cartilage called 1. Medial semi lunar cartilage. 2. lateral semi lunar cartilage. The surface inferior the lateral condyle articulate with fibula, these two condyle extend anteriorly to meet tibial tuberosity which the patellar ligament attached. Posteriorly there is a notch called posterior inter condyle area. 7 B-the shaft:- it’s triangular in shape, except the lower part which is rounded, have three border & three surface. The surface are: 1. anterior. 2. medial. 3. Lateral. The border are: 1. anterior. 2. medial. 3. Lateral. *the lateral border interosseous border C-Lower end:- it’s concave in shape articulate with talus bone, take a part information of ankle joint, there is a prolongation from medial side called medial malleolus & there is a fibular notch on lateral side to articulate with fibula. 2.Thefibula:- it has upper & lower end & shaft. A-Upper end called head &articulate with tibia. B-Lower end lateral malleolus projects. It has two articulated surface: medial articulate with tibia. Inferior articulate with talus. The shaft is long to which attached of several muscle &the interossous membrane which binds tibia &fibula together. D-bones of foot:1. The tarsal bone: 7 bones in two rows superior &inferior Inferior row have two bones called a) Talus (upper) Superior row have four bones called a) Medial cuneiform bone c) Lateral cuneiform bone b) Calcaneus (lower) b) Inter medial cuneiform bone d) Cuboid bone The 7th bone is navicular bone, it’s lie between the inferior & superior rows from the medial side. 2. Metatarsal bone: they are 5 bones, from the medial side the first one. The first 3 bones articulate with the three cuneiform bone &the other 2 are articulate with cuboid bone. 3. The phalanges: there are two in a great toe & three in other four toes. 8 the vertebral column It’s the central axis of the body &consists of irregular bones called vertebrae. It protects the spinal cord &supports the weight of the head & trunk. 1. Seven cervical. 4. Five sacral. 2. Twelve thoracic. 5. Four coccygeal. 3. Five lumber. Typical vertebrae:- consist of 1. Rounded body anteriorly with flattened upper& lower surface. 2. Vertebral arch posteriorly. Which consist of two pedicles 3. Vertebral foramen occupied by spinal cord. 4. Transverse process.(two) one in each side. 5. Spinous process(one posteriorly). 6. Articular process(four, two in each side inferior &superior articular process). The cervical vertebrae:The seven cervical vertebra differ from the basic plan &it’s found in first two. *First cervical vertebrae is called the atlas, it has an anterior arch in place of body. *Second called axis has projecting up wards from the body called odontoid process. The chief characteristics of cervical vertebrae:1. The bodies small &oval. 2. The arch is large. 3. The transverse process has a foramen in which the vertebral artery runs. 4. The spinous process of the first six vertebrae is bifid at the tips. The thoracic vertebrae:-(2 in number) 1. Bodies are heart in shape, they articulate from both side with heads of ribs. 2. The spinous process is long &down ward directed. 3. The transverse process is articulate with tubercles of the ribs. The lumber vertebrae(5 in number) 1. The bodies are large & wide. 2. The vertebral foramen is triangular in shape. 3. The spines are quadrangular &project back ward. The sacrum:The sacrum is triangular in shape &consist of five vertebrae fused into one bone. The coccyx:The coccyx is small triangular bone composed of four rudimentary vertebrae. 9 The thoracic cage The thoracic cage:- it’s composed of bones &muscles, the bones consist of twelve thoracic vertebrae posteriorly & the sternum anteriorly &the encircling ribs. Between the ribs there are inter costal muscle & separating the thorax from abdomen is the diaphragm. The sternum:- it forms the middle portion of anterior wall of the thorax &consist of three parts: The manubrium: is triangular bone which articulate with the clavicles, on either side of its upper border the manubrium articulate with the body at sterna angle, at this level the 2nd costal cartilage lie. The fist costal cartilage at the lateral aspect of manubrium below the clavicles. The body:- is long &narrow &articulate with manubrium at the second costal cartilage below these it’s articulate with3rd,4th,5th,6th,7th,costal cartilage. The xipoid:- is the smallest &lowest piece of the sternum it may be cartilaginous or bony. The Ribs:- they are 12th ribs, articulate posteriorly with thoracic vertebrae& arched around the thorax to connected (the 7th Ribs) to the sternum. The 8th,9th,10th, ribs have cartilage attached to each other &join the 7th costal cartilage. The 11th,12th Ribs are floating ribs. The anterior end is concave to facilitate the connection with cartilage. The posterior have head, neck, tubercles, to facilitate articulation with thoracic vertebrae.(costal vertebrae joint). Between the ribs are the inter costal space which are occupied by the inter costal muscles, nerves, blood vessels. *there are two types of ribs:1.True ribs:- it include the first seven ribs which connect with sternum directly from the anterior end by costal cartilage. 2.false ribs:- it include all the false ribs which is the lower five ribs & it is two types: A-false floating ribs. B-false non floating ribs. 10 The skull The skull:- it’s consist of groups of bones attached to each other by sutures which make these connection very strong & with out movement. The skull consist of two main parts. 