* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GHG-Eras - Dearborn High School
Belle Époque wikipedia , lookup
Origins of society wikipedia , lookup
Societal collapse wikipedia , lookup
Universal history wikipedia , lookup
Guns, Germs, and Steel wikipedia , lookup
Civilization wikipedia , lookup
Contemporary history wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Elizabethan era wikipedia , lookup
Early modern period wikipedia , lookup
20th century wikipedia , lookup
Modern history wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Columbian era wikipedia , lookup
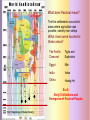
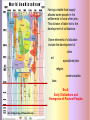
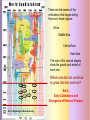
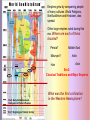
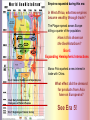
Eras of World History Using the GeoHistoGram Goals: Introduce Students to the GeoHistoGram Connect the Era titles to significant events Eras of World History Using the GeoHistoGram The history of the world has been divided into eras to help organize the information. Each of the eras has been named to help define the events during that time. We will use the GeoHistoGram to look at both the dates and the areas to get a basic understanding of the history of our world. The GeoHistoGram The GeoHistoGram shows both time (chronology) and place (region) The GeoHistoGram This is the basic form of the GeoHistoGram – seven vertical bars. Space goes across the diagram, from west on the left to east on the right. The GeoHistoGram Time goes .up the side, from the distant past on the bottom to the present at the top. Each curve.in each bar represents 1000 years of history in that region. The GeoHistoGram Here is a simple use of the GeoHistoGram: to show ancient empires in Mesopotamia. The bars represent major world regions, from the Americas in the west to Polynesia in the east. (before the Common Era, and roughly in the middle of the world’s land). The GeoHistoGram By varying the width of the empire “blob”, you can show how its power expanded at different times. Adding a shape in northeast Africa can show how Egypt lasted a long time but varied in importance. The GeoHistoGram Some words you need to know: Era: a period of time Migration: the act or process of moving from one region or country to another Pastoral: herding or keeping animals for food, transportation, etc. Agriculture: farming; cultivating the land, producing crops, and raising livestock Civilization: a highly developed society: with a high level of culture and social organization Empire: lands, a group of nations, territories, or people ruled by a single authority. Colonization: to establish a colony in another country or place Revolution: a dramatic change in ideas or practice Imperialism: the policy of extending the rule or influence of a country over other countries or colonies Nationalism: excessive devotion to a nation and its interests, often associated with a belief that one country is superior to all others GeoHistoGram Activities Mark the Eras on the Geohistogram The first era is “Beginnings of Human Society” (Beginning to 4,000 BCE) The “Beginning” was about 200,000 years ago! The first humans migrated out of Africa and had populated most areas of the world by 10,000 BCE Why do you think humans migrated out of Africa? How did people survive? By the end of this era, humans had learned to herd animals and plant crops. This was a major lifestyle change and led to permanent settlements. Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society Pre-history - Homo sapiens spread across the world GeoHistogram Activities Mark the Eras on the Geohistogram The second era is “Early civilizations and Cultures and the Emergence of Pastoral People” (4000 – 1000 BCE) What is a “civilization”? What are “pastoral people”? What does Pastoral mean? The first settlements occurred in areas where agriculture was possible, namely river valleys. What rivers were located in these areas? The Fertile Crescent Tigris and Euphrates Egypt Nile India Indus China Huang He Era 2: Early Civilizations and Emergence of Pastoral Peoples Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society Having a stable food supply allowed some people in the settlements to have other jobs. This division of labor led to the development of civilizations. Some elements of civilization include the development of cities art specialized jobs religion communication laws Era 2: Early Civilizations and Emergence of Pastoral Peoples Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society These are the names of the civilizations that began during this era in these regions: Africa Middle East Central Asia East Asia The size of the colored shapes show the growth and extent of each one. Which one did not continue to grow into the next era? Era 2: Early Civilizations and Emergence of Pastoral Peoples Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society GeoHistogram Activities Mark the Eras on the Geohistogram The third era is “Classical Traditions, World Religions, and Major Empires” (1000 BCE to 300 CE) What are the major “classical” civilizations? What “world religions” were predominant? What “major empires” developed? With the rise of civilizations and development of new technology, trade helped spread ideas. In East Asia, the Qin Dynasty united China a territory which is now ___??