* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 and 2
Recursion (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Object-oriented programming wikipedia , lookup
APL syntax and symbols wikipedia , lookup
Name mangling wikipedia , lookup
Buffer overflow protection wikipedia , lookup
Falcon (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Structured programming wikipedia , lookup
Corecursion wikipedia , lookup
Go (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
One-pass compiler wikipedia , lookup
Control flow wikipedia , lookup
Standard ML wikipedia , lookup
C Sharp (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
1
Chapter 1: Evolution of C++
• Introduction
• Procedural, Structured, and Object-Oriented
• Preparing to Program
• C++, ANSI C++, Windows
• Compiler and Editor
• Developmental Cycle
• First Program in C++
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
2
Introduction
• Developmental Language of choice
for majority of professional
programmers
• Relatively new to the market – about
30 years
• Can write powerful commercial
software applications
• Can be extended and change in a
convenience matter
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
3
Procedural, Structured, Object-Oriented
• Procedural: In procedural programming language,
programs are written as a series of actions performed
on a set of data.
• Structured: Structured programming language was
invented to provide a systematic approach to
organizing these "procedures," and to managing large
amounts of data. The principle idea of structured
programming is to divide and conquer.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
4
Procedural, Structured, Object-Oriented –
cont’
• Object-Oriented: The essence of object-oriented
programming is to treat data and procedures
that act upon the data as a single "object" – a
self-contained entity with an identity and certain
characteristics of its own.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
5
Preparing To Program
C++, perhaps, more than other language, demands that
programmer design the programs before writing it.
The better the design, the lesser troubles, cost and time
the programmers save. A good design can also make
the program relatively bug free and easy to maintain.
It's been estimated that fully 90 percent of the cost of
software is the combined cost of debugging and
maintenance.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
6
C++, ANSI C++, Windows
• C++ is a language, an Object-Oriented
Programming Language. DOS, Windows, UNIX,
and MacOS are operating systems. When we
learn C++ we'll want to learn it as a portable
language without regard to which machine and
operating system you'll run our programs on.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
7
C++, ANSI C++, Windows – cont’
(American National Standard Institute) ANSI
C++ is just another way of saying
"standard" C++ -- the internationally
agreed upon version that is portable to any
platform and any development
environment.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
8
Compiler and Editor
• Compiler is an application program to
compact our source codes into a portable
single program. It searches for error, links
object files, and makes an executable file
for it.
• Editor is a plain text editor such as DOS,
notepad or build in editor. It does not have
the ability of searching for errors, links
objects, and makes executable files.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
9
Compiler and Editor-Compile,
Link, and Make EXE file
• The source code is edited in the editor,
and the file is being saved as .cpp
• Then, compile to create an object file
• After the object file is created, the file
needs to be linked and build an
executable file
• An executable file is a file that can be run
on any machine
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
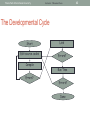
The Developmental Cycle
Start
Edit source codes
Compile
Errors?
Link
Errors?
Run Time
Errors?
Done
10
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
11
Name a C++ File
• Starts with an underscore “_” or a letter, lowercase or uppercase,
such as a letter from a to z or from A to Z. Examples are Name,
gender, _Students, pRice
• Can include letters, underscore, or digits. Examples are:
keyboard, Master, Junction, Player1, total_grade, _Score_Side1
• Cannot include special characters such as !, %, ], or $
• Cannot include an empty space
• Cannot be any of the reserved words
• Should not be longer than 32 characters (although allowed)
Phnom Penh International University
12
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Keywords or reserved words
C++ Reserved Words
asm
auto
bad_cast
bad_typeid
bool
break
case
catch
char
class
const
const_cast
continue
default
delete
do
double
dynamic_cast
else
enum
except
explicit
extern
false
finally
float
for
friend
goto
if
inline
int
long
mutable
namespace
new
operator
private
protected
public
register
reinterpret_cast
return
short
signed
sizeof
static
static_cast
unsigned
struct
switch
template
this
throw
true
try
type_info
typedef
typeid
typename
union
unsigned
using
virtual
void
volatile
wchar_t
while
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
First Program in C++
#include <iostream.h>
int main()
{
cout <<"Hello World!\n";
cout <<"Welcome to Phnom Penh
International University!\n";
return 0;
}
13
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
14
Practical Exercises for chapter 1
1.
2.
3.
C++ is a procedural programming language. True
or false.
What are the steps of compiling a program?
Write a program similar to the sample program
within this chapter by changing from "Hello World!"
to "Hello to the World of Computing!" and
"Welcome to Phnom Penh International University!"
to "Welcome to the C++ Programming Language!"
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Chapter 2: Part of a C++
Program
In this chapter we will study
• Part of a C++ Program
• How these parts work together
• Comments
• What a main function is?
15
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
16
Part of a C++ Program
• # include (preprocessor directive) this # symbol
is a signal to the processor telling it to find the
include directory which contains the header file
• <header file> this header file can be called h file
or include file. The frequently used header file in
C++ is iostream.h
• body of a program: the codes enclosed with in
the curly braces after main is called body of
main. It tells the compiler to execute line by line
in a consecutive manner unless there is a jump
statement
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
17
Part of a C++ program – cont’
• cout object: the cout object is an object
printing the message to the screen. It’s
like the printf in C programming language
• << (output redirection operator) this
symbol “<<“ is called output redirection
operator and it’s is used after cout
• return 0: C++’s main function always
needs a return type, and it’s usually int. If
it’s int, the return value is 0 which signals
success
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
18
Comments
• Comment is very important in all kind of
programming languages. It facilitates the
programmer with better understanding of
the program. The better the comment is,
the better the program design is and the
least time the programmer takes time to
maintain
• There are two type of comments in C++
• Line comment // comment goes here
• Block comment /* multiple line of comments
goes here
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
19
Main() Function
• main() function is always a must in C or
C++.
