* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint Seven - Kaskaskia College
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
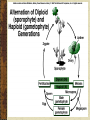
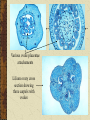
Plant Reproduction By Brian Cambron Kaskaskia College Angiosperms vs. Gymnosperms Flowers = type of organ (many tissues and parts working for one function Parts: Floral shoot (at tip of shoot) Receptacle = region of shoot where parts are attached Sepals = base leaves, outermost, still green Calyx = collective term for all sepals Petals = next layer of leaves, colored, highly modified Corolla = collective term for all petals Stamens = fertile male reproductive organ Pistil = fertile female reproductive organ Stamens “Male” reproductive organ Consists of two parts Anther = consists of 4 pollen chambers fused together Filament = stalk that supports anther Pollen chambers called microsporangia All stamens collectively called androcia Pistils “Female” reproductive organ Consists of three parts Ovary = enlarged basal part with ovules Style = stalk that extends from ovary to stigma Stigma = flattened receptive area at top of pistil Carpels = ovule bearing units, maybe many in one pistil fused together or separate Gynoecium = collective term for all carpels Placentae = ovule attachment within carpel Petals and Sepals Modified leaves Alternately whorled May be fused into odd arrangements Regular and irregular symmetry Non-photosynthetic Reproductive Morphology Flower Variation 1. 2. 3. 4. Complete flower = has all major parts Incomplete flower = lacks one or more flower parts Perfect flower = flower with both stamens and pistils Imperfect flower = with only stamens or pistils 1. 2. 5. Staminate Pistillate (carpellate) Varied ovary position 1. 2. Superior = other flower parts attached below ovary base Inferior = other flower parts attached to top of ovary Alternation of Generations Only in plants Two generations to every life cycle Sexual reproduction in plants entails meiosis Sporophyte = produces spores Gametophyte = produces gametes (sperm and egg cells) Various ovule placentae attachements Lilium ovary cross section showing three carpels with ovules Development of the female gametophyte inside the ovule through multiple divisions starting with a megaspore. Typical events of pollen tube formation and fertilization. Plants require Double Fertilization. Two sperm cells fertilize the ovule, one for the egg and one for the endosperm.