* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Weight Management
Ketogenic diet wikipedia , lookup
Calorie restriction wikipedia , lookup
Waist–hip ratio wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Cigarette smoking for weight loss wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Fat acceptance movement wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
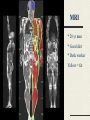
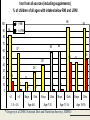
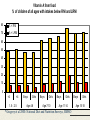
- Weight Management - Paul Clayton FDIN 28/6/07 - Weight Management - still waiting … Paul Clayton FDIN 28/6/07 1897 1919 1952 1952 1952 2001 Ob / ob/ob normal Reduced energy expenditure 2800 kcal per day 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 1600 60 1940 65 70 50 75 60 80 Year 85 70 90 95 80 DoH ’98, USDA ’02, NIH ’03, NCHS ‘04 Positive energy balance 2800 kcal per day 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 1600 60 1940 65 70 50 75 60 80 Year 85 70 90 95 80 DoH ’98, USDA ’02, NIH ’03, NCHS ‘04 Obesogenic culture (AHA ’03) Avge US adult sedentary 8 hours / day, < 2,000 steps / day (NYS Public Health Assocn ‘05) Amish 16,000 steps /day: obesity 9% women, 0% men (Bassett et al ’04) MRI * 28 yr man * Good diet * Desk worker Yellow = fat TOFI – something to chew on Thin Outside – Fat Inside Dangers of inner fat (J Bell, Imp. College) Inner fat prevalent when normal BMI maintained by diet: 45% women, 60% men Lean people get CAD, NIDDM too Exercise the only way to reduce inner fat Unfitness more dangerous than fatness Why is weight gain so easy? Multiple satiation mechanisms (enteroendocrine) Protein (aa’s, fish > whey > casein) Fat (FA’s esp LCP’s) Digestible carbs (glucose, CNS) Fermentable carbs (propionic acid, liver?) Insufficient calorific throughput Social / stress over-ride High calorific density foods / ‘fast foods’ AHA 2002: ‘obesogenic culture’ Fewer bus-stops, remote parking Exercise to be mandatory at all levels of educational system No ‘junk foods’ to be sold / served in schools Fat - but starving W.H.O. ‘02: ‘Globally, overweight greater health problem than underweight.’ W.H.O./F.A.O ’03: ‘Poor diet the major cause of degenerative disease’. U.N. ’06: Overweight but malnourished 40-60% hospital admissions malnourished (1-3) 25-30% malnourished in the community J Nutr Hlth Ageing 3:133-139, ‘99 > 3.6 million malnourished in UK (BANT ’07) Percentage of Population Depleted In Vitamins (USDA 1997) Vitamins C % E A B1 B2 Niacin Folate B6 B12 --------------------------------------------------------------------37 68 55 32 31 27 34 54 17 Iron from all sources (including supplements) % of children of all ages with intakes below RNI and LRNI 100 90 96 % < RNI 84 93 % < LRNI 80 70 60 50 44 39 40 48 43 28 30 20 60 59 57 16 14 4 10 0 1 1 3 3 Boys Girls Boys Girls Boys 2 0 <4 >4 1.5 - 4.5 Age 4-6 Age 7-10 Girls Age 11-14 * Gregory et al 2000. National Diet and Nutrition Surveys, HMSO Boys Girls Age 15-18 Vitamin A from food % of children of all ages with intakes below RNI and LRNI 80 % < RNI 70 % < LRNI 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 <4 >4 1.5 - 2.5 Boys Girls Age 4-6 Boys Girls Age 7-10 Boys Girls Age 11-14 * Gregory et al 2000. National Diet and Nutrition Surveys, HMSO Boys Girls Age 15-18 RSM 2005: Pathogenic culture? Type 2 diabetes . RSM 2005: Pathogenic culture? Type 2 diabetes increased heart disease, stroke, cancers, . kidney disease, blindness, Alzheimer’s RSM 2005: Pathogenic culture? Type 2 diabetes increased heart disease, stroke, cancers, . kidney disease, blindness, Alzheimer’s asthma, allergy food intolerance / eosinophilic GI disease osteoporosis lymphoma, leukaemia, melanoma, germ cell tumours in teens & young adults ARMD ADD / ADHD / dysphasia / dyspraxia Positive energy balance 2800 kcal per day 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 1600 60 1940 65 70 50 75 60 80 Year 85 70 90 95 80 DoH ’98, USDA ’02, NIH ’03, NCHS ‘04 Fat – but starving Do we really want to encourage people to eat less? They can at least eat better: Increased nutrient / calorie ratios (functional foods, nutraceuticals, supplements) OR Be more physically active so they can eat more? Burn more calories without exercise? (thermogenic strategies) Low fat / cholesterol Reduced fat / cholesterol