* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Technical features - Huawei Enterprise
Survey
Document related concepts
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
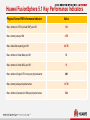
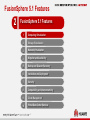
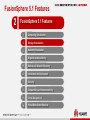
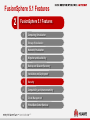
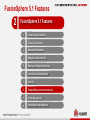
Friday, July 17, 2015 Huawei FusionSphere 5.1 virtualization Technical Promotional Theme Slides (Detailed Version) Contents 1 FusionSphere 5.1 Overview 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 3 Product Support 5 Huawei FusionSphere 5.1 Architecture Huawei Open API Cloud Storage API SNMP/REST NBI FusionManager Resource Management Configuration API Adapter Cloud Storage Management VDC/VPC Open API RBAC Third-party Virtualization Architecture Backup & DR Huawei Virtualization Architecture UltraVR eBackup VMware vSphere FusionCompute FusionStorage Portal FusionNetwork FusionSphere SOI Alarm Physical Infrastructure Server Storage 6 Network & Security Log FusionSphere 5.1 Enhancements Category Feature Enhanced/New VM Lifecycle Management Enhanced Shared Nothing VM Live Migration Enhanced VM Cloning Enhanced Large VM Memory Enhanced CPU Virtualization Enhanced Large-Scale Physical Server Enhanced Support for 1024 Powered-On VMs on a Single Server Enhanced Support for UEFI Firmware on VMs New Online CPU and Memory Resource Modification Enhanced Host-based Replication DR Enhanced VM Backup Self-Service and Self-Maintenance, Service Catalog and Service Definition, Out-of-the-Box Service Catalog, Service Application Approval, Application Form Management, Custom Approval Procedure Enhanced Root Cause Analysis New Capacity Report New Computing virtualization Backup and disaster recovery (DR) Service FusionSphere SOI 7 New What's New in FusionSphere 5.1 Computing Virtualization VM Lifecycle Management (Enhanced) In FusionSphere 5.0, a VM can start only after the BIOS successfully starts. FusionSphere 5.1 eliminates this restriction and allows a VM to start even when the BIOS has not waited, thereby reducing VM startup time by 5 seconds. Shared Nothing VM Live Migration (Enhanced) The VM migration enhancements allow you to: • Change both the host and data store of a VM with snapshots created. • Specify the destination disk mode. The destination disk can be in the common, thin provisioning, or thick provisioning lazy zeroed mode and can be in the same or different modes with the source disk. • Query the progress of a migration task. • Cancel a migration task. VM Cloning FusionSphere supports cloning of either a running or stopped VM when FusionStorage is used. Support for UEFI Firmware on VMs FusionSphere 5.1 supports use of Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) firmware on VMs. With this function, you can migrate a system disk larger than 2 TB from a physical server to a VM by setting UEFI boot firmware and the GPT partition. Online CPU and Memory Resource Modification (Enhanced) FusionSphere 5.1 allows you to add CPU and memory resources to or reduce the resources from a running VM. For some OSs, you need to restart the VM for the CPU and memory resource modification operations to take effect. 8 What's New in FusionSphere 5.1 Backup and DR Host-based Remote Replication DR (Enhanced) FusionSphere 5.1 enables one-click service switchover between the production and DR sites. VM Backup (Enhanced) FusionSphere 5.1 provides the LAN-free mode backup and file-level data restoration. 9 What's New in FusionSphere 5.1 Self-Service Capabilities Self-Service and Self-Maintenance FusionSphere 5.1 enables users to perform common service operations using service catalogs and enables VDC administrators to perform routine operation and maintenance (O&M) on the portal provided for tenants. Out-of-the-Box Service Catalog Featuring out-of-the-box, the service catalog pre-defined in the FusionSphere system enables you to quickly deploy resources and applications based on service requirements. Service Application Approval, Application Form Management, and Custom Approval Procedure FusionSphere 5.1 allows you to view administrator-defined services in service catalogs on the self-service portal. You can select services based on your service requirements and submit service applications. When applying for a service, you can also specify service specifications and the validity period. Tenants and administrators can query application form status and progress and approve service applications. Users can customize the approval procedure based on service requirements. 