* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download eukarya kingdom protista i
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
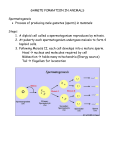
EUKARYA KINGDOM PROTISTA I Origin of Eukaryote: The Endosymbiotic Theory (1960) Pages 229, 307 Prove: Endosymbiotic Plastid and mitochondria have their own DNA & ribosome that are 70s not 80s They divide in a way similar to Prokaryotes, lack microtubules Their DNA is circular, naked Their ribosome are sensitive to the same antibiotics that interfere with prokaryotes ribosome Evidence of symbiotic relationship between bacteria & protists, marine invertebrates, algae & protozoan (Fig. 12-11) Mitochondria arose first (common to all Meiosis & Life cycles For meiosis see page 236 In eukaryote a diploid stage undergo meiosis to produce a haploid stage These two stages alternate in three patterns Gametic meiosis: most animals & some protists * Sporic meiosis (alternation of generations: plants & many algae* Zygotic meiosis: Fungi & some algae* Gametic Meiosis e.g. Human & some protists + Gamete Gametes - gamete - + - + Meiosis (spermatogenesis) This cell undergo meiosis Fertilization Zygote Diploid individual Sporic Meiosis e.g. Plants + Gamete spores - Gamete - + - + Meiosis This cell undergo meiosis Fertilization Zygote Sporophyte (Diploid individual) Reproductive Cycles Animals and Plants Sporophyte Spore Gametophyte Meiosis Adult ♂ 2n 1n Sperm Adult ♀ Egg Zygote Embryo Fertilization Zygotic Meiosis e.g. Fungi + Gamete Haploid cells - Gamete - + - + Meiosis Fertilization Zygote Classification of the Protists Protista is established to hold problematic species Each algal group must have its own evolutionary line Organisms of uncertain origin are paced in the Protista Protista includes: Plant-like organisms but gametes & zygotes not protected Fungi-like organisms but have flagella & lack chitin in cell wall Animal-like organisms but no embryonic development Ecology of Aquatic Algae Marine algae & cyanobacteria form phytoplankton Importance Important in carbon cycle (absorb ½ CO2 produced by human activities) Transform CO2 into (CH2O)n & CaCO3 Cause algal blooms (red & brown tides) Increase sulfur oxides in our atmosphere Lake Neatahwanta, Fulton, NY Euglenoids: Phylum Euglenophyta e.g. Euglena* Like green algae, have chl(a), (b) & carotenoids suggesting a symbiotic relationship Only 1/3 of the phylum has chloroplast, the rest are heterotrophic Euglenoids occur in freshwater rich in organic matter Euglena Reproduce by mitosis & lengthwise Plasmodial Slime Molds: Phylum Myxomycota The name mold “thought to have a relation with fungi” Seems to have no close relation to other organisms Plasmodium: amoeboid body with no cell wall* Phagocyte: heterotrophic Sclerotium Plasmogamy Oomycetes: Phylum Oomycota They are not Fungi because Cell wall has cellulose-like polymers Chromosomes not highly condensed as in fungi spores are flagellated They are saprobic, few are parasitic Pathogens of Coca, pineapple, tomatoes, rubber, papayas, onions, citrus e.g. the genus Plasmopara* e.g. Phytophthora infestans (Late blight of potato)* Downy mildew in Grapes: Plasmopara viticola http://www.inra.fr/Internet/Produits/HYP3/pathogene/3plavit.htm#det Downy mildew in grapes, threaten the entire wine production in France (introduces from the States 1870) Late Blight of Potato (Phytophthora infestans) Responsible for the great famine of 1846-47 in Ireland Dinoflagellates: Phylum Dinophyta Mostly unicellular & biflagellate* Have chl. a, c, & carotenoid Important part of marine phytoplankton Many produce toxins (red & brown tides) Dinoflagellates Ceratium http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artsep01/dinof2.html Unique: flagella move within 2 groves Red tide in Texas Bay, Gymnodinium breve Diatoms: Phylum Bacillariophyta Very important component of phytoplankton Occur in huge # 30-50 m/1 cm of a submerged rock (1/4 of total carbon fixed) They lack flagella & have unique shells * Pennate diatoms: bilaterally symmetrical* * Centric diatoms: radially symmetrical* - Centric float better therefore more abundant Pennate Diatoms Diatoms: often compared to a shoe box and its lid (frustules) Lower valve (the box) Upper valve (lid) Cell wall has an outer layer of silica (glass) Chrysophytes: Phylum Chrysophyta Have chl(a) & (c) masked with a golden-brown fucoxanthin (=chrysophyte)* Mostly unicellular or colonial; flagellated Found in fresh & salt water all over world Reproduction is asexually by zoospores Synura sp. http://www.spea.indiana.edu/e455-jones/synura.jpg