• The operating system needs main to start
every C++ program
• Others functions are called or invoked
from main()
• In C++, usually, main() needs an int return
type
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
20
Practical Exercises for chapter 2
1.
What does include do?
2.
What is the difference between backslash-star
comment and double slashes comment?
3.
Why is comment so important?
4.
What can main do?
5.
What can cout do and what does it needs?
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
21
Chapter 3: Variables and Constants
•What is a variable
•Constant
•Enumerated Constant
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
22
What is a variable?
• Variable is a storage location to store value.
Without variable our program is just like a dead
being.
• Setting aside memory: when we declare a
variable, a certain amount of memory is being
allocated for the specified variable types. The
size of memory depends on the type of
variable being declared
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Variable Types
Type
Size
Value
unsigned short int
2 bytes
0 to 65,535
short int
2 bytes
-32,728 to 32,727
unsigned long int
4 bytes
0 to 4,294,967,295
long int
4 bytes
-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
char
1 byte
256 character value
bool
1 byte
True or false
float
4 bytes
1.2e-38 to 3.4e38
double
8 bytes
2.2e-308 to 1.8e308
long double
10 bytes
3.4e-4932 to 1.1e4932
23
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
24
Variable - cont’
• Defining/Declaring variables: First of all,
for a variable to be in used is to declare it
first. To declare a variable we just type the
data type of the variable type in front of a
variable name e.g., unsigned short int
myAge;
• Case Sensitivity: C++ is also case
sensitive which means upper case letter
and lower case letter is not the same.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
25
Variable – cont’
• Set value/Assign variable value/variable initialization: to
set variable value we can set it at declaring time or set
it later on when we need to use the value: e.g., int
counter=0; or we can declare int counter; then we set it
to 0 at other location within the program
• Keywords: keywords are reserved words in C++. We
should not use keywords as variable or other kind of
names
• User input: to accept user input from keyboard we used
an object call cin followed by an input indirection “>>”
then follow by the variable name. E.g: cin>>a;
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
26
Sample program on user input
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{
int a,b;
cout<<"Enter the length of a rectangle: ";
cin>>a;
cout<<"Enter the width of a rectangle: ";
cin>>b;
cout<<"The area of the rectangle is: "<<a*b<<" meter
squares\n";
}
Another sample program
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
27
#include <iostream.h>
void main()
{
int length, width, height, CA;
cout<<"Enter the length of the cube: ";
cin>>length;
cout<<"Enter the width of the cube: ";
cin>>width;
cout<<"Enter the height of the cube: ";
cin>>height;
CA = length * width * height;
cout<<"The cubic area of the cube is: "<<CA<<endl;
}
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
28
Sample program on string
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char University[] = "Phnom Penh International University";
char Faculty[]("Computer Sciences");
cout << "Welcome to the Student Orientation Program.\n";
cout << "For your studies, we have selected:\n";
cout << "Institution: " << University << "\n";
cout << "Faculty: " << Faculty << "\n";
return 0;
}
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
29
Variable-cont’
• Typedef: we can create or define our own type of
data based on the existing variable types. To
create or define our own variable type, we used
keyword typedef: e.g: typedef unsigned short int
myInt; myInt a;
• Now myInt becomes a data type called unsigned
short int; and when we assign it to a, a becomes
unsigned short int
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Sample program on typedef
#include <iostream.h>
typedef unsigned short int myInt;
int main()
{
myInt age = 22;
cout<<"Your age is: "<<age<<endl;
return 0;
}
30
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
31
Constants
Constants are variables that contain unchangeable value
• Literal Constants: a literal constant is a constant value
typed in directly in program. E.g. int counter=0;
• Symbolic constant: symbolic constant is a constant whose
value cannot be changed within the whole course of
program execution. The old way of declaring symbolic
constant is used the keyword define right after the # sign.
The new way is used with keyword const. E.g: #define n
10 or const int n=10;
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
32
Enumerated Constants
• Enumerated constants is a list of consecutive
constants and represented by just one name.
The keyword of enumeration is enum
• E.g:enum dog {Ky, Khno, Khmao, Popeal}; in
this case a dog called Ky holds a value of 0
and Khno holds a value of 1 and so forth
• sizeof is a keyword used to show the size of a
variable type: e.g sizeof(int); sizeof(float)
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Sample program on enum
#include <iostream.h>
int main()
{
enum Code {Sok=1, Vichea=2, Dara=3,Dany=4,Leak=7};
cout<<"Sok's code is: 00"<<Sok<< endl;
cout<<"Vichea's code is: 00"<<Vichea<< endl;
cout<<"Dara's code is: 00"<<Dara<< endl;
cout<<"Dany's code is: 00"<<Dany<< endl;
cout<<"Leak's code is: 00"<<Leak<< endl;
return 0;
}
33
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
34
Practical Exercises for chapter 3
1. Determine to see which ones are true and which are
false.
a.
A variable is a storage location
b.
Keywords are used to name a variable names (F)
c.
