* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Consumer Behaviour in Services
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Brand loyalty wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Value proposition wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
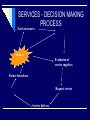
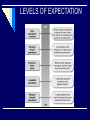
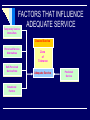
Consumer Behaviour in Services CONSUMER PROBLEM TIME DEFICIENCY REASONS: dual career couples, single parent families IT LEADS TO: demand for different services SEARCH, EXPERIENCE & CREDENCE PROPERTIES SEARCH QUALITIES: attributes that a consumer can determine before the purchase EXPERIENCE QUALITIES : attributes that a consumer can determine only after the purchase CREDENCE QUALITIES : attributes that consumer may find impossible to evaluate even after purchase & consumption Continuum of Evaluation for Different Types of Products/services Most Goods High in search qualities Most Services High in experience High in credence qualities qualities SERVICES - DECISION MAKING PROCESS Need awareness Memory Memory Evaluation of service suppliers Future Intentions Request service Service delivery UNDERSTANDING DIFFERENCES AMONG CONSUMERS GLOBAL DIFFERENCES ROLE OF CULTURE DIFFERENT VALUES, ATTITUTEDS DIFFERENT CUSTOMS CUSTOMER EXPECTATION OF SERVICE Customer expectations are the beliefs about service delivery that serve as standards or reference points against which performance is judged. LEVELS OF EXPECTATION DUAL CUSTOMER EXPECTATIONS Desired Service Adequate Service THE ZONE OF TOLERANCE Desired Service Zone of Tolerance Adequate Service ZONES OF TOLERANCE FOR DIFFERENT SERVICE DIMENSIONS Desired Service Zone of Tolerance Desired Service Adequate Service Zone of Tolerance Adequate Service Reliability Tangibles FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE DESIRED SERVICE Lasting Service Intensifiers Desired Service Personal Needs Zone of Tolerance Adequate Service Lasting Service Intensifiers are individual, stable factors that lead the customer to a heightened sensitivity to service. FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE ADEQUATE SERVICE Temporary Service Intensifiers Desired Service Perceived Service Alternatives Self-Perceived Service Role Situational Factors Zone of Tolerance Adequate Service Predicted Service FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE DESIRED AND PREDICTED SERVICE Explicit Service Promises Implicit Service Promises Word-of-Mouth Desired Service Zone of Tolerance Adequate Service Past Experience Predicted Service CUSTOMER PERCEPTION OF SERVICE Customers perceive services in terms of quality of service & how satisfied they are overall with their experiences. CUSTOMER PERCEPTIONS OF QUALITY AND CUSTOMER SATISFACTION BUILDERS OF CUSTOMER PERCEPTION SINGLE TRANSACTION SPECIFIC ENCOUNTER: how the customer has been treated in a particular encounter with a particular employee. CUMULATIVE PERCEPTION: customer’s overall experience with the company. CUSTOMER SATISFACTION It is a judgment that a product or service feature or the product or service itself provides a pleasurable level of consumption related fulfillment. It is the customer’s evaluation of a product or service in terms of whether it has met the customer’s needs & expectations. Its failure leads to dissatisfaction. DETERMINANTS OF CUSTOMER SATISFACTION PRODUCT & SERVICE FEATURES CUSTOMER EMOTIONS- your mood ATTRIBUTION FOR SERVICE SUCCESS OR FAILURE: how much the customer blames or credits the failure or success of a service on the service provider PERCEPTION OF EQUITY OR FAIRNESS: have I been treated fairly compared to other customers? PERCEPTION OF FAMILY MEMBERS, FRIENDS, PEERS ETC OUTCOMES OF CUSTOMER SATISFACTION Increased customer retention Positive word-of-mouth communications Increased revenues RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CUSTOMER SATISFACTION AND LOYALTY IN COMPETITIVE INDUSTRIES Source: James L. Heskett, W. Earl Sasser, Jr., and Leonard A. Schlesinger, The Service Profit Chain, (New York, NY: The Free Press, 1997), p. 83. SERVICE QUALITY The customer’s judgment of overall excellence of the service provided in relation to the quality that was expected. Service quality assessments are formed on judgments of: outcome quality interaction quality physical environment quality THE FIVE DIMENSIONS OF SERVICE QUALITY Reliability Assurance Ability to perform the promised service dependably and accurately. Knowledge and courtesy of employees and their ability to inspire trust and confidence. Tangibles Physical facilities, equipment, and appearance of personnel. Empathy Caring, individualized attention the firm provides its customers. Responsiveness Willingness to help customers and provide prompt service. THE SERVICE ENCOUNTER is the “moment of truth” occurs any time the customer interacts with the firm can potentially be critical in determining customer satisfaction and loyalty types of encounters: remote encounters, phone encounters, face-to-face encounters is an opportunity to: build trust reinforce quality build brand identity increase loyalty Common Themes in Critical Service Encounters Research Recovery: Adaptability: employee response to service delivery system failure employee response to customer needs and requests Coping: Spontaneity: employee response to problem customers unprompted and unsolicited employee actions and attitudes UNDERSTANDING CUSTOMER EXPECTATION AND PERCEPTION THROUGH MARKETING RESEARCH Customer CUSTOMER Expected Service (Customer Gap) GAP 1 Perceived Service COMPANY Company Company Perceptions of Consumer Expectations WHY DO SERVICE RESEARCH? To identify dissatisfied customers To discover customer requirements or expectations To monitor and track service performance To assess overall company performance compared to competition To assess gaps between customer expectations and perceptions To gauge effectiveness of changes in service To appraise performance of individuals/teams for rewards To determine expectations for a new service To monitor changing expectations in an industry To forecast future expectations CRITERIA FOR AN EFFECTIVE SERVICE RESEARCH PROGRAM Includes both qualitative and quantitative research Includes both expectations and perceptions of customers Balances the cost of the research and the value of the information Includes statistical validity when necessary Measures priorities or importance of attributes Occurs with appropriate frequency Includes measures of loyalty, behavioral intentions, or actual behavior STAGES IN THE RESEARCH PROCESS Stage 1 : Define Problem Stage 2 : Develop Measurement Strategy Stage 3 : Implement Research Program Stage 4 : Collect and Tabulate Data Stage 5 : Interpret and Analyze Findings Stage 6 : Report Findings PORTFOLIO OF SERVICES RESEARCH Research Objective Type of Research Identify dissatisfied customers to attempt recovery; identify most common categories of service failure for remedial action Customer Complaint Solicitation Assess company’s service performance compared to competitors; identify service-improvement priorities; track service improvement over time “Relationship” Surveys Obtain customer feedback while service experience is fresh; act on feedback quickly if negative patterns develop Post-Transaction Surveys Use as input for quantitative surveys; provide a forum for customers to suggest service-improvement ideas Customer Focus Groups Measure individual employee service behaviors for use in coaching, training, performance evaluation, recognition and rewards; identify systemic strengths and weaknesses in service “Mystery Shopping” of Service Providers Measure internal service quality; identify employeeperceived obstacles to improve service; track employee morale and attitudes Employee Surveys Determine the reasons why customers defect Lost Customer Research Forecast future expectations of customers; develop and test new service ideas Future Expectations Research