1. Mandible 2. Cranium The cranium consist of calvaria box of cranium Base of skull Facial bone 1. The mandible:- it’s consist of body which arch like convex from out side, this body have two border inferior which can by catch it by hand &superior border which called (alveoli process)which carry the tooth of mandible. The Rami:- it’s two, one of them left & the other right attached to the end of bone arch &extend up ward in a postero- lateral directions. Condylar process:- it’s extend from up ward posterior to the rami consist of head & neck. the head formed the (tempro –mandibular joint ) Coronoid process:- it’s triangular in shape, it’s base connect with upper anterior side to rami. 2. The cranium:I. Calvaria. II. Skeleton of the face I. Calvaria:- it’s the part of skull consist of two parts superior(box of the skull) inferior(base of the skull). Box of the cranium:- consist of these bones. a) Frontal bone: it’s formed the upper part of cranium. b) Parietal bones: they formed upper- middle part of cranium &attached to each other by sagittal suture. c) Temporal bone: they extend at the sides of cranium. d) Occipital bone: it’s found at the upper posterior part of cranium at posterior side of base. e) Ethmoid bone: it’s found in anterior middle part of base. f) Sphenoid bone: it’s found in the base of cranium. 11 Base of skull:- have three fossa each one lie posterior &down ward the fossa which before it. 1. Anterior cranial fossa, It’s contain the frontal lobe of brain. The bone which formed this fossa are Ethmoid bone Frontal bone Sphenoid bone (bri form plate) (Orbital plate) (lesser wing) 2. Middle cranial fossa, it's contain pituitary gland the bone which formed this fossa are Sphenoid Sphenoid Temporal bone (body) (great wing) 3. Posterior cranial fossa,it’s contain:cerebellum,pons,medulla oblongata The bone which formed this fossa. Occipital Sphenoid Temporal bone (body) II. Facial bone(skeleton of the face):1. Maxillary 2. Nasal 3. Zygomatic 4. Lacrimal 5. Inferior conchae 6. Vomer 7. Palatine bone 8. Mandible Nasal sinuses:- they are cavities neighborhood to the nasal passage lined by mucus membrane. &they formed from 1. Frontal sinus. 3. Ethmoidal sinus. 2. Maxillary sinus. 4. The two sphenoidal sinuses. 12 The joints The joints:- the joints are articulation occur when two or more one meet. They are classified as fibrous, cartilaginous &synovial. I. Fibrous joints:1. No significant movement. 2. Example: the suture of skull, inferior tibio-fibular joint. II. Cartilaginous joints:1. Allow a slight amount of movement. 2. Fibro cartilaginous plate between the to bone end. 3. At the external surface there’s ligament which connect the bone. 4. Example: the pubic symphasis, between the bodies of the vertebrae(intra vertebral disk are situated). III. Synovial joints: 1. Free range of movement. 2. The articular surface of the bones are covered by hyline cartilage. The joint are surrounded by a ligament capsule. 3. The bone in the joint covered with synovial membrane. 4. The joint contain synovial fluid. 5. Example: all the joints of extremities. Joints of upper limp:1. Sterno-clavicular joint(synovial) Sternum &clavicle. 2. Acromio-clavicular joint Acromial process of scapula with clavicle. 3. Coroco-clavicular joint Coracoid process of scapula+ clavicle. 13 Joints of upper limp:1. Shoulder joint(scapula +humerus). 2. Elbow joint(humerus +radius &ulna). 3. Radio-ulnar joint(radius +ulna). 4. Wrist joint(radius +scaphoid +lunate bone). 5. Intracapal joint. 6. Carpo-metacarpal. 7. Metacarpo-phalangeal joint. 8. Inter phalangeal joint. Joints of pelvic girdle:1. Sacro –iliac joint(iliac +sacral vertebrae)(synovial). 2. Joints between the pelvic girdle: a) Pubic symphasis (cartilaginous joint),it’s articulation between the two pubic bones. b) The articulation between the three hip bones are(cartilaginous joint). 3. Hip joints(synovial joint)between femur &hip bone Joints of lower limp:1. Knee joint (synovial between femur &tibia.) 2. Tibio-fibular joint a) Superior joint(synovial b) Inferior (fibrous joint). 3. Ankle joint(synovial)tibia &fibula with talus. 4. Inter-tarsal joint. 5. Tarso-metatarsal joint. 6. Metatarso-phalangeal joint. 7. Inter phalangeal joint. Joints of the trunk:1. Inter-vertebral joint(cartilaginous joint). 2. Costo-vertebral joint. 14 The muscular system Muscular system of head &face: 1. Muscles of expression. 2. Muscles of mastication. 3. External muscle of eye ball. Muscles of expression: These muscles are responsible for all face expression in different action these muscles are controlled by facial nerve هذه العضالت تكون مسؤولة عن التعابير المختلفة للوجه وتقع تحت سيطرة العصب الجبهي(العصب القحفي السابع)وتشمل a) Muscles of scalp. b) Muscles of face. A)muscles of scalp:-(occipito-frontalis) Its consist of two parts: 1. frontal belly 2. Occipital belly B)muscles of face:1. Platysma muscle. 2. Buccinator muscle. 3. Orbicularis oris muscle. 4. Orbicularis occuli muscle. --platysma muscles extend upper part of chest &the anterior part of neck until the lower part of the face. --buccinator muscles it’s important muscle in bucal help in mastication movement. muscles of the neck A. Anterior muscles. 1. Super 2. Deep m. facial m. B. Posterior muscles. 1. trapizius 2. deep m. 3. orbicularis 4. orbicularis oris m. occli m. A. anterior muscles of neck:1.super facial muscles: They consist of i. ii. iii. platysma muscle. Sterno-cliedo-mastoid muscle. Supra hyoid muscle. iv. Infra hyoid muscle. 15 2.deep muscles: i. ii. iii. iv. Scalene muscle cervical vertebrae 2nd-3rd ribs. Pharyngeal muscle surround the pharynx. Laryngeal muscle Anterior muscles of vertebral column --Sterno- cliedo-mastoid muscle:-extend from upper to lower side in oblique direction, connect from upper side by temporal bone from down side connect the manubrium. --supra hyoid muscles:-upper the hyoid bone it’s formed the base of mouth, it’s connect the lower jaw or the tongue or hyoid bone, it’s seen when swellwed &mastication &speak movement. --infra hyoid muscles:-lower than hyoid bone connect from upper side by hyoid bone &from lower side by manubrium. B. Posterior muscles of neck:1. Trapizius 2. Deep muscle: connect skull or vertebrae. 