C++ is case sensitivity (T)
d.
sizeof is a function in C++ (F)
e.
enum is a keyword used for a range of character. (F)
2. Write a program to calculate an area of a circle given
the radius of the circle. Define pi as symbolic
constant.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
35
Chapter 4: Expression and Statement
• What is a statement?
• What is an expression?
• Operators
• Mathematical Operators
• Logical Operators
• Relational Operators
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
36
Statement
• In C++ or C a statement is anything that ends with a
semicolon. E.g x=a+b; is a statement, cout<<“The value
is\n” <<a; is also a statement
• White space: white spaces are space, tab and new line.
White space is legal in C++.
• Compound statement: statement can be single or
compound. A compound statement is a block of related
statement enclosed within curly braces
• E.g: { temp=a; a=b; b=temp;}
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
37
Expression
• In C++ or C, expression is something that return
a value. A=x+y; A is holding the value of x+y;
I=0;I++; I is now holding 1
• Note: All expressions are statements but not all
statement are expressions
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Operators
• Assignment Operator (=): “=“ is called
assignment operator. The value on the right
side of this operator is being assigned to the
left side. E.g: x=3+4; x is being assigned to the
value of 7
• r-value: the value on the right side of the assignment
operator is called r-value. By default all constants
are r-value
• l-value: the value on the left side of the assignment
operator is called l-value.
• Note: All r-values are l-values but not all l-values are
r-values
38
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
39
Operators – cont’
• Mathematical operators: mathematical
operators are used for mathematical
operations. They include plus (+), minus (-),
multiply (*), divide (/) and modulus (%)
• Relational operators: relational operators are
operators used to compare two or more
values: they are equal to (==), less than (<)
less than or equal to (<=), greater than (>),
greater than or equal to (>=) or not equal to
(!=)
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Operators – cont’
• Logical Operator: Logical operator are frequently
used with set operations such as union, intersect
and differentiation. They include: or (||), and (&),
and not (!)
• Increment or Decrement: (++) or (--) are increment
and decrement operators used to increase or
decrease a value by 1
• Prefix and postfix: we can write ++I, this called
prefix increment or I++, this is call postfix
increment. The result is the same for simple logic
but when involving complex expression and
logics, the value would be very much different
40
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
41
Operators – cont’
• Precedent/Priority: When writing a program,
precedent or priority of the operators have to
take into much consideration. E.g: (a+b)*c is
different from a+b*c
• Parentheses: Parentheses () are also of
considerably important in writing a program,
especially involving compound logical
operations
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Operators – cont’
• Short cut operator:
x+=a <==> x=x+a
x-=a <==> x=x-a
x*=a <==> x=x*a
x/=a <==> x=x/a
42
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
43
Operators
• Relational precedent
• when there is a complex or compound of conditions
brackets are needed to specified the priority of the
condition
• if (x>5 && y>5 || z >5) can have two scenarios
1. The programmer means that it's true only if x greater
than 5 and either y or z is greater than 5.
2. Or the programmer means that it's true only if both x and
y are greater than 5 or z is greater than 5
3. To make the code clear we would write: if ( (x>5) &&
(y>5 || z>5) ) for the first case and if ( (x>5&& y>5) || (z>5) )
for the second case
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
44
Practical Exercises for chapter 4
1. Write a program to convert from Fahrenheit
degree to Celsius given that the formula
is: Celsius = 5(Fahrenheit – 32)/9
2. Write a program to swap two numbers.
3. Write a program to find the net payment of
an item being bought at one of the shops
given that the discount rate is 15%.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Part II. Control Structures,
Functions and Array in C++
1. Control Structure
2. Functions
3. Array
45
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Chapter 5: Control Structures –
Programming Flows
• if statement
• Advanced programming flows
• loop
• for loop
• while loop
• do while loop
• Switch case statement
46
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
47
If statement
• Normally, the flow of a program is in a
consecutive manner, a top down approach
• But often there are cases where we don’t
want to follow this pattern of programming
approach
• In such case, the control structure has a
significant impact on the programming flow.
As such, the program is more effective and
efficient
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
48
If statement – cont’
• One of the control structure is the implementation
of conditional statement
• The conditional statement, as its name
suggested, is used to test whether a condition has
been met.
• It’s one of the most frequently used statement
regardless of whatever the programming
language.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
49
if statement – cont’
• Simple if
• syntax of if statement
if (expression/condition)
statement/compound statements;
else
statement/compound statements;
• Note: it’s not necessary that all if
statements need to have else. It depends
on the design of the program
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
if statement – cont’
• a sample program
#include <iostream.h>
int main()
{
int year;
cout<<“Key in a year: “;
cin>>year;
if (year % 4== 0)
cout<<year<<“ is a leap year\n”;
else
cout<<year<<“ is not a leap year\n”;
return 0;
}
50
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
51
Without using if (expr ? True : False)
#include <iostream.h>
int main()
{
int year;
cout<<"Key in a year: ";
cin>>year;
(year % 4== 0) ? cout<<year<<" is a leap year\n":
cout<<year<<" is not a leap year\n";
return 0;
}
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
52
if statement – cont’
• Nested if
• In a complex situation, there are often multiple
layers of if. The if within if approach of conditions is
called nested if
• The flow of condition will test the first layer to see if
it’s true, if it’s true, it will go to the next inner if, if it’s
not true it would go for the alternative option, if there
exists one
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
if statement – cont’
syntax of nested if
if (expression1/condition1)
if (expression2/condition2)
if(expression3/condition3)
.