content Reduced fat / cholesterol absorption Olestra (sucrose esters) "... will very probably increase the risks of cancer, heart disease, stroke and blindness." Willett & Stampfer, Harvard School of Public Health Reduced cholesterol absorption AND Reduced lipophile absorption Take Control, Benecol etc (sterol/stannol esters) Fat vs carb reduction Lose more calories by reducing fat Health issues? Reducing carbs loses fewer calories But probably a healthier option Projected benefits of reducing CHO by 30g Projected benefits of reducing CHO by 30g 1 30% reduction in type-2 DM 1. Salmeron et al 1997ab; Meyer et al, 2000 Projected benefits of reducing CHO by 30g 1 2 1.0 % fall in HbA1c 30% reduction in type-2 DM 25% reduction in retinopathy 1. 2. Salmeron et al 1997ab; Meyer et al, 2000 Diabetes Control and Complications Trial, 1996 Projected benefits of reducing CHO by 30g 1 2 3 1.2% fall in HbA 1.0 % fall in HbA1c 1c 30% reduction in type-2 DM 25% reduction in retinopathy >30% reduction in CHD 1. 2. Salmeron et al 1997ab; Meyer et al, 2000 Diabetes Control and Complications Trial, 1996 3. De Vegt et al 1999; Khaw et al, 2001 Potential appetite suppressors Pinoleic acid: q6 PUFA from Korean pine nut oil. (‘PinnoThin’, Lipid Nutrition Nl) PUFA’s in small bowel trigger cholecystokinin (CCK) PUFA’s at end of small bowel trigger Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1) CCK and GLP1 influence meal termination Clinical trial ‘inconclusive’ Potrential appetite suppressors Oleoylethanolamide (cannabinoid receptor blocker): cocoa, soybeans, hazelnuts, oats Fish & whey protein isolates (anti-stress) PeptideA, Lactium Caralluma fimbriata Indian food plant – edible succulent 1 g/day, 4 weeks, n=26: weight loss, no adx (Lawrence & Choudhary, 12th World Conf Anti-aging Medicine, ’04) 1 g/day, 8 weeks, n=50 Appetite reduction, weight loss, no adx (Kuriyan et al, Appetite 48:338-44, ’07) Some evidence of adipocte inhibition Differentiation of pre-adipocyte into mature adipocyte Pre-adipocyte Immature adipocyte Immature multilocular adipocyte Mature unilocular adipocyte Metabolic shift Capsiate: sweet red pepper CH-19 (1) Up-regulates UCP 1, 2 (1) and 3 (2) BUT, increases physical endurance (3) Animal weight /fat loss data (4) Clinical studies underway in Japan, USA Anti-cancer effects (5, 6) NIDDM, CAD? (7) Metabolic shift Adrenaline REsearch Thermo-regulatory clothing Thermal receptors at base of brain Up-regulate brown adipose tissue Up-regulate UCP 1 and 2 Appetite increase, weight loss ..dubious … USA: ‘Weight loss’ patches. Guarana, Garcinia, Menthol, Fucus Vesiculosus (kelp) UK: hypnosis. ‘You don’t have to clear your plate’ Austria: caffeine-laced tights. ‘The caffeine is absorbed locally and breaks down cellulite’. The Backlash Fat Acceptance Movement ’86 Fat Liberation ’88 Fat Pride ‘89 Fat Positive ‘93 National Association to Advance Fat Acceptance Council on Size and Weight Discrimination International Society for Size Acceptance Co-conspirators For every $ spent on food in the US, 48 cents is spent in fast food restaurants … … which operate in a very competitive commercial environment … … and are extremely sensitive to changing consumer demands BK’s ‘Enormous Omelet Sandwich’ 730 calories, 70 g fat: $2.99 Hardee’s ‘Monster Thickburger’ 1420 calories, 107 g fat: $5.49 Atkins and other low-GL diets Efficacy? (6 vs 12 months; 1 +ve vs 3 –ve) High fat / protein, low fruit / veg diet increases risk of bowel & other cancer 1 in 3 adults have renal impairment; worsened by high protein diet Knight et al ’03 low phytate diet Curran et al ‘04 Who has renal impairment? Overweight, IGT Low cal-GL / high micronutrient Low GL 5 – 9 portions fruit and vegetables Vegetable > animal protein Increased intake of fermentable carbs Limited amounts of fats and oils V limited digestible carbs Supplements New Food Cals/g 9 3 High GL Pyramid Oils, fats: 25g Meat, dairy: 150g Pulses, legumes, seeds, nuts, soy: 300g 0.5 Wide variety fruits / veg (not potatoes): 800g supplements New Food Cals/g 9 3 High GL Pyramid Oils, fats: 25g Meat, dairy: 150g Pulses, legumes, seeds, nuts, soy: 300g 0.5 Wide variety fruits / veg (not potatoes): 800g Total calories less than 2000 / day supplements - Weight Management - still waiting … Paul Clayton [email protected]