3. Orbicularis oris: surrounded the mouth &formed the two lips help in speak &eat &expression movement. 4. Orbicularis occuli: surround the orbit of eye &covered the frontal & temporal it’s work to close the eye to protect it from the external effects. Muscles of mastication 1. Temporalis muscle. 2. Masseter muscle. They are group of muscles which work with each other to complete mastication movement. It’s work are controlled by Trigeminal nerve. External muscles of eye ball 1. I. II. III. IV. Recti muscles Superior rectus m inferior rectus m. medial rectus m. lateral rectus m. 2. Oblique muscles I. superior oblique. II. Inferior oblique. 16 1. Recti muscles:-extend from common tendinous ring to seclara. &it’s responsible for eye movement. The first three muscles are controlled by occuto mator nerve. The lateral rectus muscle is controlled by abducent nerve. 2. Oblique muscles:- the superior oblique muscle are found on the upper medial side of orbit it’s controlled by trochlear nerve, it’s move the eye ball inferior-lateral word. The inferior oblique muscle found in the anterior border of the orbit, it’s move the eye ball Muscles of the upper limp Muscles of the upper limp: It’s a group of muscle which move the upper arm &attached the upper arm with shoulder girdle, vertebral column &thoracic cage it’s contain:1. Limp-vertebral m.(the upper arm with vertebral column). 2. Limp-thoracic m.(the upper arm with thoracic) 3. Muscles of shoulder. 4. Muscles of upper arm. 5. Muscles of forearm. 6. Muscles of hand. 1.limp-vertebral m.: A. Trapezius m. C. Rhomboid m. B. Latissmus dorsi m. D. Levator scapula m. A.Trapezius muscle:It’s triangular muscle covered the posterior part of neck &back (upper part).it’s attached by occipital bone &ligmentum nuclear &spinous process of seven cervical vertebrae &all the spinous process of thoracic vertebrae. It’s under the control of accessory nerve It’s function: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Fixed the scapula. Raise the shoulder &scapula. Help to raise the arm up ward. Move the two shoulder posterior. Pull the head back ward. 17 B. latissmus Doris muscle: it’s large flat muscle, triangular in shape, covered the lumber region &the lower part of back. It’s under the control of nerve to latissmus Doris. It’s function: A. B. C. D. Adduction the humerus to trunk. Help to move the am back ward. Help in rotating the humerus. Help in pulling the trunk up ward when hundling the body. C.Rhomboid muscle: It’s two muscles. They lie between the vertebral column &scapula. It’s help in fixed of scapula &the movement of it. D.Levator scapula: It’s long muscle lie on the posterior-lateral aspect of neck. 2.limp-thoracic muscles: It’s connect the upper limp with the anterior and lateral surface of the chest. A. Pectoralis major triangular muscles covered the anterior part of chest &connect the humerus by thoracic cage. B. Pectoralis minor it’s smallest &covered by Pectoralis major muscles connect the scapula with the thoracic cage. C. Serratus anterior muscle it’s wide muscle at lateral side of chest. It’s fixed the scapula. 3.muscles of shoulder: It’s a group of muscles connect the humerus by (scapula &clavicle) it’s contain:A. Deltoid m. B. Sub scapularis m. C. Supra spinatus m. D. Infra spinatus m. A. Deltoid m.: it’s super facial muscle .triangular in shape, it’s head down ward, it’s lie on the anterior boarder of lateral part of clavicle, it’s under the control of axillary nerve. 18 B. Sub scapularis muscle: it’s deep muscle on the ribs surface of scapula, it’s help to fixed the humerus in the glenoid cavity, &help in medial rotation of humerus. C. Supra spinatus muscle: it’s super facial muscle. Found on the supra spinous fossa of scapula, it’s help in fixation of humerus in glenoid cavity, &help in abduction movement of humerus. D. Infra spinatus muscle: it’s super facial triangular muscle, found on the infra spinous fossa, it’s help in fixation of humerus in glenoid cavity &help in lateral rotation. 4.muscles of upper arm(humerus): Anterior muscles A. Biceps brachil: it’s connect scapula by two heads. These head extend & meet at the middle of humerus &they end by tendon at radial tuberosity. It’s rotate the forearm laterally &adduction of forearm to humerus. It’s under the control of musculo-cutaneous nerve. B. Coraco-brachialis muscle: it’s covered the upper medial part of humerus, it’s lie on the carcoid process of scapula. It’s under the control of musculo- cutaneous nerve. C. Brachialis: anterior to elbow joint, help in adduction the forearm under the control of musculo- cutaneous nerve. D. Triceps muscle: covered the posterior part of humerus, it’s have three head الراس الطويل من لوح الكتف والراسان االخران انسي ووحشي يرتكزان على الجزء الخلفي لعظم العضد وتمتد حتى E. Anconeus: it’s triangular muscle connect from upper side by lateral epicondyle from the lower part it’s connect the posterior part of ulna. 5.Muscles of forearm: I. Anterior muscles of forearm:A. Super facial muscle:- contain 5muscles attached from upper side by medial epicondyle &from lower side by metacarpal &phalangeal bone. 1. Flexor Carpi radialis. 2. Palmaris longus. 19 3. Flexor Carpi ulnaris. 4. Flexor digitorum super ficialis. 5. Pronator teres. *under the control of ulner nerve &median nerve. B. Deep muscle: 1. Flexor digitorum pro fundus. 2. Flexor pollicis longus. II. 3. Pronator quadrates. Posterior muscles of forearm:A. Super facial:1. Brachio radialis. 2. Extensor carpi radialis longus. 3. Extensor carpi radialis brevis. 4. Extensor digitorum. 5. Extensor digiti minimi. 6. Extensor carpi ulnaris. *it’s work to extend finger + wrist B. Deep muscle:It’s under the super facial muscle connect from upper side by posterior side of ulna &lower by radius &lateral epicondyle. It’s work in abduction of the thumb from other finger. 