* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download intro to proofs with angle relations
Coxeter notation wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
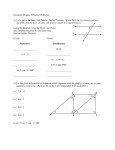
Geometry Unit 3: Angles and Lines – Beginnings of proofs! Name: One of the main goals in studying geometry is to develop your ability to reason critically, to draw valid conclusions based upon observations and proven facts. Master detectives do this sort of thing all the time. In geometry, we follow a similar deductive thought process. Class Example Recall the: Now let’s use deductive reasoning to prove it! Exterior angle Theorem for Triangles: Notice that each step in the proof was justified by a previously known or demonstrated fact. We end up with a newly proven fact (that an exterior angle of any triangle is the sum of the measures of the opposite interior angles of the triangle). This ability to identify the steps used to reach a conclusion based on known facts is deductive reasoning Exercise 1: Prove that vertical angles are congruent. Always make a plan! 1. What do you know about ∠𝑤 𝑎𝑛𝑑 ∠𝑥? What about ∠𝑧 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑦? 2. What conclusion can be drawn from the givens above? 3. Write out you proof: Basic Property Reference Sheet Now You Try! 1. Given the diagram at the right, prove 𝑚∠𝑤 + 𝑚∠𝑥 + 𝑚∠𝑧 = 180𝑜 (what do you know about angles x, y and z?) 2. Given the diagram to the right, prove 𝑚∠𝑤 = 𝑚∠𝑦 + 𝑚∠𝑧. 3. Given the diagram, prove 𝑚∠𝑥 + 𝑚∠𝑤 = 𝑚∠𝑦 + 𝑚∠𝑧. (hint: label the missing angle as a and use it in your proof) ̅̅̅̅ and 𝐵𝐶 ̅̅̅̅ //𝐷𝐸 ̅̅̅̅ , prove 𝑚∠𝐴𝐵𝐶 = 𝑚∠𝐸𝐷𝐶. 4. Given that ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐵 //𝐷𝐶 (what do you know about parallel lines and transversals?) Geometry Unit 2: Lines and Angles – Intro to proof! HW Name: 1. In the diagram to the right, use the information to prove 𝑚//𝑛. Be sure and provide exact reasons for all your claims! 2. In the diagram below, prove that the angles marked by the arrows sum to 360o. (hint: label all the angles, use vertical angle thm and triangle angle sum) ̅̅̅̅ ⊥ 𝐸𝐹 ̅̅̅̅ . (Don’t forget the reasons!) (and remember ⊥ = 90𝑜 ) 3. Use the figure below to prove that 𝐷𝐶 Exit Ticket Name: In the diagram to the right, prove that the labeled angles sum to 180o. Exit Ticket Name: In the diagram to the right, prove that the labeled angles sum to 180o.