10 What's New in FusionSphere 5.1 FusionSphere SOI Root Cause Analysis FusionSphere 5.1 introduces a new component, FusionSphere SOI, to perform in-depth analysis of performance anomalies, to quickly identify the cause for performance deterioration, and to locate workload that may adversely affect performance. FusionSphere SOI also provides historical information about health status indicators associated with an event and displays the performance change trend in graphics to facilitate fault locating and rectification. Capacity Report FusionSphere 5.1 allows reports to be generated by different granularities to display VM, host, and cluster performance and capacity data and prediction results. A report can contain graphics, tables, and text descriptions. 11 Industry-Leading Comprehensive Virtualization Performance SPECvirt_sc2010 Test Results Published by SPEC in 2014 http://www.spec.org/virt_sc2013/results/specvirt_sc2013_perf.html Hypervisor Server Processor Number of SPECvirt VMs SPECvirt Score Ranking Huawei FusionSphere 5.0 ProLiant DL380p Gen8 Intel Xeon E5-2690 37 632 1 Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.4 (KVM) Flex System x240 Intel Xeon E5-2690 37 625 2 VMware ESXi 5.1 ProLiant DL380p Gen8 Intel Xeon E5-2690 27 472 3 Oracle DB Performance Test: Huawei vs. VMware Key Technologies for High I/O Provided by FusionSphere Oracle Database Performance Test Result (Average Value) VM Configuration Difference Huawei TPM VMware TPM Single VM (8 vCPUs and 8 GB RAM) without multipathing 179474 175580 +2.20% Two concurrently running VMs (each with 8 vCPUs and 8 GB RAM) 109710 111447 -1.56% Single VM (8 vCPUs and 16 GB RAM) without multipathing 198404 185858 +6.75% Single VM (8 vCPUs and 16 GB RAM) 177765 175580 +1.24% Two concurrently running VMs (each with 8 vCPUs and 16 GB RAM) 128302 117520 12 +9.17% I/O request optimization FusionCompute automatically increases the number of I/O requests that a VM can process based on the Oracle database read/write capacity and reduces service load by a half. Optimized storage multipathing Storage multipathing is optimized to greatly reduce the latency caused by I/O path selection for VMs. I/O scheduling optimization The virtualization I/O scheduling algorithm is optimized to reduce the overheads of the virtualization platform in computing scheduling, thereby improving VM I/O processing capabilities. Huawei FusionSphere 5.1 Key Performance Indicators Physical Server/VM Performance Indicator Value Max. number of vCPUs (virtual SMP) per VM 128 Max. memory size per VM 4 TB Max. virtual disk capacity per VM 64 TB Max. number of virtual disks per VM 60 Max. number of virtual NICs per VM 12 Max. number of logical CPU cores per physical server 480 Max. memory size per physical server 12 TB Max. number of powered-on VMs per physical server 1024 13 Huawei FusionSphere 5.1 Key Performance Indicators Value Management Indicator Max. number of physical servers per logical cluster 128 Max. number of VMs per logical cluster 3000 Max. number of logical clusters supported by a VRM node 32 Max. number of hosts supported by a VRM node 1024 Max. number of VMs supported by a VRM node 10,000 Max. number of VRM nodes that can be cascaded Max. number of physical servers supported by cascaded VRM nodes Max. number of VMs supported by cascaded VRM nodes 14 16 4096 80,000 (best practice in the industry) Contents 1 FusionSphere 5.1 Overview 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 3 Product Support 15 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 1 Computing Virtualization 2 Storage Virtualization 3 Network Virtualization 4 Migration and Availability 5 Backup and Disaster Recovery 6 Installation and Deployment 7 Security 8 Compatibility and Interconnectivity 9 Cloud Management 10 Virtual Data Center Services 16 FusionCompute control domain Compatible with OSs Intended for Special Application Scenarios PV backend driver VM VM VM VM VM VM Custom PV driver PV driver PV driver PV driver PV driver PV driver FusionCompute Vendors must provide applicable PV drivers to enable FusionCompute to be compatible with a new OS. Huawei is capable of developing applicable PV drivers. In addition to mainstream Windows and Linux OSs, FusionCompute is compatible with the NeoKylin OS. (Certain OSs may need customized drivers.) 