____, the most populous country in the world. Growing civilizations, needing more land and resources, used force to expand, and became empires. Era 3: Classical Traditions and Major Empires These are the two large (classical) European empires that characterize this era. Era 2: Early Civilizations and Emergence of Pastoral Peoples Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society What famous Greek leader conquered Egypt and advanced into Central Asia? Empires grew by conquering people of many cultures. World Religions, like Buddhism and Hinduism, also spread. Other large empires ruled during this era. Where are each of them located? Persia? Mauryan? Han Middle East India Asia Era 3: Classical Traditions and Major Empires Era 2: Early Civilizations and Emergence of Pastoral Peoples Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society What was the first civilization in the Western Hemisphere? GeoHistoGram Activities Mark the Eras on the Geohistogram The fourth era is “Expanding and Intensified Hemispheric Interactions” (300-1500 CE) What do “expanding” and “intensifying” mean? What “hemispheric interactions” took place? Empires expanded during this era: The eastern Roman Empire became the Byzantine Empire, but had many enemies. What does its shape tell you? By about 700 CE, what dynasty in Asia had expanded westward? Era 4: Expanding Hemispheric Interactions Era 3: Classical Traditions and Major Empires Islam spread by both trade routes and conquering armies into north Africa and central Asia. What was the major trade route connecting China to Europe? Era 2: Early Civilizations and Emergence of Pastoral Peoples Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society Mongols conquered both Chinese and Muslim empires and spread into Europe. Empires expanded during this era: In West Africa, what two empires became wealthy through trade? The Plague spread across Europe killing a quarter of the population. How is this shown on the GeoHistoGram? Era 4: Expanding Hemispheric Interactions Marco Polo sparked a new interest in trade with China. Era 3: Classical Traditions and Major Empires What effect did the demand for products from Asia have on Europeans? Era 2: Early Civilizations and Emergence of Pastoral Peoples Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society See Era 5! GeoHistoGram Activities Mark the Eras on the Geohistogram The fifth era is “Emergence of the First Global Age” (15th to 18th Centuries) What is a “global age”? What important event marks the beginning of this era? Era 5: Emergence of 1st Global Age The ability to navigate the ocean caused many changes in trade and power. Era 4: Expanding Hemispheric Interactions Columbia Exchange was an important trading system between the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. What 3 regions were involved? What was exchanged? Era 3: Classical Traditions and Major Empires European Colonialism starts in this era. What color shows its spread? Which direction did it spread? Era 2: Early Civilizations and Emergence of Pastoral Peoples Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society What other Empire expanded its power during this era? GeoHistoGram Activities Mark the Eras on the Geohistogram The sixth era is “Global Revolutions” (Late 1700’s through 1914) What is a “global revolution”? Era 6: Age of Global Revolutions Era 5: Emergence of 1st Global Age Explain the saying “The Sun never sets on the British Empire” During this era, revolutions freed many colonies from their European conquerors or feudal leaders. Era 4: Expanding Hemispheric Interactions American French Era 3: Classical Traditions and Major Empires Era 2: Early Civilizations and Emergence of Pastoral Peoples Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society Latin American Chinese Russian As the Ottoman Empire declined, Europe’s power increased. Many changes occurred including an increase in world migration and industrialization. Nationalism and imperialism grew in Europe, Asia, and America. GeoHistoGram Activities Mark the Eras on the Geohistogram The seventh era is “Global Crisis and Achievement” (1900-1945) What is a “global age”? Era 6: Age of Global Revolutions Era 5: Emergence of 1st Global Age Era 7: Global Crisis and Achievement Increasing government, economic and political power changed the global balance of power. Two World Wars occurred as well as mass genocide in several regions. Era 4: Expanding Hemispheric Interactions What major event ended WW II? Era 3: Classical Traditions and Major Empires Era 2: Early Civilizations and Emergence of Pastoral Peoples Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society Important advances were made in technology, medicine and communications during this era. What countries emerged as super-powers? GeoHistoGram Activities Mark the Eras on the Geohistogram The eighth era is “The Cold War and Its Aftermath: The 20th Century since 1945” What was the “Cold War”? Era 7: Global Crisis and Achievement Era 6: Age of Global Revolutions Era 5: Emergence of 1st Global Age Era 8: Cold War and Aftermath The Cold War was a conflict between democracy and communism. What two countries were the leaders in this “war”? Era 4: Expanding Hemispheric Interactions Era 3: Classical Traditions and Major Empires Era 2: Early Civilizations and Emergence of Pastoral Peoples Era 1: Beginnings of Human Society Some “hot spots” caused mounting tension, and conflicts in Korea and Vietnam became major clashes. One of the fears that surfaced was the threat of nuclear war. What event signified the end of the “Cold War”? GeoHistoGram Activities What might the next era be called? How long will it last?