1. Extensor indicis. 2. Extensor pollicis brevis. 3. Extensor pollicis longus. 4. Supinator. 6.muscles of hand: 1. Thenar muscle. 2. Hupo thenar muscle. 3. Lumbrical muscle. 4. Interosseous muscle 20 Muscles of lower limp Muscles of lower limp:- it’s divided into 5 groups 1. 2. 3. 4. Muscles of the iliac region. Muscles of the gluteal region. Muscles of the femur. Muscles of the leg. 5. Muscles of the foot. 1.muscles of the iliac region:These muscles are connect the iliac fossa or transverse process of lumber vertebrae. Extend down ward to attach lesser trochanta. It’s work are controlled by femur nerve it’s help in, flextion the femur & rotating the femur medially 2.muscles of the gluteal region:They are 9 muscles, the important muscles are: 1. Gluteal maximus. 2. Gluteal medius. Gluteal nerve 3. Gluteal minimus. The function of these muscles: 1. Extension of femur. 2. Pull the femur back ward. 3. Rotating the femur medially. 3.muscles of the femur: A. Anterior m. B. Posterior m. C. Medial m. A. anterior muscles:1. quadriceps femoris: it’s controlled by femoral nerve &it have four head ends by tendon meet in patella help in flextion of femur to trunk & fixation of pelvis. 2. Sartorius: it’s long muscle extend on femur. It’s controlled by femur nerve. It’s help in flextion of femur &thigh &help in rotating in femur laterally. B. Posterior muscles:They are three muscles called Hamstring muscles supplied by sciatic nerve It’s attached from upper side by ischial tuberosity from lower side by: 1. Biceps femoris fibula 21 2. Semi membranosus tibia 3. Semi tendinosus The wok in flextion of thigh& C. Medial muscles: It’s a group of muscles ,covered the median side of femur help in adduction of femurs together. 1. Gracilis muscle. 2. Pectineus muscle. 3. Adductor muscle. 4.muscles of leg: A. Anterior m. B. Posterior m. C. Lateral m. A. Anterior muscles:1. Tibialis anterior muscle. 2. Extensor digitorum longus muscle. 3. Extensor hallucis longus muscle. *It’s connect from upper side by tibia & fibula& attached from lower side by metatarsal bone& phalanges. *These muscles are controlled by deep peroneal nerve. B. Posterior muscles:The super facial muscle are: 1. Gastrocnemius muscle. 2. Soleus muscle. These muscles are connect from upper side by tibia &fibula &from lower side by calcaneus The work flextion of leg. It’s work controlled by medial popleteal nerve. C. Lateral muscles:1. Peroneus longus. 2. Peroneus brevis. They controlled by super facial peroneal nerve. It’s work fixation of leg on feet &help in eversion of the foot. 5.muscles of foot: 1. Pantar muscle all found on the small finger. 2. Extensor digitorum brevis. found on dorsal side of foot. 22 Muscles of the trunk 1. Chest muscles A. Super facial m. I.Pectoralis major II. Pectorali s minor III. Serratus anterior B. Deep m. I. Inter costal m. ”it’s 22 muscles between the ribs” II. Diaphragm. Function of abdominal muscles:1. Protect the internal organ. 2. Respiratory movement. 3. Urination &elimination 4. Movement of body to anterior side. 5. Movement of body to right &left. 23 2. Abdominal muscles I. Rectus abdominis. II. External oblique. III. Internal oblique. IV. Transverse abdominis. V. Pyramidalis. Digestive system Digestive system: It’s long canal with irregular part. It’s help in digest food &convert it to simple substance &then absorbed it to rele use it to blood fluid. It’s consist of: 1. Mouth. 2. Pharynx. 3. Oesophagus. 4. Stomach. 5. Small intestine. 6. Large intestine. The mouth: It’s the widest part of digestive system cavity of mouth divided to two parts: 1. Real cavity 2. vestibule Roof of mouth is divided to three parts: 1. hard palate. 2. Soft palate. 3. Uvula The Salivary gland: It’s gland found in mouth secret saliva which help in mastication. 1. Parotid gland. 2. Sub mandibular gland. 3. Sub lingual gland. The Tongue: Muscular organ covered by roof mucus membrane have papillae. On the tongue there are taste buds. The Teeth: It’s bony structures have a blood &nerve supply found on the upper &lower jaw help in mastication. Divided to 1. Temporary(20) 2. Permanent(32) 1. 2. 3. 4. incisors. canine. premolars. molars. Four in each jaw Two in each jaw Four in each jaw Six in each jaw 24 The Pharynx: It’s muscular cyst covered from inner side by mucus membrane& it’s wall consist of muscle called constrictors of pharynx supplied by accessory nerve. The Oesophagus: It’s a tubular structure, it’s wall consist of muscle covered by mucus membrane it’s extend from the pharynx to the cardiac orifice of stomach. The stomach: It’s the widest part of the digestive tract, it’s found in the left upper part of the abdominal cavity, it’s divided to three parts:1. Fundus: it’s the upper part of stomach on the left side of diaphragm. 2. Body of the stomach. 3. Pylorus. Gastric orifice: 1. Cardiac orifice. it’s the internal to stomach. 2. Pyloric orifice. from it the digested food pass to duodenum. &have a pyloric sphincter. The stomach wall: consist of four layers 1. 2. 3. 4. Peritoneum. Muscular coat. Sub mucus coat. Mucus membrane. The small intestine: They extend from the stomach to the ilio caecal valve where it joins the large intestine. It’s divided into: 1. Duodenum. 2. Jejunum. 3. Ileum. The duodenum: this part lies on the posterior abdominal wall, it’s -C-in shaped embracing the head of pancreas, it’s divided to four parts, at the second part on median wall of it there’s duodenal papilla where the orifices of the bile duct &pancreatic duct are situated. The jejunum &Ilium: the jejunum start at the duodino-jejunal flexures &lies in the umbilical region. 25 The large intestine: It’s extend from the ilio-caecal junction to the anus &consist of: 1. The caecum: is a dilated pouch like structure into which the ilium open, from it the appendix projects. *The appendix is a worm-like structure it’s end blindly. 