17 Flexible Management and Optimal Scalability FusionCompute Web Client FusionCompute Web Client VRM nodes for cluster management (active/standby) VM VM VM CNA VM VM CNA VM VM CNA VM CNA VM VM CNA VRM nodes for cluster management (active/standby) VRM nodes for cluster management (active/standby) VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM VM CNA SAN Local storage Logical cluster 1 Logical cluster 2 Technical features & benefits • • • • CNA CNA SAN Logical cluster 10 CNA CNA Local storage Logical cluster 11 CNA CNA CNA Local storage Logical cluster 20 CNA CNA SAN Logical cluster 21 Each logical cluster supports up to 128 physical servers, which is the industry best practice. FusionSphere reduces the number of redundant physical servers and is suitable for deploying large-scale service clusters requiring high performance. Each logical cluster supports up to 3,000 VMs, which makes FusionSphere applicable to scenarios requiring a large number of VMs that do not have high performance requirements, such as in desktop cloud scenarios. VRM nodes can be deployed in active/standby mode on both physical servers and VMs to ensure system availability. Up to 16 VRM nodes can be cascaded. Cascaded VRM nodes support up to 4,096 physical servers and 80,000 VMs, which is the industry best practice. 18 GPU Virtualization Implementation VM 1 VM 2 VM 3 Technical features vGPU driver vGPU driver vGPU driver vCPU support vGPU vGPU GPU vGPU VMs running engineering drawing software, such as Pro/ENGINEER, CATIA, and AutoCAD, and graphics rendering software, 3D games, and GIS applications Industrial design, multimedia editing, energy industry, financial service and trade, medical imaging, and education industry Benefits 19 Provides GPU virtualization based on NVIDIA GRID and improves user experience on graphics-intensive applications. Supports vGPU management and scheduling to balance load of physical GPUs. Supports the OpenGL and DiretX multimedia application programming interfaces (APIs). Supports AERO visual effects, multiple monitors, and hardware-based performance acceleration for DXVA videos. Application scenarios Huawei UVP GPU virtualization is to create multiple vGPUs on a physical GPU that supports virtualization. vGPUs can be attached to each VM to allow the VM to directly access hardware resources of the physical GPU. Improves user experience on graphics-intensive applications in a virtual environment. Flexible VM Configuration Modification Virtual resource pool VM Function details App Technical features The number of vCPUs on a VM and the VM memory size need to be flexibly adjusted based on service requirements. Benefits 20 FusionSphere 5.1 enables you to change the number of vCPUs on a VM and its memory size when the VM is running. The changes take effect immediately and do not need the VM to be restarted. For a VM running an OS that does not support vCPU or vRAM hot add or remove, you must restart the VM to make the modifications take effect. Application scenarios FusionCompute vRAM: Hot and cold add and remove vCPU: Hot and cold add and remove Flexibly adjust VM configurations based on service requirements. Add vCPUs and vRAM to expand capacity of a VM based on VM QoS requirements. Add VMs to expand capacity of a cluster based on cluster QoS requirements. Memory Overcommitment, Improving VM Density by 30% Memory swapping Memory sharing and copy-on-write VM 1 VM 2 VM VM 3 VM Memory ballooning VM 1 VM 2 Idle Idle Memory ballooning Used Disk Physical memory Memory sharing: Multiple VMs share the same physical memory block (marked in blue), and the VMs only read data from the memory block. Copy-on-write: When a VM needs to write data to its memory block, another memory block (marked in red) is allocated to the VM to write the data and the mapping between the allocated block and the VM is created. Memory ballooning: The hypervisor uses the memory ballooning mechanism to release the idle memory on a VM and allocate the memory to another VM with high memory usage, thereby improving memory utilization. Technical features Memory swapping: The memory data that is not retrieved by the VM for a long time is swapped to a disk, and a mapping between the memory data and the disk is created. When the VM needs to access the memory data again, the memory data is swapped out from the disk back to the memory block. Used By leveraging the preceding memory overcommitment techniques, Huawei FusionSphere increases the memory overcommitment ratio by 130%, which makes Huawei overtake its competitors in terms of memory utilization, such as Citrix. Benefits With the same memory resources, the VM density of the FusionSphere platform increases by 130%, which helps to reduce procurement costs on memory components by 30%. 