.
.
else
else
else
53
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
54
if statement – cont’
• In a tax department, there is a policy requiring all
employees paying tax to the government.
• The policy is as follow:
1. equal to or below $200 tax free
2. $100 above 1 is subject to a 3% tax
3. $100 above 2 is subject to a 5% tax
4. $100 above 3 is subject to a 10% tax
5. $300 above 4 is subject to a 20% tax
6. any thing beyond this is subject to 30% tax
• for example if one gets a $670 monthly salary his
monthly tax would be
• $200*0+$100*.03+100*.05+100*.1+(670-500)*.2 = $52
• Click here to see the sample code
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
55
if statement – cont’
• compound if/else if statement
• We use compound if when there is a series of
conditions
• The flow of the condition is from top down
• Note: in C++ or C, 0 means false whereas
nonzero means true
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
56
if statement – cont’
syntax of else if
if (expression1/condition1)
statement/compound statements
else if (expression2/condition2)
statement/compound statements
else if (…)
.
.
.
else
statement/compound statements
Click here to see a sample code for compound if
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
57
Loop
• Loop is the process of doing the same thing in a
repetitive manner. For example a production chain of
a product in a manufacture.
• Many of the programs achieve most work by looping
as well
• Root of loop (goto)
• goto is an old way and primitive way of looping. To use a
goto statement we need to give a label to it and then use the
goto statement at the location where we want to jump to the
label. Goto was very popular during the 1980s.
• Click here to see goto example
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
58
loop – cont’
• goto statement can cause a jump to any
place in the program.
• It’s advisable not to use goto statement in a
well-designed program
• To avoid the use of goto statement, a tightly
control looping command and sophisticated
tool is being established. This modern tool
is divided into: for, while and do while loop
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
59
loop – cont’
Some comments on goto from one of the well-known
publisher called: Macmillan Computer Publishing
goto has received some rotten press lately, and it's well
deserved. goto statements can cause a jump to any
location in your source code, backward or forward. The
indiscriminate use of goto statements has
caused
tangled, miserable, impossible-to-read programs
known as "spaghetti code." Because of this, computer
science teachers have spent the past 20 plus of years
or so drumming one lesson into the heads of their
students: "Never, ever, ever use goto! It is evil!"
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
60
loop – cont’
• for loop
• For loop is the most frequently used loop in C++ or C
due to its compactness of code
• syntax of for loop
• for (initialization;destination;step)
• e.g: for (i=1;i<=b;i++)
• initialization and step can be left out if we explicitly set it
already
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
61
loop – for loop – cont’
A sample program of factorial
#include<iostream.h>
int main()
{
int f,a,i;
cout<<“Enter a number: “;
cin>>a;
f=1;
for (i=1;i<=a;i++)
f=f*i;
cout<<“The factorial of “<<a<<“ is: “<<f<<endl;
return 0;
}
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
62
loop – for loop –cont’
//sample program to find the summation of a
series:S=2+4+…+2n
#include <iostream.h>
void main()
{
int s, i, n;
cout<<"Enter the n elements of even number to be summed:
";
cin>>n;
s=0;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
s=s+2*i;
cout<<"The summation of those numbers is: "<<s<<endl;
}
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
63
loop – for loop - cont’
Another sample program to list the numbers evenly
divisible
by 7 from 1 to 1000
#include <iostream.h>
void main()
{
int n=1000,i,num=0;
for (i=1;i<=n/7;i++)
{
//Increment num by 7
num += 7;
cout<<num<<" ";
}
}
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
64
loop – while loop
• While loop is another loop that can be very
useful in the looping process
• The concept is more or less like the for loop
but the syntax is quite different
• if, for and while loop are usually called pre-test
condition which means they check for the
condition before going to execute the
expression or statements within the loop
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
while loop – cont’
syntax of while loop
initialization
while (condition/expression)
{
expression/statement
step
}
65
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
while loop – cont’
Sample program to find a factorial of a number
#include <iostream.h>
void main()
{
int f, i,a;
cout<<“Enter a number: “;
cin>>a;
f=i=1;
while (i<=a)
{
f=f*i;
i++;
}
cout<<“The factorial of “<<a<<“ is: “<<f<<endl;
} Click here for another sample program
66
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
67
do while loop
• do while loop is known as a post-test
loop which means it execute the
statement or expression with the loop
before checking for the condition.
• We use do while loop when we are
certain about the condition
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
68
do while loop – cont’
• Syntax of do while loop
initialization
do
{
expression/statement
step
}
while (condition/expression);
Note: there is a semicolon after the while condition,
but there is none with if, for and while loop
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
do while loop – cont’
sample program for factorial
#include <iostream.h>
void main()
{
int f, a,i;
cout<<“Enter a number: “;
cin>>a;
f=1;
do
{
f=f*i;
i++;
{
while (i<=a);
cout<<“The factorial of “<<a<<“ is: “<<f<<endl;
}
69
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
70
switch case statement
• To master any programming languages one
needs to have the combination of talent,
creativity, innovation, and hard-work.
• C++ and C provides several ways of creativities
for the initiative and the hungry thirst learners.