2. The ascending colon: lies in the right lumber region runs from cecum to the transverse colon. 3. The transverse colon: it’s extend from hepatic to spleenic flexures. 4. The descending colon: it’s extend from spleenic flexures down ward at the left lumber region to joint the pelvic colon. 5. The pelvic colon: it’s in the cavity of pelvis. 6. The rectum: it’s lie in the pelvis in front of sacrum &coccyx it is ened by anal canal which surrounded by anal sphincters. The liver: It’s large organ, it’s irregular in shape. It’s base to the right &it’s apex to the left. It’s divided into two lobes, large right lobe &small left lobe. The liver structure is spongy in consistency &is enclosed with a thin fibrous capsule. The biliary apparatus: It consist of the ducts through which the bile is transport &the gall-bladder which concentrate The gall-bladder: is appear-shaped organ. It’s attached to the under side of the liver &it’s blind end. The pancreas: It’s lies on the posterior abdominal wall at the level of the first lumber vertebrae. It’s consist of head, neck, body &tail. The head enclosed on three sides by the duodenal loop. Behind it the common bile duct. the pancreatic duct stars in the tail of the gland &runs to the right to enter the duodenum in company with the common bile duct at the duodenal papilla. 26 The respiratory system 1.the pharynx 2.the larynx 3.the trachea 4.the bronchi 5.the lungs 6.the pleura 1.The pharynx: A. Naso pharynx B. Oro pharynx Naso pharynx lying above the soft palate. It’s communicate with middle ear by Eustachian tube. In haled air pass from the naso pharynx to the oro pharynx 2.the larynx: It’s the organ of voice production. As being an air passage, it’s lie between the root of the tongue&the trachea in front of 3rd ,4th ,5th &6th cervical vertebrae. The skeleton of larynx are cartilaginous &with in it the vocal cord laryngeal cartilage. I. Epiglottis II. The thyroid III. The cricoid I. Epiglottis: is a leaf-shaped which project up ward in front of the opening of larynx. It’s prevents food from entering the larynx during swallowing. II. The thyroid: is the largest &consist of two lamina which fuse in the mid line to form the “ADAM’S APPLE”. III. The cricoids: is smaller but stronger it’s lie posteriorly &the cartilage completely encircle the larynx. 3.The trachea: it’s extend from the 6th cervical vertebrae to the 5th thoracic vertebrae where it’s divided into two main bronchi. It’s consist of fibrous tissue with-C-shaped cartilage. 4.The bronchi: they formed by the division of trachea &the pass to reach the root of lung. The right bronchi run more vertical so the inhaled of foreign bodies are more likely Accour in right lung. It’s give brunch to the upper middle &lower lobe of lung. The left bronchi give brunch to upper &lower lobe of left lung. *the bronchi are divided to bronchiole which terminate by irregular sac(alveoli) through which the gaseous exchange accoure. 27 5.the lungs: these are two, spongy in structure, divided into lobes by fissures. *the right lung divided into three lobes upper, middle &lower. *the left lung divided into two lobes upper &lower. 6.the pleural: it’s a thin serous membrane lined the wall of thorax &covered the lung: I. Partial pleural lined the chest wall Between them there’s plural cavity II. Visceral pleural covered the lungs 28 The urinary system The kidney: are the secretory glands of the urinary system. it’s lie behind the peritoneum on the posterior abdominal wall have convex lateral surface& concave medial surface which contain hilum through which the renal vessels, lymphatic’s &ureter pass. The kidney are enclosed by fibrous capsule if the kidney are divided vertically it will be seen to consist of outer part “cortex”& inner portion the “medulla” which composed of serious pyramids &the third part which is renal pelvis. where is urine collected. The cortex consist of large number of malpignia balls, which are consist of : I. Bowman capsule II. Glomerulus The pyramids are found in medulla &they are composed of collecting tubules which drain the urine. The ureters: Each kidney connect to the bladder by ureter which is a muscular tube at it’s upper end funnel shape pelvis. The ureter consist of abdominal &pelvis portion. The urinary bladder: it’s lie in the pelvic cavity behind the pupis &in front of rectum in the male. It’s a muscular organ lined by mucus membrane it’s capable to contain 400 cm3 of urine. There are thee opening into bladder one for each ureters& one for the urethra which surrounded by internal sphincter. The urethra: In male: It’s part of reproductive system it’s divided to three parts: I. The prostatic urethra is surrounded by prostate gland. The ejaculatory duct open. II. The membranous part. III. The penile part In female: It’s lies anterior to the vagina. 29 The male reproductive system The testes: are oval in shape &lie on each side of the secrotum in which they are suspended by the spermatic cords. they are composed of seminiferous tubule which enclosed by a fibrous capsule called tunica-albuginea. A double layer of serous membrane called tunica vaginalis separates the testis from the secrotum. The function of testis is to produce spermatozoa &secretion of testosterone which responsible for the secondary sexual characteristics. The secrotum: It’s a pouch composed of muscle &skin &it’s divided into two comparatment in which testis lie. The epididymes: It’s lie on postero - lateral aspect of the testis. They transmit the seminal fluid from the testis to the seminal duct. The seminal ducts: It’s begin at the lower poles of epididymus &run with spermatic cord to the pelvis to join the seminal vesicle to form ejaculatory ducts which open into prostatic urethra. The spermatic cord: It’s consist of vas deferens, testicular artery, a plexus of vein, lymphatics &muscle. The seminal vesicles: These are glands lie on poster-inferior aspect of bladder &there secretion are discharge via the ejaculatory duct. The prostatic gland: It’s a single mid line, it’s surrounded the upper part of urethra. It’s secretion mixed with the seminal fluid in the prostatic urethra. the penis: this is the organ by which the semen is deposit to the female genital tract. It’s composed of three structure 1. the two corpora caver nosa. 2. Corpus spongiosum. 