21 NUMA Affinity-based Scheduling Implementation The NUMA topology is presented to VMs to enable the guest OS to allocate resources to applications running on it based on logical NUMA nodes, thereby improving application performance. Technical features Application scenarios Benefits Guest NUMA implements NUMA-topology-based optimizations and enables a CPU to preferably use memory resources on one NUMA node. 22 Large-size and high-performance VMs are required. VMs run key applications, such as Oracle and SQL Server databases. Reduces memory access latency and improves VM access efficiency, thereby improving application performance. FusionSphere 5.1 Features 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 1 Computing Virtualization 2 Storage Virtualization 3 Network Virtualization 4 Migration and Availability 5 Backup and Disaster Recovery 6 Installation and Deployment 7 Security 8 Compatibility and Interconnectivity 9 Cloud Management 10 Virtual Data Center Services 23 Thin Provisioning, Cutting Storage Investments VM VM VM Implementation VM FusionCompute Technical features Common Thin provisioned Thin provisioned 20 GB 40 GB 80 GB 40 GB 20 GB 20 GB Physical storage device Virtually allocated: 120 GB Actually allocated: 80 GB Physical space: 100 GB 100 GB 24 The configured capacity is displayed for VM users. However, the allocated disk space is dynamically adjusted based on actual usage. Disk usage is monitored, and alerts are generated if the allocated disk space is about to become insufficient. Disk space reclamation is supported. Application scenarios Thin provisioning operates by allocating disk storage space to users based on the minimum space required by each user at any given time. Only the disk space actually used by a user is allocated to the user, and FusionCompute increases disk space allocated to users with the increase of data on user disks until all disk space requested by the users are allocated to them. Large storage capacity and low IOPS are required. Benefits Improves storage space utilization and lowers storage costs. Page 24 Online Virtual Disk Capacity Expansion VM VM VM VM Implementation Technical features FusionCompute FusionCompute SCSI On-demand, scalable disk capacity expansion is required. Benefits 25 This function is based on Virtual Hard Disks (VHDs). The newly added virtual disks take effect without requiring the VMs to be restarted. Application scenarios This function enables you to expand disk capacity without stopping or restarting the VM. This feature avoids unnecessary service interruption and ensures service continuity. RDM for SAN Devices VM VM VM VM Implementation FusionCompute Technical features SCSI SCSI LUN LUN 26 Applications requiring high storage performance, such as Oracle RAC Benefits LUN VMs can read data from or write data to physical storage devices through SCSI commands. Supports both IP SAN and FC SAN devices. Application scenarios SAN storage device Raw device mapping (RDM) provides a mechanism for a VM to have direct access to a LUN on IP SAN or FC SAN devices. RDM enables VMs to identify SCSI disks. RDM enables applications requiring high storage performance to be deployed on VMs. VM Snapshot Memory CPU Disk VM CPU and memory snapshot Read/write redirection Delta disk VM snapshot 1 VM snapshot N VM snapshot 2 Technical features • Incremental and memory snapshots store all information about a VM. • Snapshots can be created for a running VM. • Snapshots can be used to restore any VM. • Snapshots of running VMs can be merged. 