* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.3 Notes - Trimble County Schools
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Frictional contact mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rolling resistance wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
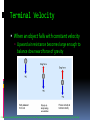
3.3 MOTION & FORCE Objectives Explain how forces and motion are related. Compare and contrast static friction and sliding friction. Describe the effects of air resistance on falling objects. Force Push or pull that one object exerts on another Vector with size (strength of force) & direction SI Units = Newtons (N) Can cause the motion of an object to change Example: hitting a tennis ball shooting pool/billiards Balanced Forces Forces equal in size but opposite in direction doesn’t change velocity Net Force When 2 or more forces act on an object at the same time Sum of all forces acting on an object Unbalanced Forces When forces combine to produce a net force that is not zero Forces that aren’t equal The object moves Changes the velocity of an object Friction The force between two objects, in contact, that opposes the motion of either object Unbalanced force Why does a ball stop rolling? Why do we have to keep applying gas to the engines in our cars to keep moving? Better yet, why do we put oil in a car’s engine? Why do runners wear running shoes? Why do parachutes work? Friction Friction depends on the surfaces of the objects in contact Smooth things tend to have less frictional force they are more slippery Ice, oil on concrete, my old shoes, my road bike tires Rough things tend to have more frictional force less slippery Asphalt, my new running shoes, my mountain bike tires Frictional Force Increases when the force pushing surfaces together increases Static Friction = frictional force that prevents 2 surfaces from sliding past each other Sliding friction = force that acts in opposite direction to the motion of a surface sliding past another surface Rolling friction = similar to sliding friction why it is easier to move something on wheels Friction Air Resistance is a form of friction Caused by the interaction between an object and the air molecules it comes into contact with The bigger the object the more air resistance The faster the object the more air resistance Air Resistance Causes objects to fall at different acceleration and speed Acts in opposite direction to velocity Air resistance not mass causes objects to fall at different rates v v v v v Terminal Velocity When an object falls with constant velocity Upward air resistance becomes large enough to balance downward force of gravity http://www.iop.org/activity/education/Teaching_Resources/Teaching%20Advanced%20Physics/Mechanics/Images%20200/img_mid_4140.gif