30 The female reproductive system The female genital organ: I. Internal organ. II. External organ. I.INternal organ: 1. The ovaries 2. The uterus 1. The ovaries: are oval structure, lying on the lateral wall of the pelvis cavity. Each ovary consist of fibrous tissue in which lie several thousands is land of cells known as grafion follicles which contain ovum& secretes hormone (estrogen). 2. The uterus : it’s divided into three parts: a. Fundus b. body c. cervix It’s situated between the bladder &rectum. It’s covered by double layer of peritoneum which known as the broad ligament which connect the uterus &uterine duct& ovaries. The cervix have external orifice project in to the vagina. The uterine tube: The uterine tube(the fallopian tube)it’s a muscular tube lined by ciliated columnar epithelium the fertilization of ovum by spermatozoa are usually accoure in the fallopian tube. The vagina: runs from external orifice of cervix to the vulva it’s lined by skin moistened by mucus gland * the lower end is partially closed by the hymen. II.External organs: 1. The vulva 2. The breasts 1. The vulva: Through which the urethra &vagina open. 2. The breasts: They are accessory organs of reproduction &developed during puberty, they are circular &contain much fat, they lies on the pectoralis major muscle at the level of 2nd rib to 6th rib. It’s consist of serious lobules in which lacti forus duct are run each duct end in a nipple which is a small arised area surrounded by the pigment areola. 31 The circulatory system The circulatory system: is made up of 1. The heart. 3. Veins. 2. The arteries. 4. Capillaries. The heart: Is the powerful muscular organ which pumps blood round the body. It’s consist of 2 halves right &left, each half contain two chamber which suprated by valve. *The right side consist of right atrium into which blood flows from the systemic veins of the body. &the right ventricle through which the pulmonary artery pass to the lung. Between the atrium &ventricle there is tricuspid valve. * the left side consist of left atrium into which the pulmonary vein carrying the blood from lung. &the left ventricle from which the aorta carrying the blood to the body. Between the atrium &ventricle there is mitral valve. *there are valves also at the origins of the pulmonary artery &aorta. They consist of three flups of half moon shaped. The purpose of all these valve is to prevent the flow of blood in the revers direction. The aorta artery: is the largest artery, divided into:1. Ascending aorta 2. Arch of aorta 3. Descending aorta 1. Ascending aorta: pass up ward for ward &give brunches to coronary artery. 2. Arch of aorta: give three brand a. Innominate artery b. The left c. The left I. Right II. Right common sub clavian sub carotid carotid artery clavian artery artery 3. Descending aorta: give brunch to bronchial arteries, oesophagus &pericardium. 32 *the pulmonary artery & vein: 1. Pulmonary artery a rise from right ventricle divided into right & left to reach the hilum of right &left lung. 2. Pulmonary vein there are two come from lung& entre left atrium carrying the oxygenated blood. Arteries of upper limp: Axillary artery this artery cross axilla & renamed brachial artery Radial artery ulner artery They unite at the palm forming palmer arch from which the digital brunches run to the fingers. Arteries of lower limp: 1. Femoral artery 2. Popletial artery Anterior tibial artery. Posterior tibial artery. Arteries of abdomen: Abdominal aorta divided to two common iliac artery. The chief visceral brunches are: 1. Coeliac artery liver, stomach, pancreas, spleen. 2. Right &left renal artery Kidney. 3. Inferior mesenteric Large intestine. 4. Testicular male organ. Ovarian Female organ. Common iliac arteries : divided into 1. Internal iliac artery rectum, bladder, uterus. 2. External iliac artery enter the thigh Arteries of the head &neck: Common carotid artery external External carotid artery Internal carotid artery internal face, scalp, neck. brain 33 Veins: Veins of brain drains into large vessels to reach the internal jugular vein in the neck to sub clavian vein to form the innominate vein. Veins of upper limp: Radial+ulna join the axillary vein The super facial vein 1. cephalic vein 2. Basilica vein lateral side. medial side. Veins of lower limp: Anterior +tibial popletial vein femoral vein posterior Super facial vein: Long saphenous vein 34 external iliac vein The nervous system The nervous system: there are separated nervous system in the body. 1. Somatic nervous system a) Central nervous sys. b) Peripheral nervous sys. 2. Autonomic nervous system a) Sympathetic nervous sys. b) Parasympathetic nervous sys. THE SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM:Central nervous system:It is the system which controls all the voluntary movement of the body. It consist of the brain,& the spinal cord, &has 3coverings which protects from outer strain, these coverings are:1. Dura mater. 2. Arachnoid mater. 3. Pia mater. THE BRAIN:- it’s the centre which receives the different sensations to differentiate it &keep it as large group in the brain making the memory. The brain is consist of: 1. cerebrum 2. cerebellum 3. Brain stem. 4. Ventricules of the brain. The brain stem consist of: a) Mid brain b) Pons c) medulla oblongata. 