27 Application scenario • VM data backup and recovery Virtual Cluster File System – VIMS VM VM VM VM Implementation FusionCompute Technical features NAS Local disk 28 VMs that require advanced storage features, such as storage live migration, snapshot, and linked cloning Benefits SAN Supports FC SAN, IP SAN, and NAS storage as well as local disks. Supports fixed, dynamic, and differencing disks. Application scenarios VIMS The Virtual Image Management System (VIMS) is a high-performance cluster file system. Data stores are first converted into the VIMS format and then attach to CNA nodes for VMs to use. Simplifies storage resource management and improves administrator working efficiency. Supports heterogeneous storage devices and is reliable and easy to use. FusionSphere 5.1 Features 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 1 Computing Virtualization 2 Storage Virtualization 3 Network Virtualization 4 Migration and Availability 5 Backup and Disaster Recovery 6 Installation and Deployment 7 Security 8 Compatibility and Interconnectivity 9 Cloud Management 10 Virtual Data Center Services 29 Auto-Sensing NIC Performance Optimization, Improving Network Processing Efficiency by 30% Implementation 2000 1500 1000 500 CPU(% ) 0 Pre-Optimization (Virtualization Platform) Post-Optimization (Virtualization Platform) Pre-Optimization (VM) Technical features Rx(kp ps) Post-Optimization (VM) Postoptimization (Virtualization Platform) Preoptimization (VM) Postoptimization (VM) Rx (kpps) 538.9 1676.0 314.2 508.4 CPU (%) 306.4 607.3 506.1 527.2 Item 30 Single-thread network packet handling is optimized. The multiple-threads-and-no-lock technology is used to improve the concurrency performance, and the receive and send performance of 30% small packets can be improved. Application scenarios Preoptimization (Virtualization Platform) The NIC uses the auto-sensing interruption aggregation technology for receiving network packets. Therefore, the NIC can receive small packets in batches, reduce the number of interrupts, and improve the receive and send speed of 10% of small packets. Network games and instant messaging that have large numbers of network packets smaller than 512 bytes and that require low latency Benefits Increases the real-time processing efficiency of small network packets by 30%. Support for Trunk Ports by vNICs VM vNIC 0 vNIC 1 VM vNIC 7 ... VLAN 100 VLAN 101 Access port VLAN 107 vNIC 0 Trunk port VLAN 100 to VLAN 200 Virtual switch Virtual switch FusionSphere 3.1 FusionSphere 3.0 A VM supports up to 8 vNICs. Therefore, a maximum of 8 VLANs and 8 subnet gateways are supported. vNICs support trunk ports so that a vNIC can support multiple VLANs. Benefits Because vNICs support trunk ports, a vNIC can support multiple VLANs for more flexible networking and for more complex service scenarios. 31 10GE Gateway for Key Applications and I/O-Demanding Scenarios Control domain VM VM Control domain FusionCompute Control domain PF driver queue VM VM VF driver VF driver FusionCompute FusionCompute queue Characteristics VM VIF Bridge VIF Bridge Differences VM queue PF ... Common vNIC VMDq-enabled NIC SR-IOV-enabled NIC (Enhanced in FusionSphere 5.0) Domain 0 bridge queue Independent VM packet queue • Address translation implemented by the SRROV technology One-time data copy • One-time address translation implemented by • The hypervisor does not need to implement the hypervisor, which consumes little computing address translation, which reduces resources computation consumption. • High CPU overhead which adversely affects VM density • Smooth VM live migration and snapshot • Little CPU overhead • Smooth live migration, snapshot, IP-MAC address binding (VMware cannot provide this function.) • Little CPU overhead • Limitations: Smooth live migration and snapshot features are unavailable (the same as VMware) NIC throughput: 9.1 Gbit/s (TCP) NIC throughput: 9.15 Gbit/s NIC throughput: 9.5 Gbit/s 32 Distributed Virtual Switch (DVS) VM 2 VM 1 VM 12 VM 11 VM 3 VM 13 FusionCompute FusionCompute Virtual switch 1 (Web) Virtual switch 2 (App) Server A Implementation Enables the virtualization administrator to configure and maintain physical and virtual ports of the DVSs on multiple hosts. Technical features Enables centralized configuration and management and helps customers understand the network structure. Supports VLAN configuration, layer 2 network security policies, and network bandwidth control. 