* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System PPT - Effingham County Schools
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
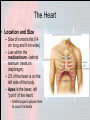
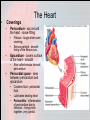
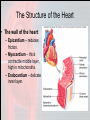
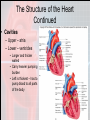
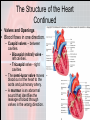
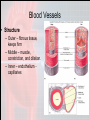
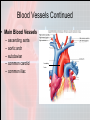
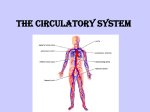
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System Organs • Heart - begins beating in the 4th week of development. – Pumps 7,000 liters of blood each day. – Contracts 2.5 billion times in a lifetime. • Closed Vessel System – Arteries - carry blood away from the heart. – Veins - carry blood toward the heart. – Capillaries - attach arteries and veins. Function • Circulates blood to every cell in the body and removes waste. The Heart • Location and Size – Size of a man’s fist (14 cm long and 9 cm wide) – Lies within the mediastinum - behind sternum (rests on diaphragm). – 2/3 of the heart is on the left side of the body. – Apex is the lower, left “point” of the heart. • Stethoscope is placed here to count the beats. • The Heart Coverings – Pericardium - sac around the heart - loose-fitting • • – Epicardium - covers surface of the heart - smooth • – Fibrous - tough white outer covering, Serous parietal - smooth lining of the fibrous sac. Also called serous visceral pericardium Pericardial space - area between pericardium and epicardium • • • Contains fluid - pericardial fluid Lubricates beating heart Pericarditis - inflammation of pericardium due to infection - linings stick together, very painful. The Structure of the Heart • The wall of the heart: – Epicardium – reduces friction. – Myocardium – thick contractile middle layer, high in mitochondria. – Endocardium – delicate inner layer. The Structure of the Heart Continued • Cavities – Upper – atria – Lower – ventricles • Larger and thicker walled • Carry heavier pumping burden • Left is thickest – has to pump blood to all parts of the body The Structure of the Heart Continued • Valves and Openings • Blood flows in one direction. – Cuspid valves – between cavities. • Bicuspid (mitral) valve left cavities. • Tricuspid valve - right cavities. – The semi-lunar valve moves blood out of the heart to the aorta and pulmonary artery. – A murmur is an abnormal sound that identifies the leakage of blood through valves in the wrong direction. The Structure of the Heart Continued • Blood Supply – Ventricles get blood from the right and left coronary arteries. – Atria get blood from the small branch coronary artery. – Anastomosis is branching of the main arteries “detours” – Myocardial infarction - death of the heart muscles due to a clot (heart attack). Blood Vessels • Structure – Outer – fibrous tissue, keeps firm – Middle – muscle, constriction, and dilation. – Inner – endothelium capillaries Blood Vessels Continued • Function – Transportation of nutrients to cells • Capillaries perform this function • Arteries = distributors arterioles venules veins • Veins = carry and pool blood capillaries Blood Vessels Continued • Main Blood Vessels – – – – – ascending aorta aortic arch subclavian common carotid common iliac Ascending Aorta Blood Vessels Continued Blood Vessels Continued • Portal Circulation – Organs that do not pour blood into inferior vena cava. – Blood sent to the liver by the portal vein. Blood Vessels Continued • Fetal Circulation – Gets oxygen and food from mother, not own lungs and digestive tract. – Additional vessels Shed at birth • Umbilical arteries (2) – carry fetal blood to placenta • Placenta – exchanges oxygen and other substances between mother and fetus • Umbilical vein – returns oxygenated blood to liver of fetus • Foramen ovale – opening between right and left atria bypass lungs, closes with first breath.