* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mr. Coach Risinger 7Y Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
River bank failure wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil contamination wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
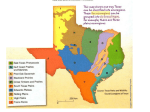
Texas Ecoregions Effects of Weathering, Erosion and Deposition Factors Affecting Our Ecoregions Weathering – chemical and physical break down of rocks into sediment Erosion – the movement of sediment from one place to another Deposition – the placement of sediment after being carried from place of origin CHEMICAL WEATHERING • THE PROCESS THAT BREAKS DOWN ROCKS B Y CHEMICAL CHANGES OR REACTIONS. Piney Woods 1. It is the wettest region of the state. This allows for a high rate of decomposition to occur resulting in healthy, nutrient-rich soils. 2. The topography is gently rolling to near flat through out the region. 3. Pine trees, woody vines, and hardwood trees dominate the vegetation. 4. It is a fire climax system. Fire is necessary in order for pines to maintain dominance in the area. 5. Unless an area has been clear-cut of vegetation for construction, the amount of trees and plants can prevent erosion. Gulf Coast-Coastal Plain 1. Soil in the region is primarily sand-based. 2. If there isn’t enough vegetation to keep the soil in place, rainfall received can cause severe erosion. 3. Catastrophic events such as hurricanes can increase wave erosion and deposition. Prairie & Lakes1. These areas have nutrient-rich soils and receive good amounts of rainfall through the year. 2. If the land is clear-cut of natural vegetation for construction, nutrients can easily be eroded. 3. If the land is used for farming and it is not managed well, nutrients will be quickly used up. Blackland Prairie & Post Oak Savannah Hill Country- Edwards Plateau 1. This region is located between dry western plains and moist prairies and woods. 2. Unfortunately, erosion has left most of the region with very shallow soils (less than 10 inches) lined with limestone rock layers. 3. High amounts of rain in a short amount of time can cause flash flooding. Prairies & LakesWestern and Eastern Cross Timbers 1. This is a small, thin region running North to South on either side of the prairies and plains. 2. The soil is not as prone to flooding because it allows water to infiltrate very easily. 3. The region is described as rough, hilly terrain. Panhandle- High Plains 1. “Texas Panhandle” 2. Largest and most completely flat areas of it size in the world! 3. The region extends to the Palo Duro Canyon-the nation’s 2nd largest canyon. 4. Palo Duro Canyon was formed by water erosion from the Prairie Dog Town Fork of the Red River. 5. The water deepens the canyon by moving sediment downstream. 6. Wind and water erosion gradually widen the canyon. South Texas Plains 1. The area is known as “Brush Country” due to the shorter trees and many shrubs. 2. Overgrazing of the land has allowed nutrient-rich topsoil to erode way. 3. Rocky, dry soil cannot support grasses, trees can thrive because of their deeper root system. Big Bend Trans-Pecos • Rain does not fall evenly over the area. • “Desert portion” of Texas. • The weathered bedrock in this area has high amounts of calcium. • As a result of erosion and deposition in the area, the soil has high amounts of calcium called caliche. Big Bend- Mountain Forest of West Texas 1. Home of the tallest mountain in Texas, Guadalupe Peak. Elevation is 8,749 feet. 2. Pines and Oaks dominate the tree species. 3. Soils are shallow and rocky. Weathering continues to play a role in developing soil and will for thousands of years to come. 4. Soils in the canyon bottoms and valleys are deeper as a result of deposition. v. Rolling Plains 1. This region is part of the Great Plains of the central United States. 2. Soils in this area are most fertile and sought after for crop production. 3. Periods of drought and then sudden increase in rainfall causes large amounts of erosion and deplete the soil of nutrients.