33 Server B Application scenarios Virtual switching networks of a large number of hosts need to be centrally managed. Benefits Provides more flexible network policy control. Support for IPv6 for the Service Plane Benefits IPv6 (external network) IPv4 (external network) • VMs support both IPv4 and IPv6. Each VM NIC can have an independent IPv4 or IPv6 address or have Firewall/VPN Switch (L3) both of them configured. • The provided service plane network services, such as Load balancer DHCPv6 External network security groups, network port binding, network QoS, and VPC external network management, also support both IPv4 and IPv6. Switch [L2] • The system service plane supports IPv6, which provides more IP addresses than IPv4 and enables Direct network more flexible and convenient networking. VMs (IPv4/IPv6) 34 DVS Uplink Port Bonding System priority, port priority, and active port LACP LACP PDU Server LACP PDU LACP PDU Implemented based on the standard LACP protocol included in IEEE 802.3ad Technical features 35 Application scenarios High server bandwidth and high reliability are required. Supports manual link aggregation and static LACPbased link aggregation. The static LACP-based link aggregation can only be manually configured. (The system will not automatically create or delete aggregation groups.) The static LACP-based link aggregation detects links through LACP packets and can discover link faults, such as ports in errordisable mode. vSwitch iNIC Implementation Access switch Benefits Increases server network bandwidth and improves network link reliability. Automatically detects the faults at the link layer and incorrectly connected links and performs link switchover, significantly reducing the network access failure rate. Enhanced ARP Attack Defense Capability VM 1 VM1 VM 2 VM 3 VM 1 VM 2 VM 3 VM2 ARP req ARP req ARP rsp Normal condition: If VM 1 wants to communicate with VM 2, the ARP requests of VM 1 broadcasts at layer 2 and the VM 2 IP address is contained in the request. Therefore, only VM 2 responds to the request. ARP rsp ARP rsp Man-in-the-middle attack If VM 1 wants to communicate with VM 2 and VM 3 wants to intercept the conversation, then VM 3 sends a fake message to VM 1 and claims to be VM 2. Therefore, VM 1 actually sends data packets to VM 3. Flood attack To initiate a flood attack, VM 3 sends a lot of ARP packets to the system, eventually interrupting the network communication. Benefits ARP attack defense avoids ARP spoofing that uses faked IP or MAC addresses. The ARP attack defense capacity provides protection against a malicious VM from encrypting other VMs' data packets using a fake gateway address, causing network interruptions, or interrupting VM communication at layer 2 by initiating flood attacks. 36 VM Network QoS Control 256 Kbit/s Token 128 Kbit/s Queue Traffic classification 128 Kbit/s Token Bucket FR iNIC Implementation Network QoS provides traffic shaping and bandwidth priority control for virtual NICs and system ports. Technical features QoS control can be implemented for both inbound and outbound traffic. Traffic shaping can be implemented for outbound traffic based on the token bucket algorithm. 37 Application scenarios High-quality network communication between the network plane and user VM network is required. Benefits QoS control on inbound traffic avoids resource contention and ensures traffic fairness. The burst size and peak bandwidth can be configured to allow a burst when the system has significant idle resources. Traffic shaping avoids packet loss, network jitter, and other adverse impacts on services caused by rate limiting. Virtual Service Appliance (VSA) Technical features VSA Application Based on trunk ports and the sub-interface mechanism, the VSA supports unlimited number of VLANs. DHCP The VSA provides comprehensive services, such as NAT, ACL, routing, DHCP, and load balancing. Gateway Interface NAT ACL Router VXLAN gateway of a DVS. VIF 1 VIF 2 ... VIF N vNIC 1 vNIC 2 vNIC 3 The VSA supports VXLAN and can function as the vNIC 4 VXLAN interface Benefits The VSA can function as a software gateway and provide application services to implement flexible Trunk network control and software-defined networking (SDN). DVS 38 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 1 Computing Virtualization 2 Storage Virtualization 3 Network Virtualization 4 Migration and Availability 5 Backup and Disaster Recovery 6 Installation and Deployment 7 Security 8 Compatibility and Interconnectivity 9 Cloud Management 10 Virtual Data Center Services 39 VM Live Migration (VM Motion) App App App Technical features • • VM live migration efficiency is improved one-fold by leveraging the memory compression technology. The source and destination hosts involved in live migration can use CPUs of different generations. FusionCompute FusionCompute Application scenarios • Server B Server A Short-time service interruption is tolerable and services must be quickly restored, such as lightweight database services and desktop cloud services. VM live migration does not interrupt VM services and is insensible to users. 