• switch case statement can be alternatively used
to replace the long series of compound if or if
else conditions
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
71
switch case statement – cont’
Syntax of switch case
switch (expression)
{
case value 1: statement/block of statements
case value 2: statement/block of statements
…
case value n: statement/block of statement
default: statement/block of statement
}
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
72
switch case – cont’
• break is used with switch case statement to skip or
end the case
• continues is also a jump statement which is used to
skip the rest of the code
• default is used somewhat similar to the else statement
in compound if conditions
• Click here to see a sample code
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
73
switch case statement – cont’
• Multi-values cases – Often there are cases where several
conditions share the same operation. If there is such case we can
use multi-value cases
• syntax
switch (expression)
{
case value 1:
case value 2:
case value 3:
statement/block of statement
…
This is the same as if (expression 1) || (expression 2) || (expression
3) in the if else statement
Click here to see a sample code
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
74
Practical Exercises for chapter 5
1. Write a program to sort two numbers in an
ascending order.
2. Write a program to find the root of a given quadratic
equation. ax2 + bx + c = 0
3. Write a program to find the power of power of three
c
numbers by using one of the loops (ab) .
4. Rewrite the calculator program shown in class by
changing from a, b… to 1 ,2…
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
75
Practical exercises for chapter 5 – cont’
5. Write a program to count the number of
characters being typed in by using while loop
or do while loop. White space, tab and enter
are not considered as a legal character.
6. Write a program to count the number of words
being typed in by using while loop or do while
loop.
7. Write a program to count the number of lines
being typed in by using while loop or do while
loop.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
76
Chapter 6: Function
• What is a function?
• Anatomy of function
• Function overloading or
polymorphism
• Domain and Scope of variable
• Manipulator function
• Recursive function
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
77
What is a function?
• Function is a subprogram that can act on data and
return a value.
• Every C++ program has at least one function,
main().
• main() might call other functions, and some of
which might call still others.
• A well-designed function will perform a specific task.
This means, it does one thing, does it well, and then
returns the value.
• Complicated task can be broken down to multiple
functions, and then each can be called in turn.
• This makes our code easier to understand and
easier to maintain.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
78
Anatomy of a function
• Function prototype/function declaration
• Return type, name and parameters
• double power (int a, int b);
• Function Definition
• Function Header
• Return type
• Function Name
• Parameters lists (optional)
• Function body: it’s a chunk of code enclosed within the curly
braces
• Example: double power (int a, int b)
• double is return type, power is name, a and b are parameters
• Note: function header is almost the same as function
prototype except that it doesn’t have a terminating semicolon
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
79
Anatomy of function – cont’
• Function call: in order to put function in
used, a function need to be called
• To call a function with return type, we need
to assign the return value to a variable with
the same type of data: e.g: p = power(a,b);
p is the return value and the data type is
exactly the same as the return type of
function. a and b are parameters
• To call a function without return type, void
function, we simply write: power(a,b);
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
80
Function overloading or polymorphism
• C++ enables user to have multiple functions of exactly
the same name.
• The form of having functions with the same name is
called polymorphism which comes from the word “poly”,
many, and “morph”, means form
• e.g: int myFunction(int x, int y);
int myFunction(long x, long y);
int myFunction(long x);
Note: even if the names are exactly the same but, the
number of parameters and the data types are all
different. It’s not a good design to have such
approach of programming.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
81
More sample programs
• Sample program to determine
whether a number is a prime number
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
82
Manipulator Function
• Manipulator functions are special stream functions that
change certain characteristics of the input and output.
They change the format flags and values of a stream.
• Change base: there are three main bases in C++, they
are decimal number, hexadecimal number and octal
number
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
83
Manipulator function – cont’conversion of base
#include <iostream.h>
void main()
{
int value;
cout<<"Enter a number: ";
cin>>value;
cout<<"In decimal format: "<<dec<<value<<endl;
cout<<"In hexadecimal format:"<<hex<<value<<endl;
cout<<"In octal format: "<<oct<<value<<endl;
}
Click here to see another sample program
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
84
Show precision of floating point
• To show the precision we use the precision,
setf(ios::fixed, ios::floatfield) manipulator.
• Click here to see example
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
85
Set field width
• Set width is used to set the width of a value. For
example if we want to display a value with width 7 we
can use the manipulator setw(7) or cout.width(7).
• Click here to see example
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
86
Fill empty space after set width
• Manipulator fill is used to fill the empty string with
whatever kind of character we like to.
• Click here to see sample program
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
87
Domain or Scope of variable
• Local variable – a local variable is a variable
declared within a function
• Global variable – a global variable is a variable
declared outside the function.
• It’s advisable not to use too many global variables
within a program
• Note: the value of a local variable is being
destroyed after a function it resides in is called
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
88
Recursive Function
• Recursion is a programming technique that
allows the programmer to express operations
in terms of themselves.
• In C++, this takes the form of a function that
calls itself.
• A useful way to think of recursive functions is
to imagine them as a process being
performed where one of the instructions is to
"repeat the process".
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
89
Recursive Function’ cont
• This makes it sound very similar to a loop
because it repeats the same code, and in
some ways it is similar to looping.
• On the other hand, recursion makes it easier
to express ideas in which the result of the
recursive call is necessary to complete the
task.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
90
Recursive Function – cont’
• One simple example is the idea of building a wall
that is ten feet high; if we want to build a ten foot
high wall, then we will first build a 9 foot high wall,
and then add an extra foot of bricks.
