* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Graphic Organizer
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Rostow's stages of growth wikipedia , lookup
Social market economy wikipedia , lookup
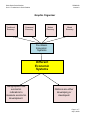
Sixth Grade Social Studies Unit 1: Foundations in Social Studies SS060108 Lesson 8 Graphic Organizer Traditional Economy Command Economy Market Economy Mixed Economy Four Basic Economic Systems Different Economic Systems Geographers use economic indicators to measure economic development. Nations are either developing or developed. Page 1 of 7 July 8, 2009 Sixth Grade Social Studies Unit 1: Foundations in Social Studies SS060108 Lesson 8 Big Ideas of Lesson 8, Unit 1 1. Economic systems are different ways that people use resources to make and exchange goods and services. 2. There are four basic economic systems existing throughout the world. 3. The four economic systems used in the world are traditional, command, market, and mixed. 4. Geographers look at figures such as literacy rate, life expectancy, and Gross Domestic Product to measure economic development. 5. Some countries have a wide mix of economic activities, while others may have only one or two main economic activities. 6. Geographers group the countries of the world into groups based on their level of economic development. 7. Countries are divided into 2 categories based on economic development: developing or developed nations. Page 2 of 9 July 8, 2009 Sixth Grade Social Studies Unit 1: Foundations in Social Studies SS060108 Lesson 8 Word Cards 73. economic systems 74. traditional economy different ways that people use resources to make and exchange goods and services goods and services are traded, but money is rarely exchanged Example: Bartering is the oldest economic system in the world. Example: A traditional economy is more likely to be in a remote community in which people grow their own food and make their own goods. (SS060108) (SS060108) 75. barter 76. market economy what is produced and distributed is based on what consumers are willing to buy and the price they will pay to trade Example: He bartered and traded a pencil for a ruler in the class barter game. Example: In a market economy, the price people are willing to sell goods for depends on the price people are willing to pay. (SS060108) (SS060108) 77. command economy 78. mixed economy a central authority plans and controls what is produced and distributed a combination of command and market economies Example: In a command economy prices are set by the central authority. (SS060108) Example: In countries with mixed economies, the government may own some industries, while others belong to private owners. (SS060108) Page 3 of 9 July 8, 2009 Sixth Grade Social Studies Unit 1: Foundations in Social Studies SS060108 Lesson 8 79. economic indicator 80. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) data that helps to show the economic condition of a country the total value of all the goods and services produced in an economy in a given year Example: The Gross Domestic Product is an example of an economic indicator. Example: The Gross Domestic Product is an example of an economic indicator. (SS060108) 81. Per Capita Income (SS060108) 82. life expectancy the amount of money people make in a country, divided by the number of people in the country the average life span of a newborn; life expectancy is an indicator of the overall health of a country Example: In wealthy countries the Per Capita Income is high. Example: The higher the life expectancy, the better economic shape a country is in. (SS060108) 83. infant mortality (SS060108) 84. literacy the number of deaths of infants, one year or younger Example: The infant mortality rate has continued to decline over the past several years. (SS060108) the ability to read and write Example: Literacy is important because it affects people’s ability to prepare for and hold jobs. (SS060108) Page 4 of 9 July 8, 2009 Sixth Grade Social Studies Unit 1: Foundations in Social Studies SS060108 Lesson 8 85. developing countries 86. developed countries countries with less productive economies and a lower quality of life countries with strong economies and a high quality of life Example: Almost two-thirds of the people in the world live in developing countries. Example: Developed countries like the United States and Germany have a higher per capita GDP and high levels of industrialization. (SS060108) (SS060108) Page 5 of 9 July 8, 2009 Sixth Grade Social Studies Unit 1: Foundations in Social Studies SS060108 Lesson 8 TYPES OF ECONOMIC SYSTEMS TRADITIONAL MARKET COMMAND MIXED Page 6 of 9 July 8, 2009 Sixth Grade Social Studies Unit 1: Foundations in Social Studies SS060108 Lesson 8 COMPARING ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT Guided Notes Directions: Use an atlas and the CIA World Factbook (online) to complete the chart below. Compare the economic development of two countries in the Western Hemisphere to that of the United States, Japan, and Germany to categorize them as developed or developing nations. Country United States Status GDP GDP/ Infant Life Literacy Person Mortality Expectancy Rate developed $13.84 trillion $45,800 6.3 (per 1000 live births) 78.1 99% Germany developed $3.3 trillion $34,100 4.03 (per 1000 live births) 79.1 99% Japan developed $4.3 trillion $33,500 2.8 (per 1000 live births) 82.07 99% Economic Activities fishing, manufacturing/ commerce, stock raising, agriculture agriculture, manufacturing/ commerce fishing, agriculture, manufacturing/ commerce Page 7 of 9 July 8, 2009