40 VM Cloning App App App App App App OS OS OS OS OS OS Technical features • VM cloning is to quickly create a copy of an existing VM. The new VM has the same specifications and storage content as those of the original VM. FusionCompute Application scenarios • Quick VM creation is required and VMs to be created need to have the same specifications FusionStorage as existing VMs. FusionSphere allows online and offline VM cloning when VIMS or FusionStorage is used. 41 Enhanced VM HA Mechanism App App App App App App OS OS OS OS OS OS X Physical Ÿ server A Physical Ÿ server B • Fault detection for hosts, virtualization platforms, and VMs is supported. • Supports both VM HA and VRM-independent HA. • The network plane used for HA heartbeat monitoring can be configured, which helps to lower the network pressure. • Multiple fault diagnosis mechanisms are supported to ensure fault diagnosis accuracy and completeness. • HA of VMs using shared or local storage is supported. APP APP APP OS OS OS Technical features Benefits N hours 3 minutes Physical host Physical Ÿ Ÿ A resources (reserved) server C H 42 VM Significantly reduces the time for fault rectification and service downtime, and ensures service continuity. Fault Tolerance (FT) Technical features • Switchover takes only a few seconds and has no impact on IT services. (Packet loss rate < 1%) Transaction service Transaction service Settlement service Settlement service • (VMware vSphere supports FT for App App FT can be enabled for VMs that has two vCPUs. Real-time data synchronization four-vCPU VMs.) • Performance loss is between 5% to 30%. FusionCompute FusionCompute X Application scenarios • FT (no service interruption) Server A' Server A 43 Systems with high reliability requirements, such as the transaction system and enterprise resource planning (ERP) system Dynamic Resource Scheduling (DRS) App App App FusionCompute App FusionCompute Technical features • • • • • • FusionCompute Automatically balances cluster loads based on the scheduling policies. Provides optimized scheduling algorithms and performs scheduling based on the VM load change trend to avoid VMs from being repeatedly migrated among hosts. Provides the unique scheduling baseline threshold configuration function to avoid unnecessary migration. Allows FusionCompute to be configured so that it does not migrate specific VMs or manually migrates specific VMs. Allows manual migration performed by administrators or automatic periodic migration based on configured policies. Automatic migration can be implemented at specified intervals by day, week, or month. 44 App App App App FusionCompute Application scenarios & benefits • VM load dramatically changes and VM users have high performance requirements. • DRS helps to balance load on hosts to fully utilize host computing resources and improves efficiency of service systems running on VMs. Distributed Power Management (DPM) App App App FusionCompute Technical App FusionCompute features • The system automatically migrates VMs on light-load hosts to other hosts and powers off the light-load hosts based on user-defined DPM policies. If the loads on hosts in the system exceed the configured threshold, the system automatically selects hosts and powers on them to balance the host loads in the cluster. • The system can select one or multiple hosts to power on or power off. • The system powers on or powers off hosts based on both the DPM and DRS policies to avoid mutual influence. • The scheduling policies can be configured at a specified interval by day, week, and month. 45 App App FusionCompute FusionCompute Application scenarios & benefits • • • VM loads dramatically change and VM users need to reduce power consumption. When hosts are light-load, some VMs on the hosts are migrated to other hosts and idle hosts are powered off to reduce system power consumption. The prerequisite is that each VM must have sufficient resources for running after being migrated. When hosts are overloaded, some hosts are automatically powered on and VMs are migrated to these hosts to ensure VM performance and customer experience. Refined Resource QoS Control, Ensuring High Availability of VIP Services BT download Web Oracle FusionCompute Common user Silver VIP Gold VIP FusionCompute QoS control based on service priority QoS control based on user priority Set the QoS priority based on the importance of Set the resource priority based on the enterprise or carrier applications. importance of customers. Supports QoS control by CPU, memory, network, and storage and meets customers' requirements for flexible QoS control. 