1.Cerebrum:- it’s the largest part of the brain consist of two hemispheres called the “cerebral hemispheres” lies in frontal &middle part of the skull. The two hemispheres are connected together by a large bunch of nervous fibrous called “the corpus callosum”. Each hemisphere devided into:I. frontal lobe. II. Parietal lobe. III. Occipital lobe. IV. Temporal lobe. Between these lobes, there are deep fissures, the most important are:I. Central fissure: between the frontal lobe &the parietal lobe. II. Lateral fissure: between the temporal lobe &the parietal &fontal lobe. III. Parieto-occipital sulcus: between the parietal &occipital lobes. IV. Superior& inferior temporal sulci. The cerebrum is divided into:A. Outer portion called “cerebral cortex”. B. Inner portion which forms the largest part of the cerebrum. 35 A. cerebral cortex:this contain many gyri & has certain names,(the cerebral cortex) has many functions &each part has a certain function, the important ones are:1. motor area on area 6,4. 2. Sensory area on area 3,1,2. 3. Visual area on area 17. 4. Auditory area on area 40,41. B. inner part:consist of nervous fibrous either coming from the cortex or going to it, & between these fibrous there are group’s of cell called as “ganglia” each ganglion has a certain function, the most important ganglia are:1. basal ganglia: it controls the different movement of the body. 2. Thalamus: it receives the sensory bundles from different parts of the body. 3. Hypothalamus: it has many functions: - Hormonal secretion. -Controlling the automatic nervous system. -Controlling body temperature. -Controlling the epitie. Each hemisphere contains an irregular cavities called as * lateral ventricules two in number. * third ventricule. * fourth ventricule. 2.cerebellum:- it lies at the posterior part of the skull. It consist of:A. Two hemispheres connected together by a connecting part. B. Inner part consist of nerve fibrous, in between has cellular groups as ganglia& an outer part contains the gyri & sulci. The function of the cerebellum is to control the contractions & relaxations of the muscles. The cerebellum has 3piars of peduncles:1) Superior peduncles. 2) Middle peduncles. 3) Inferior peduncles. 36 3.brain stem:it’s a structure has two parts, each part hold a hemisphere & called the cerebral peduncle. The brain stem consist of:A. Mid brain. B. Pons. C. Medulla oblongata. A. mid brain:- it consist of the cerebral hemisphere with the Pons ,& contain some of the nervous ganglia. B. pons:- it’s a bridge like structure between the two cerebellar hemisphere with the middle cerebellar peduncles. C. medulla oblongata:- it lies at the posterior part of the skull, in front of the cerebellum below the Pons & pass down ward to the foramen magnum to continue with the spinal cord. THE SPINAL CORD:- it lies at the vertebral canal starting from the foramen magnum &ends at the lower surface of the first lumber vertebrae &it’s about 45cm. Transverse section of the spinal cord:- It consist of two different areas: the grey matter. The white matter. the grey matter which surrounds the central canal, &the white matter which surrounds the grey matter, this arraignment is the opposite to what is seen in the cerebrum & cerebellum. 37 Peripheral nervous system:This system contains the peripheral nervous which originated from the central nervous system. these peripheral nerves, give stimuli to all parts of the body & they are two types: 1. Cranial nerves: 2. Spinal nerves: These are twelve pairs of nerves originated These are thirty one from the brain & perforate the skull through pairs nerves special openings to wards different somatic originated from the parts. spinal cord passing The cranial nerves are: to all parts of the 1) Olfactory nerve. body which 2) Optic nerve. surrounds the spinal 3) Oculomotor nerve. cord as the trunk, 4) Trochular nerve. upper& lower 5) Trigeminal nerve. limps. a)ophthalmic nerve. b)maxillary nerve. c)mandibular nerve. 6) Abducent nerve. 7) Facial nerve. 8) Auditory nerve. 9) Glosso-pharyngeal nerve. 10) Vagus nerve. 11) Accessory nerve. 12) Hypoglossal nerve. THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM:It controls the involuntary vital organs. It’s connected with the central nervous system in some of the parts. It controls the function of the heart, blood vessels, smooth muscles of the digestive canal, bladder &ureters, & a direct action on the glands of the body. It consist of:1) Autonomic ganglia 2) Autonomic nerve fibers. 3) Autonomic plexus The autonomic nervous system is divided into two systems:1. Sympathetic nervous system. I. Sympathetic ganglia. II. Sympathetic nerve fibers. III. Sympathetic plexuses. 2. Parasympathetic nervous system. I. Parasympathetic ganglia II. Parasympathetic nerve fibers. 38 These sympathetic ganglia are seen in groups in the following areas:1) Cervical sympathetic ganglia are 3 in number: upper, mid &lower. 2) Thoracic sympathetic ganglia are12 or11arranged as the spinal segment. 3) lumber sympathetic ganglia are 4in number arranged as the lumber segment of the spinal cord. 4) sacral sympathetic ganglia are 4 or5 in number arranged according to the sacral segment of the spinal cord. the Parasympathetic ganglia are scattered all over the body &near the tissues which supplies, so called the “collateral ganglia”. This system has two different origins:A. cranial part: B. sacral part: contains the parasympathetic ganglia contains the which is scattered all over the body &the parasympathetic nerve fibers coming to the ganglia with ganglia found in the the following cranial nerve:walls of the bladder, -occulomotor nerve. uterus, rectum. -facial nerve. -vagus nerve. 