* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What Is An Information System?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
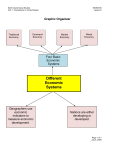
An Introduction to Information Systems Chapter 1 Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 1 Chapter 1 Outline • • • • • • • Information Concepts System and Modeling Concepts What’s an Information System? Computer-based Information Systems Business Information Systems Systems Development Why Learn About Information Systems? Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 2 Information Concepts Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 3 Definition of an Information System “A set of interrelated components that collect, manipulate, and disseminate data and information, and provide feedback to meet an objective” • Examples: ATMs, airline reservation systems, course reservation systems Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 4 Data vs. Information • Data: raw facts • Information: a collection of facts that are organized so that they have value (often for decision making) beyond that of the facts themselves Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 5 Types of Data Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 6 The Characteristics of Valuable Information Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 7 The Characteristics of Valuable Information Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 8 Transforming Data Into Information Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 9 System and Modeling Concepts Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 10 Definition of a System “A set of elements that interact to accomplish goals” Systems consist of: • Input(s) • Processing • Output(s) • Feedback: output used to make changes to inputs or processing • Other system terms: – System boundary: distinguishes the system from its environment – A configuration: the way system elements are organized or arranged. Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 11 Components of a System: Input, Processing, Output and Feedback Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 12 System and Modeling Concepts Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 13 Classifying System Types Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 14 More System Terms and Concepts • Performance and Standards – Efficiency: output/input – Effectiveness: extent to which system attains its goals – Performance standard: specific objective of a system • System variable - item controlled by decision-maker • System parameter - value that cannot be controlled Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 15 System Performance and Standards System variableitem controlled by decision-maker System parametervalue that cannot be controlled Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 16 System Models • “an abstraction used to represent reality” • 4 major types of models: • 1. A narrative model is based on words and is a logical, not physical model • 2. A physical model is a tangible representation of reality • 3. A schematic model represents reality using graphs and charts • 4. A mathematical model uses formulas and calculations to represent reality Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 17 System Model Types Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 18 What Is An Information System? Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 19 Components of an Information System Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 20 Computer-Based Information Systems (CBIS) Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 21 CBIS Components: hardware, software, databases, telecom, people and procedures Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 22 CBIS Elements • • • • Hardware Software Databases Telecommunications, Networks and the Internet (Connectivity) • People • Procedures Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 23 7 Firms Making Excellent Use of the Internet Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 24 7 Firms Making Excellent Use of the Internet Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 25 Business Information Systems Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 26 Business Information Systems • Electronic Commerce (EC) – E-Commerce Types: B2B, B2C, C2C, B2G, G2C • • • • • • Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) Management Information Systems (MIS) Decision Support Systems (DSS) Enterprise Resource Planning Systems (ERP) Artificial Intelligence (AI) Systems Virtual Reality Systems (VR) Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 27 Electronic Commerce (including EDI) Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 28 Transaction Processing Systems “an organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases and devices used to record completed business transactions” Examples include: – – – – Processing business exchanges Maintaining records about the exchanges Handling routine, yet critical, tasks Performing simple calculations Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 29 Example of a TPS: Payroll Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 30 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) • “an integrated group of programs that can manage a company’s entire set of business operations” • Often used to coordinate planning, inventory control, production, and ordering Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 31 Management Information Systems (MIS) “an organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases and devices used to provide routine information to managers and decision makers” • Focus is on improving operational efficiency (“doing things right”) • Uses transaction data as main input • Databases are used to integrate MIS from different functional areas • MIS Output types: – Scheduled reports – Demand reports – Exception reports Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 32 Management Information Systems (MIS) Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 33 Decision Support Systems (DSS) • “an organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases and devices used to support problem-specific decision making” • Focus on decision-making effectiveness (“doing the right thing”) • Typically used for: – Interactive support for non-routine decisions or problems – End-users (and their expertise) are more involved in creating a DSS than an MIS Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 34 Essential DSS Elements Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 35 Special-Purpose Business Information Systems • Artificial Intelligence (AI) Systems – Expert Systems – Learning Systems • Virtual Reality Systems • Other Special-Purpose Business Information Systems Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 36 The Major Elements of Artificial Intelligence Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 37 Virtual Reality: Head Mounted Display Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 38 Virtual Reality: Data Glove Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 39 Systems Development Life Cycle Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 40 Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) • Systems development is “the activity of creating or modifying existing business systems. • The SDLC is a formal way of looking at this process. • Nearly every company will develop or use some sort of proprietary software, and the process involves more than just IS personnel. • So, it’s important to understand the SDLC to participate effectively in corporate environment. Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 41 Systems Development Life Cycle Note: this last block is really two phases: system maintenance and system review Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 42 Why Learn About Information Systems? Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 43 Why Learn About Information Systems? • • • • Advance in your career Solve problems Realize opportunities Meet your career goals Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 44 Computer and Information System Literacy • Computer literacy - knowledge of computer systems and equipment • Information system literacy - knowledge of how data and information are used Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 45 Where are Information Systems used in Business and Industry? • • • • • • • • Finance and Accounting Sales and Marketing Manufacturing Investment firms Banks Publishing companies Healthcare organizations Management consulting firms – i.e., pretty much everywhere Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 46 Summary • Data - raw facts • Information - data transformed into a meaningful form • System - set of elements that interact to accomplish a goal • Systems development - creating or modifying existing business systems Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 47 Principles and Learning Objectives • The value of information is directly linked to how it helps decision makers achieve the organization’s goals. – DISTINGUISH DATA FROM INFORMATION AND DESCRIBE THE CHARACTERISTICS USED TO EVALUATE THE QUALITY OF DATA. Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 48 Principles and Learning Objectives • Models, computers, and information systems are constantly making it possible for organizations to improve the way they conduct business. – NAME THE COMPONENTS OF AN INFORMATION SYSTEM AND DESCRIBE SEVERAL SYSTEM CHARACTERISTICS. – IDENTIFY FOUR BASIC TYPES OF MODELS AND EXPLAIN HOW THEY ARE USED. Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 49 Principles and Learning Objectives • Knowing the potential impact of information systems and having the ability to put this knowledge to work can result in a successful personal career, organizations that reach their goals, and a society with a higher quality of life. – IDENTIFY THE BASIC TYPES OF BUSINESS INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND DISCUSS WHO USES THEM, HOW THEY ARE USED, AND WHAT KINDS OF BENEFITS THEY DELIVER. Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 50 Principles and Learning Objectives • System users, business managers, and information systems professionals must work together to build a successful information system. – IDENTIFY THE MAJOR STEPS OF THE SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT PROCESS AND STATE THE GOAL OF EACH. – DISCUSS WHY IT IS IMPORTANT TO STUDY AND UNDERSTAND INFORMATION SYSTEMS. Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 51 End of Chapter 1 Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition 52