* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.02 Plant parts
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
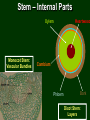
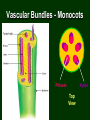
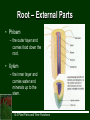
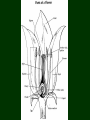
B. Plant Physiology 3.02 Discuss the anatomy and functions of plants 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Six Major Plant Parts • • • • • • Roots Stems Leaves Flowers Fruit Seeds Leaves – External Parts • Petiole • leaf stalk or part that connects leaf to stem. • Midrib • Large central vein of the leaf 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Leaves – External Parts • Blade – the large, flat part of a leaf. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Leaves – External Parts • Veins – the structural framework of a leaf. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Leaves – External Parts • Margin – the edge of the leaf. • There are several different styles (draw these) – – – – Entire Serrated Lobed Crenate 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions margin Leaves – External Parts • Apex – leaf tip 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions apex Leaves – Internal Parts • Upper and lower epidermis – skin of the leaf that prevents the loss of too much moisture. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Leaves - Internal Parts • Stomates – small openings under the leaf for breathing or transpiration. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Leaves – Internal Parts • Guard cells – opens and closes the stomata. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Leaves – Internal Parts • Chloroplasts – small green particles that contain chlorophyll, gives leaves their green color and are necessary for photosynthesis. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Functions of the Leaf • Photosynthesis is a process by which plants capture sunlight and use it to convert carbon dioxide and water into food • Respiration converts sugars and starches into energy • Transpiration is the release of water vapor from the leaves of plants – It also cools the plant 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Leaves – Additional Notes • Sessile – leaves with no petiole. Sessile 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Leaves – Additional Notes • Bracts – modified leaves usually found on a poinsettia. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Leaves – Additional Notes • Needles and scales – Modified leaves found on a pine tree 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Leaves – Additional Notes • Glabrous – Leaves or stems have a smooth, non-hairy feel – Southern Magnolia 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Leaves – Additional Notes • Pubescent – Leaves or stems have a hairy feel – African Violets 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Stem – External Parts • Lenticels – breathing pores. Stem – External Parts • Bud scale scar – shows where the terminal buds were located the previous year. Bud scale scar 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Stem – External Parts • Leaf scar – shows where leaves were attached. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Stem – External Parts • Terminal bud – bud at the end or tip of the stem. terminal buds 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Stem – External Parts • Axillary bud – Bud located at the axil of the leaf 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Stem – External Parts • Lateral bud – bud on the side of the stem. lateral bud 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Stem – Internal Parts • Xylem – tissue that transports water and nutrients up from roots to stems and leaves. • Phloem – tissue that transports food down from the leaves to the roots. • Cambium – thin, green actively growing tissue located between the bark and wood and produces all new stem cells. Stem – Internal Parts Xylem Monocot Stem: Vascular Bundles Heartwood Cambium Phloem Bark Dicot Stem: Layers Stem – Internal Parts • Bark – Old inactive phloem – Protection for the stem Stem – Internal Parts • Heartwood – Old inactive xylem. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Stem – Internal Parts • Sapwood – New active xylem. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Stem Structure - Cotyledons • Monocot ~ one seed leaf – Plant stems that have vascular bundles that contain both xylem and phloem in each bundle. – Examples: grasses, corn • Dicot ~ two seed leaves – plant stems have phloem layer and a xylem layer separated by cambium. – Examples: trees Vascular Bundles - Monocots Phloem Xylem Top View Functions of the Stem • Translocation is the movement of water and minerals through the plant – The phloem moves food down from the leaves to the roots – The xylem moves water and nutrients up from the roots to the leaves • Supports the branches of the plant 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Root – External Parts • Root cap – Located at the tip of the root and is where new cells are produced • Root hairs – absorb moisture (water) and minerals. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Root – External Parts • Phloem – the outer layer and carries food down the root. • Xylem – the inner layer and carries water and minerals up to the stem. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Types of Roots • Fibrous – many branched shallow roots. They are easier to transplant. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Types of Roots • Tap – long root with few branched ones, are more difficult to transplant. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Functions of the Roots • Anchor the plant and hold it upright. • Absorption – take water and nutrients from the soil and conduct them to the stem. • Asexual reproduction. • Store food for plant use. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Flowers • Flowers develop into seeds and fruits. • External Parts of the Flower – Sepals • green parts that cover and protect flower bud before it opens. – Petals • are really leaves that are modified to attract insects for flower pollination, the pretty part that we call flowers. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Flowers – External Parts petal sepal 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Stamen - Male Parts of the Flower • Anther – a sac like structure that contains pollen, the male sex cells. • Filament – short stalk that holds up the anther Pistil – Female Parts of the Flower • Stigma – sticky part on top of style where insects leave pollen. • Style – holds up the stigma and connects it to the ovary. • Ovary – if fertilized becomes a fruit or seed coat. • Ovules – the eggs or female sex cells that become seeds if fertilized. Functions of the Flower 1. Attracts insects for pollination. 2. Produces seeds for sexual propagation. 3. Produce fruit to protect, nourish and carry seeds. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Flower • Complete flower • Pollination – The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma – has both male and female parts. • Incomplete flower • Cross pollination – transfer of pollen from the stamen to the stigma of one flower to a flower on another plant. – has only male or female parts. • Fertilization • Self pollination – When pollen travels down the style, joining the sperm and the ovule 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions – transfer of the pollen to the stigma of a flower on the same plant. Flower Additional Notes • Corolla – all auxiliary part of the flower not including reproductive organs. – The collective term for all petals of a flower. • Calyx – the external usually green or leafy part of a flower. The collective term for all sepals of a flower. • Receptacle – the enlarged tip of a stem on which a flower is born. 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Flower – Additional Parts receptacle calyx 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions Additional Information • The fruit serves as protection for the seeds • The function of the fruit is to help with seed dispersal 14.0 Plant Parts and Their Functions