* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quantum Mechanical Model
Franck–Condon principle wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot wikipedia , lookup
Quantum computing wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
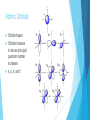
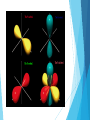
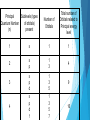
Quantum Mechanical Model Chapter 5 Section 2 Quantum Mechanical Model The model of the atom that treats electrons as waves Like Bohr the quantum model limits an electron to certain energy levels Unlike Bohr’s model it makes no attempt to describe an electrons path Vocabulary Atomic Orbital – the 3D region around the nucleus that the wave function predicts Principal quantum number (n) – indicates the relative size and energy of atomic orbitals Principal energy level – energy levels indicated by the principal quantum levels Energy sublevels – sublevels in principal energy levels Atomic Orbitals Orbital shapes Orbitals increase in size as principal quantum number increases s, p, d, and f Energy Sublevels The number of energy sublevels increases as the principal quantum number increases Designated by s, p, d, and f Principal Quantum Number (n) Sublevels (types of orbitals) present Number of Orbitals Total number of Orbitals related to Principal energy level 1 s 1 1 2 s p 1 3 4 3 s p d 1 3 5 9 4 s p d f 1 3 5 7 16 Review Questions 1. Draw and Label the parts of a wave. 2. What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency? 3. List the electromagnetic spectrum from lowest frequency to highest frequency. 4. What is the frequency and energy of a microwave 0.060 m in length? 5. Draw an atom in the ground state and the excited state. 6. Describe the photoelectric effect. 7. Describe how an emission spectra is formed. 8. Compare and Contrast the Bohr Model and the Quantum Mechanical Model.