• Conceptually, this is like saying the "build wall"
function takes a height and if that height is greater
than one, first calls itself to build a lower wall, and
then adds one a foot of bricks.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
91
Example
#include <iostream.h>
void recurse ( int count ) /* Each call gets its own copy of count */
{ cout<<count<<endl;
/* It is not necessary to increment count since each function's
variables are separate (so each count will be initialized one greater)
*/
recurse ( count + 1 );}
int main()
{ recurse ( 1 ); /* First function call, so it starts at one */
return 0;}
//This program counts the number of calls up to full of stack – Click here to
see more sample
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
92
Practical Exercise for chapter 6
1.
2.
3.
4.
Write a function program to find the root of a quadratic
equation. ax2 + bx + c = 0.
Write a function program to calculate the number of
periods of a given present value, future value, and interest
rate.
Write a function program to calculate a rate of a given
present value, future value, and number of periods.
Write a function program to calculate a present value of a
given future value, number of periods and the interest
rate.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Chapter 7 - Array
• What is an array?
• How to put array at work?
• Multidimensional array
• Array with String
93
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
94
What is an array?
• An array is a collection of data storage locations, each
of which holds the same type of data.
• Each storage location is called an element of the array.
• The first element of array is always starting at location
zero
• The last element of array is at location of array size – 1
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
95
How to put array at work,
declaration
• Array is being declare as other type of variable except
that it has a subscript which describes the size of the
array
• E.g int myArray[10]; which means myArray is a variable
to store 10 values of integer
• Common errors in dealing with array. Many
programmers often write an overflow of array which
means that the actual size of implementation is greater
than that of declaring time
Phnom Penh International University
96
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
How to put array at work – cont’
• Initialization: To initialize an array one would
write:
• int a[]={10,12,78,30};
Address
a[0]
a[1]
a[2]
a[3]
Content or
value
10
12
78
30
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
97
How to put array at work – cont’
• Initialization of string:
• char name[]=“Sithysak”;
• or char name[]={‘S’,’i’,’t’,’h’,’y’,’s’,’a’,’k’};
• or char name[8];
• name[0]=‘S’;
• name[1]=‘i’;
.
.
.
• name[7]=‘k’;
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
98
Array and loop
•
Since array is a storage location of the same type of
variable type, to deal with each element starting from
0 to n-1, we often use for loop to deal with them.
•
E.g: for (i=0;i<n;i++)
a[i]=i+1;
1.
Sort program
2.
Find the largest number
3.
Search for a number
4.
conversion of bases
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
99
Multidimensional array
• In theory, we can have array of n dimension, however,
practically, we mostly deal with array of two dimension,
except those computer engineering programmers who
are dealing with 3 D images.
• To declare a multidimensional array, we simply add in
more subscripts
• E.g: int matrix[m][n]; a matrix of integer number with m
rows and n columns where m and n are known integer
number
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
100
Multidimensional array – cont’
a1 1
.
A ai1
.
am 1
...
...
...
...
...
a1 p
.
aip
.
amp
c1 1
.
C.
.
cm1
b1 1 ... b1 j ...
. ...
. ...
B . ...
. ...
. ...
. ...
bp1... bp j
...
...
...
cij
...
...
c1 n
.
.
.
cmn
b1 n
.
.
.
bp n
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
101
Multidimensional array – cont’
• where
cij=ai1b1j + ai2b2j + … +
aipbpj =
p
a b
ik
kj
k 1
• Amp x Bpn = Cmn
• This is an example of the product of two matrices
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
102
Multidimensional array – cont’
Initialization:
int
x[5][3]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15};
or we would write
• int x[5][3]=
{ {1,2,3},
{4,5,6},
{7,8,9},
{10,11,12},
{13,14,15} }
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
103
Multidimensional array – cont’
Shop/No. of
Units
Nokia
Motorola
Acatel
Siemen
Soriya
Hongneak
MobiFirst
30
23
40
20
32
20
35
15
17
25
20
22
Brand
Unit Cost
Nokia
Motorola
$250
$230
Acatel
Siemen
$140
$200
With the given two tables let’s find
the total amount for each shop and
grand total for all the shops. This is
just like a product of two matrices.
The first is with 3 rows and 4
columns and the second is with 4
rows and 1 column
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
104
Array with string
• Since string is a bundle of characters,
therefore, it’s better to declare it as an
array
• strcpy/strncpy: strcpy() and strncpy are
functions used to copy string of
characters from source string to target
string.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
105
Array with string – cont’
• char str1[]="No man is an island!", str2[12];
• strcpy(str2,str1);
• In this case, even if str2 can store up to 12
characters only, but with strcpy function, str2 is
now storing the whole string of "No man is an
island!" As for strncpy is used to copy string up
to a maximum length. For example:
• char str1[]="No man is an island!", str2[12];
• strncpy(str2,str1,12);
• 12 is the maximum length that str2 can store.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
106
Array with string – cont’
•
•
•
•
•
•
strlen.
strlen() is a function used to count the
number of characters in a string. For
example:
char str1[]="No man is an island!",
str2[12];
int strcount;
strcount=strlen(str1);
In this case, strcount would return the
value of 20.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
107
Array with string – cont’
• strcmp.
• strcmp() is a function used to
compare two strings value. If the first
string is less than the second one,
the return value would be negative, if
the both strings are equal, the return
value is 0, or else the return value is
positive.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
108
Array with string – cont’
• char str1[]="abc", str2="def";
• int strcomp;
• strcomp=strcmp(str1,str2);
• In this case strcomp is –1 because
the value of string "abc" is less than
that of string "def". Note: The value
is referred to as ASCII value.
