* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FrRev ppt - Cabarrus County Schools
French Revolutionary Wars wikipedia , lookup
War of the Fourth Coalition wikipedia , lookup
Reign of Terror wikipedia , lookup
Germaine de Staël wikipedia , lookup
War of the Sixth Coalition wikipedia , lookup
Louis XVI and the Legislative Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Storming of the Bastille wikipedia , lookup
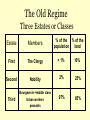
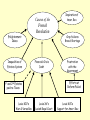
The French Revolution & Napoleon 1789-1815 The Old Regime Three Estates or Classes % of the % of the population land Estate Members First The Clergy < 1% 10% Second Nobility 2% 25% Third Bourgeoisie =middle class Urban workers peasants 97% 65% Causes of the French Revolution Enlightenment Ideas Inequalities of Estates System Crop failures Bread Shortage Financial Crisis Debt Frustration with the Government Efforts at Reform Failed 1st and 2nd Estates paid no Taxes Louis XIV’s War & Versailles Inspiration of Amer. Rev. Louis XV’s Lavish Royal Court Louis XVI’s Support for Amer. Rev. B. Estates General Louis XVI called for a meeting of the Estates General to deal with the crisis Hoped to gain support for additional taxes The Estates General was a body representing Frances’ three estates It had not met in 175 years Each group hoped to use the meeting as a chance address their individual concerns. The Estates General % of population Votes First Number of Representatives 300 < 1% 1 Second 300 2% 1 Third 600 97% 1 Estates What problem existed with this system? Members of the Third Estate demanded reforms: Want all three Estates to meet together with each delegate getting an individual vote. However, no progress was made and frustration grew when Louis rejected these demands. C. The National Assembly 1. Third Estate declared themselves the National Assembly. a. Invited delegates of other estates to meet with them b. Claimed the right to create a constitution for France. c. Third Estate was locked out of their meeting hall. Met instead on a tennis court outside the hall……took the “Tennis Court Oath” that they would fight against this oppression. 5. Storming of the Bastille July 14, 1789 The Bastille = fortress used as a prison for political opposition. Fearing the king was going to take action against the reforms, mobs of people attacked the Bastille in Paris. *Shows common people were willing to support revolutionary changes Bastille Day is celebrated as a national holiday in France. The Great Fear Peasants hungry from famine and frightened by rumors of government intervention take action: a. 1. Attacked nobles and burn their homes 2. Stole grain from storehouses The National Assembly 1789-1791 a. Peasant uprisings and the storming of the Bastille push the National Assembly to act: b. Assembly ended the privileges of the nobility. c. Assembly issued the Declaration of the Rights of Man. Based on Enlightenment principles the Declaration included: 1. Equality of all people before the law, 2. Guarantees of freedom of speech, freedom of press, freedom of religion, and protection against unfair arrest and punishment. Reaction to the new constitution varies. The Middle class generally favored the new government and it reflected their desires. Other groups felt the reforms had not gone far enough or had gone much to far. Growing factions within France The Legislative Assembly(1791) Delegates were seated based on political views. Radicals Moderates Liberals Reactionaries Conservatives Today we include two additional groups. The Legislative Assembly France goes to war • April 1792, declared war on Austria. 1. Feared Austria’s intervention. 2. Desired to spread revolution. • Prussia joined war against France. • War went poorly and turmoil increased within France. The National Convention • Made France a republic • universal male suffrage • Louis XVI was put on trial as a traitor and convicted. In January 1793, Louis XVI is executed by the guillotine before crowds of Parisians. Months later Marie Antoinette was also executed by the guillotine. Reign of Terror Committee of Public Safety ruled France. Maximilien Robespierre controlled Committee. Believed in the use of “prompt swift and severe justice”. Reign of Terror • Revolutionary courts sentenced thousands to death after hasty trials • As many as 40,000 died during the Terror the majority of which were peasants or sans-culottes. Napoleon Bonaparte What comes to mind when you think of Napoleon? B. Napoleon comes to power 1. In 1799, Napoleon participated in coup d’etat against the Directory. 2.In name, the new government was a republic but in reality it was a dictatorship. 3. Napoleon gained greater power and control over the next few years. a. French people approved each step in a plebiscite. 4. Napoleon promised order, security and efficiency. 5. In 1804, Napoleon is crowned Emperor of France. C. Napoleon introduced reforms: 1. Improved education establishing schools *Lycees – secondary schools 2. Napoleonic Code – system of laws based in part on Enlightenment ideas. 3. Economic reforms restored prosperity. Legacy of Napoleon: 1. Spread ideas of French revolution. 2. Increased nationalism. Definition: pride in one’s own country or desire for independence.