39 The endocrine system The endocrine system:- is made up of a number of glands whose secretions or hormones pass directly into the blood stream. the thyroid gland:- is situated in the neck in close relation ship with the larynx& the upper part of the trachea at the level of the lower three cervical &first thoracic vertebrae. It consists of two lobes which are joined by an isthmus. The thyroid gland produces the hormone thyroxin. The parathyroid glands:- these are small pear like structure, usually four in number, which are embedded, two on each side, in the posterior aspect of the lobes of the thyroid gland. The function of the parathyroid gland :-is to secret a hormone parathormone which plays a vital role in the regulation of the amounts of calcium & phosphorus in the blood & bone. The pituitary gland:The pituitary gland is of a great importance in the body for, in addition to producing hormones which have a direct effect on tissues, it produces a number of hormones which exert a controlling influence on other endocrine glands. It’s a single mid line structure about 1cm in diameter lying in the sella turcica& connected to the brain by a stalk through which nerve tracts run to that part of the brain known as the hypothalamus. the pituitary gland is composed of an anterior &a posterior lobe, both of which are hormone – secreting, &these are separated by a middle part which does not appear to secret any hormones. 40 The function of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland is to produce the following hormones:1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. growth hormone--- it is hormone influences the growth of tissues, particularly the skeleton. Thyroid --- stimulating hormone (T.S.H.) – it controls the activity of the thyroid gland. Adreno cortico trophic hormone (A.C.H.) --- It stimulates the cortex of the adrenal glands to secrete hydrocortisone. Prolactin --- it is parthy responsible for the production of milk by the breast . Follicle – simulating hormone (F.S.H) ---- F.S.H. is the female stimulates the development of the grafian follicle &stimulates the mature follicle to produce the oestrogen . In the male F.S.H. stimulates the production of the spermatozoa . Luteinizing hormone --- in the female it stimulates the formation of the corpus luteum after ovulation &the secretion of the progesterone by the corpus luteum. In the male it stimulates the interstitial cells of the testis to produce testosterone . The function of the posterior lobe of the pituitary glands is to produce the following hormones:The antiduretic hormone (A.D.H) ---- it plays a vital role in the control of the total amount of water in the body. The supra renal gland:The Supra renal or adrenal glands are situated at the upper pole of each kidney, they are related posteriorly to the diaphragm &anteriorly they form part of the stomach bed. Each gland consists of an outer part, “the cortex”, which surrounds the inner part, “ the medulla”. The function of the supra renal cortex is to produce Hydrocortisone & aldosterone which affect the metabolism of water, minerals, carbohydrate, protein &fat. The function of the supra renal medulla is to secret two hormones noradrenaline &adrenaline which have roughly similar actions. 41 The special senses The Eye ------------- (Sight):The organ of sight is the eye &it has various accessory structures which include the eye brows, the eyelids, the conjunctiva, the lacrymal apparatus It consists of three coats. the outer coat or sclera forms the white of the eye& is a tough fibrous layer which gives the eye its shape &is transparent anteriorly where it is called the cornea. The middle coat or choroid is vascular &pigmented &is continuous with the iris The inner most coat, the retina is continuous with the optic nerve &is composed of nerve endings which are sensitive only to light. The eye ball is divided into an anterior &a posterior chamber. The posterior chamber is occupied by the transparent vitreous humour. The retina consists of nerve –cell& is developmentally part of the brain. The cones are used for vision in good lighting, conditions, where as the rods are used for night vision. The part of retina is divided of rods &cones &is called the blind spot. The pupil is the most sensitive part, it’s called macula. The conjunctiva is a very thin mucus membrane which lines the eyelids &covers the cornea. The lacrymal apparatus consists, on each side, of the lacrymal gland, a pair of lacrymal ducts &leading from the inner part of each orbit to the inferior meatus of each side of the nose, the naso lacrymal ducts. The glands lie above the outer parts of the eyes. The ear -------------- (hearing):The ear consists of the external, middle &internal ears &in addition to being the organ of hearing it is concerned with the maintenance of the body’s equilibrium. The external ear:- consists of the pinna or auricle &the external auditory meatus, abony &cartilaginous canal which leads to the middle ear but is separated from it by the drum or tympanic membrane. The bony part of the meatus lies between the petrous temporal bone above &the tympanic part of the temporal bone below. 42 The middle ear:- is a Narrow cavity in the petrous part of the temporal bone & contains three tiny bones called the malluos (hammer). The lateral wall is formed by the tympanic membrane& the medial wall is bony but has two membrane covered apertures which separate it from the vestibule above &the cochlea below. The auditory Eustachian or pharyngo tympanic tube which connects the middle ear to the pharynx opens into the anterior wall of the middle ear cavity & enables the pressure in this cavity to be adjusted to that of the atmosphere. The internal ear:- is the part of the ear concerned with balance as well as hearing & consist of a number of communicating membranous structures, namely the vestibule, the cochlea &the semicircular canals containing fluid called endolymph. 43