Uppercase value is less than that of
lowercase.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
109
Array with string – cont’
• String concatenation: string concatenation is the
extraction of two strings together. Let’s say we
have first name and last name and we want to
write these two together we would write:
• char fname[30]=“Chhoumm ”;
• char lname[]=“ Poeuv”;
• strcat(fname,lname);
• In this case name would hold the value of
Chhoumm Poeuv
• Note: all the string functions need string.h
header file to work with.
Phnom Penh International University
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
110
Practical Exercises for chapter 7
Write a program to find the production of
two matrices. They can be either square
matrices or general matrices.
Write a program to sort a given unsorted
n number to descending order.
Write a program to reverse a given string
Write a program to count the number of
line, characters, white space and words
being typed in.
Write a program to search for a name
and delete it from the list
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Instructor: Cheam Sithy
Part III: Memory Management and
Object-Oriented Essential
C++ Programming Language
111
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
112
Chapter 8: Memory Management - Pointers
• What is a pointer?
• How to put it in use?
• Why use pointer?
• Memory Management
• Memory Allocation and Releasing
• Memory Leak
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
113
What is a pointer?
The most powerful tool of C++
programmer is the ability to
manipulate computer memory
directly by using pointers. However,
it's one the most confusing aspect to
most of the novice C++ programmer.
Nevertheless, if we spend a little
more time pondering what pointers
really are, all things will be right into
our hands.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
114
What is a pointer? – cont’
• A pointer is a variable that holds a memory
address. It's also a variable.
• A pointer is a variable holds a memory address
of another pointer being assigned to.
• Computer memory is where these variables can
be stored. By convention, computer memory is
divided into sequentially numbered memory
locations.
• Each of these locations is a memory address.
Every variable of any type is located at a unique
location in an address.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
115
How to put pointer in use?
• Pointer declaration: To declare a
pointer we need to have an
asterisk (*) in front of the pointer
variable name. For example:
*pAge. To get the address of the
pointer we use ampersand (&), or
sometimes called reference
operator. For example: &pAge.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
116
How to put pointer in use? – Cont’
• De-reference or Indirection Operator (*): The
indirection operator is also called de-reference
operator. When a pointer is de-referenced, the
value at the address stored by the pointer is
retrieved. For example:
• unsigned short int age=25, *pAge, myAge;
• pAge=&age;//pAge is holding the address of age.
• myAge=*pAge;//myAge is now being assigned to
the value of 25
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
117
Why use pointer?
We can put pointer in good use by accessing three
areas of tasks:
1. Managing Data on the free store.
2. Accessing Class member data and function.
3. Passing variable by reference to functions.
(Example in spreadsheet)
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
118
Memory management
Programmers generally deal with five areas
of memory:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Global name space.
The free store. (Most frequent used with
pointers)
Registers. (Bookkeeping or housekeeping)
Code space.
The stack. (Most frequent used with nonpointer variable
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
119
Memory Allocation and Releasing
• new: We allocate memory on the free store in
C++ by using the keyword new. new is
followed by the type of the object that we want
to allocate so that compiler knows how much
memory is required. Therefore, new short int
allocates 2 bytes, while new long int allocates
4 bytes.
• The return value from new is a memory
address. It must be assigned to a pointer.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
120
Memory Allocation – cont’
• To create an unsigned short on the free store, we
may write:
• unsigned short int *myPointer;
• myPointer = new unsigned short in;
• Then we can, of course, initialize the pointer at its
creation with:
• unsigned short int *myPointer = new unsigned short
int;
• By this, myPointer is now pointing to an unsigned
short int on the free store. We can use this like any
other pointer to a variable and assign a value into
that area of memory by writing:
• *myPointer = 26;
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
121
Releasing Memory
• When we are finished with our area of
memory, we must call delete on the pointer.
delete returns the memory to the free store.
Remember that the pointer itself is a local
variable. When the function in which it is
deleted returns, that pointer goes out of scope
and is lost. The memory allocated with the
new operator is not freed automatically,
however. That memory becomes unavailable
and this is called a memory leak.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
122
Releasing Memory- cont’
• To restore the memory to the free store we use
the keyword delete. For example:
• delete myPointer;
• When we delete the pointer, what we are doing is
freeing up the memory whose address is stored
in the pointer. We are telling it to return back to
the free store.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
123
Memory leak
• Another way, we can inadvertently create a
memory leak by reassigning our pointer before
deleting the memory to which it points. For
example:
• unsigned short int *myPointer = new unsigned
short int;
• *myPointer = 26;
• myPointer = new unsigned short int;
• *myPointer = 16;
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
124
Releasing memory – cont’
• With this scenario, the old content of myPointer is lost
and there is no way to retrieve back the original
information to myPointer. Not only that, we can't free
that memory as well. To do this in a legal way, we
should write:
• unsigned short int *myPointer = new unsigned short
int;
• *myPointer = 26;
• delete myPointer;
• myPointer = new unsigned short int;
• *myPointer = 16;
• By this, the original memory address is freed because
it's has been deleted.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Sample Program
Click here to see sample program
1.
Power of two numbers
2.
Find the largest number
3.
Sort a list of number
4.
Reverse the order of a list of numbers
5.
Reverse the order of a string
125
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
126
Practical Exercise for chapter 8
1.
2.
Write a program to list out a list of prime
numbers from 1 to 1000. Note: prime number
is a number which only divisible by itself and 1.
Write a program to convert from Celsius
degree to Fahrenheit degree given that the
formula is: Celsius = 5(Fahrenheit – 32)/9
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Chapter 9: Class
• What is a class and how it can be used?
