* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Arryhythmias post-TOF repair surgical repair
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
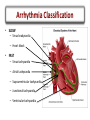
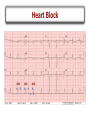
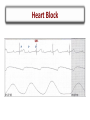
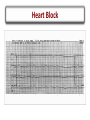
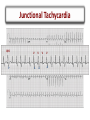
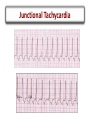
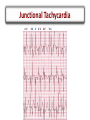
Arrhythmias Post Tetralogy of Fallot Surgical Repair Joseph Atallah, MD CM, SM Division of Pediatric Cardiology Section of Electrophysiology Outline • • • • • • Why is there a risk of arrhythmias Arrhythmia classification Recognition Treatment Longterm outcomes Summary Arrhythmias … Why? Arrhythmias … Why? • Incidence – Up to 36% of post-op TOF patients will experience some arrhythmic event, mostly insignificant and brief – Majority resolve within 48 hrs post-op • Risk factors – Young age at surgery – Longer bypass and aortic cross-clamp time – Complexity of repair Arrhythmia Classification • SLOW • FAST . Arrhythmia Classification • SLOW – Sinus bradycardia – Heart block • FAST – Sinus tachycardia – Atrial tachycardia – Supraventricular tachycardia – Junctional tachycardia – Ventricular tachycardia Arrhythmia Classification • SLOW – Sinus bradycardia • Intrinsic: sinus node dysfunction (rare) • Extrinsic: medications (sedation …), increased ICP … – Heart block • Results from damage to the AVN, His bundle or bundle branches • FAST – Sinus tachycardia • Common: medications (inotropes, sedation …), hemodynamic stress … – Atrial tachycardia • Rare – Supraventricular tachycardia • ORT or AVNRT or atrial flutter – Junctional tachycardia • Relatively common: multifactorial – Ventricular tachycardia • Rare, more of an issue 10-20-30 years post-op Definition and Recognition Heart Block • SLOW – Heart block • Incidence is 1-3% of all pediatric open heart surgeries • Often recognized in the operating room • However, may be acute or gradual in onset in first few days post-op • Highest risk surgeries – – – – LVOTO surgery VSD Closure TOF ccTGA • Definition: more P waves than QRS complexes (more As than Vs) Heart Block • SLOW – Heart block • 2nd degree (partial) – Not every atrial beat is conducted to the ventricle = ventricular rate is slower than the atrial rate (2:1, 3:1 …) • 3rd degree (complete) – No (zero) atrial beat is conducted to the ventricle – Extreme: HR (VR) = 0 … flat line … bad news … please help! – Most common: ventricular escape rhythm at a certain rate » Inadequate slow vs. acceptable rate » Narrow vs. wide complex QRS Heart Block QRS P ?T QRS P P QRS P 2 1 Heart Block QRS P P P Heart Block Narrow QRS Wide QRS Heart Block Arrhythmia Recognition • FAST – Supraventricular Tachycardia • Usual rate between 180 and 280 bpm • Sudden onset and termination • Minimal HR variation during SVT – Junctional Tachycardia • Usual rate between 160 and 230 bpm • Gradual onset and termination • HR variation during JET Junctional Tachycardia • Onset within the first 24 hrs post-op • Due to stress injury around the AV node and the His bundle • Inappropriate accelerated rhythm with the same QRS morphology as sinus rhythm • Often with more Vs then As = VA dissociation • Most common after TOF repair Junctional Tachycardia QRS P V A V A V V A Junctional Tachycardia Junctional Tachycardia AV V A V A V AV VA Treatment SLOW • Weaning sedation • Warming up • Medications – Atropine – Isoproterenol – Epinephrine • Pacing – Atrial, ventricular or both FAST • • • • • • Optimize hemodynamics Correcting electrolyte and acid-base disturbances Weaning certain inotropes (e.g. Epi, Dexmetomedine) Optimizing sedation Cooling Anti-arrhythmic drugs – Procainamide – Amiodarone – Esmolol • Overdrive atrial pacing Outcomes Long-term Outcomes • Heart Block – At least 60% resolve in the first month post-op • ~90% of those will occur in the first 10 days post-op – Remaining require a permanent pacemaker implantation despite the possibility of late recovery of AV conduction • Supraventricular tachycardia – May resolve – Medical therapy or ablation • Junctional tachycardia – May be very resilient and life threatening – Usually resolves within 2 days but may last 8 days Summary • Most common arrhythmias post surgical repair of TOF – Heart block – Junctional tachycardia • A simple analytical approach to recognition • Multiple treatment options, ultimately: – Pacing for heart block – AAD for junctional tachycardia • Long-term outcomes: – Heart block: 30-40% will require pacing – ST and JT usually resolve early on