• Navigation and accessing class member
• Class method
127
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
128
What is a class?
• Class is a collection of variables, often of different
types, but related to one another. We can think of a
computer as a collection of CPU, monitor, glass
filter, mouse, mouse pad, keyboard, cables, hard
disk, floppy disk, CD-Rom, speakers etc.
• Classes extend the built-in capabilities of C++ to
assist us in representing and solving complex, realworld problems.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
129
How is class being used?
• Data Abstraction: In OOP
(Object-Oriented Programming),
the data abstraction is defined as
the collection data and methods.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Cheam Sithy
130
How is class being used? – cont’
• Data Hiding: In C++, the class construct
allows us to declare data and methods, as
public, private and protected group. The
implementation details of a class can be
hidden. This is done by data hiding
principle.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: ChhoummPoeuv
131
How is class being used? – cont’
• Data Encapsulation: The internal data
(the data members) of a class are first
separated from the outside world (the
defined class). They are then put along
with the member function in a capsule
and this is known as encapsulation.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
132
How is class being used? – cont’
• Inheritance: C++ allows us to
build hierarchy of classes
(parents and child classes) or
class within class is known as
derived class.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
133
How is class being used? – cont’
• Polymorphism: In OOP, polymorphism is
defined as how to carry out different processing
steps by a function having the same messages.
Polymorphism treats objects of related classes
in a generic manner. e.g a generic name vs
branded name
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
134
How is class being used? – cont’
• Types: A type is a category. One of the things that
distinguish human from animal is our ability to categorize.
When we go to the zoo, we would see different types of
animals, not just one. In C++, a type is an object with a
size, state, and a set of abilities.
• A C++ programmer can create any type needed, and each
of these new types can have all the functionality and power
of the built-in types.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
135
How class is being used? – cont’
•
Classes and Members: We create a new type by
declaring a class.
•
When we put everything related together, we can
access to the necessity much easier than we don't
classify them. The process of putting everything into
one class is called encapsulation. By this, it easier
for programmer to refer to, copy, and manipulate the
needed data.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
136
Class and member – cont’
• Other functions or classes make uses of our class is call
our clients. Encapsulation will enable our clients to use our
class without knowing or caring about how our class works.
For example, when we drive a car, we don't really
understand how the engine works.
• When a normal user operates a computer-software, he/she
doesn't really know how the different parts of the software
work but he/she knows what it can do by following the
instruction.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
137
Class and member – cont’
• A class can consist of any combination of the variable
types, and also other class types. The variables in the
class are referred to as the member variables, data
members, or data fields.
• The functions in the class typically manipulate the
member variables. They are referred to as member
functions or methods of the class.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
138
How is class being used? – cont’
•
Private or Public: Two of the most important
keywords used in declaring a class are private and
public. Private means the data member is private to
the class. It can only be accessed by within the
methods of the class itself.
•
Public members can be accessed through any
object of the class. All members of the class—data
and methods—are private by default.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
139
How is class being used – cont’
• protected: Protected members are members
declared within the protected section which
mean, they are only accessible by the member
functions and friends of the class only. It’s not
accessible to the outside world.
• In this section, we will not deal much with it until
the advanced level.
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
140
How is class being used? – cont’
• Declaring a class: To declare a class, we use the class
keyword followed by the curly braces and enclosed in
them are data members and methods of that class. For
example:
• class date
{
public:
int day, month, year;
};
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
General syntax:
class user_defined name {
private:
data members
data operation
friend functions
public:
data members or methods
data operation
protected:
data operation
};
141
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Peuv
142
Navigation of class members
• Accessing Class members: To access the data
members of a class we use the dot (.) operator.
For example: Employee.age.
• click here is see a sample program
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Chhoumm Poeuv
Accessing class member – cont’
Accessing Class members of Array.
To access the class members of type array we also use the dot (.) operator.
For example:
class student{
public:
method1;
method2;
private:
member1;
member2;
};
void main(){
student array[max];
array[1].method1();
array[1].datamember;
}
143
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Cheam Sithy
144
Accessing class member – cont’
Accessing Class members of Pointer.
To access the class members of type pointer we need to use the dash and
greater than (->) operators.
For example:
class student{
public:
method1;
method2;
private:
member1;
member2;
};
void main()
{
student *ptr;
ptr->method1();
ptr->datameber;
}
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Cheam Sithy
145
Class methods
• Every class method that we declare has to be
defined. A member function begins with the name
of the class followed by two colons, the name of
the function, and its parameter. For example: float
Employee::Calsal(float sal, float tax)
• Click here to see sample program
Phnom Penh International University
146
Instructor: Cheam Sithy
Sample program with array
Shop/No. of Units
Nokia
Motorola
Acatel
Siemen
Soriya
Hongneak
30
23
20
32
35
15
25
20
MobiFirst
40
20
17
22
Brand
Unit Cost
Nokia
Motorola
$250
$230
Acatel
Siemen
$140
$200
With the given two tables let’s find
the total amount for each shop and
grand total for all the shops. This is
just like a product of two matrices.
The first is with 3 rows and 4
columns and the second is with 4
rows and 1 column
Phnom Penh International University
Instructor: Cheam Sithy
147
Practical Exercise for chapter 9
1.
2.
Write an object-oriented program to sort an unsorted n
number to ascending or descending order.
Write an object-oriented program to reverse a string of
given characters.