46 Real-time synchronization Management node (active) Management node (standby) Data Protection for Management Nodes Daily backup Technical features • All management nodes work in active/standby mode, and the active and FTP server standby nodes are deployed on two FusionCompute FusionCompute independent physical servers. • Multiple backup mechanisms are designed for system configuration data so that all the management data can be restored in the event of a failure. Daily backup Benefits • Ensures high reliability and disaster recovery capability of management Local disks of management node systems. 47 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 1 Computing Virtualization 2 Storage Virtualization 3 Network Virtualization 4 Migration and Availability 5 Backup and Disaster Recovery 6 Installation and Deployment 7 Security 8 Compatibility and Interconnectivity 9 Cloud Management 10 Virtual Data Center Services 48 eBackup-based VM Backup Plan LAN/VLAN VRM cluster 2 VRM cluster 1 Logical cluster VM Logical cluster VM Computing resource VM Logical cluster VM VM VM Logical cluster VM ... VM Computing resource eBackup backup server eBackup backup agent 1-N Storage resource SAN/iSCSI/NAS Storage resource Storage resource SAN/IP-SAN/IP connection LAN-free backup/restoration data flow Technical features Supports permanent incremental backup, reducing backup storage space occupation. Flexible data restoration. Backups can be used to restore the original VM or a specific VM. An eBackup system can protect up to 10,000 VMs. An eBackup system supports up to 64 backup servers. Supports backup of data at multiple sites. Supports SAN or LAN-free data transfer mode. (New function) Supports file-level restoration. (New function) 49 Implementation Application scenarios Huawei eBackup backup software works together with FusionCompute snapshots and the Changed Block Tracking (CBT) function to implement VM data backup. Provides flexible data backup. Improves management efficiency of the data backup system. Benefits If important data is lost, the data can be quickly restored using backups, preventing data loss. Host-based Remote Replication DR Production site DR site UltraVR (DR management software) UltraVR (DR management software) VM 1 VM 2 Implementation VRG VRG VRG VRG FusionSphere (virtualization platform) VM 2′ VM 1′ FusionSphere (virtualization platform) VM • The host-based I/O replication function is used to copy VM data from the production site to the DR site. • The DR management software on the DR site registers VMs that use DR storage with the virtualization platform and automatically starts the VMs. Application scenarios Application-level DR between virtual sites that meet the following requirements: The sites use virtualized or distributed storage, the sites are interconnected over IP networks, and the RPO is greater than 10 seconds. VM′ Technical features & benefits Host-based I/O replication • • • • Huawei virtualized or distributed storage Huawei virtualized or distributed storage 50 • Supports DR and restoration of a whole VM. No agent needs to be installed on VMs. Supports heterogeneous storage devices. DR administrators can implement one-click DR switchover, DR dills, and scheduled migration, simplifying manual operations. Supports multiple DR modes: Active-standby DR, active-active DR, and shared DR (multiple-to-one). Storage-based Remote Replication DR Control channel UltraVR (DR management software) UltraVR (DR management software) Application scenarios DR of VMs in the application systems that Site A VM Site B VM VM VM have small write pressure, and low bandwidth, IOPS, and latency requirements Technical features & benefits • Supports DR and restoration of a whole VM (including VM system and disk volumes). FusionCompute • No agent needs to be installed on VMs. • DR administrators can implement one- FusionCompute click DR switchover, DR dills, and scheduled migration, simplifying manual operations. • Remote array replication Supports both synchronous and asynchronous replication. • Supports multiple DR modes: Activestandby DR, active-active DR, and shared DR (multiple-to-one). 51 Storage-based Remote Replication DR Key Indicators Indicator Host-based Replication DR Storage-based Replication DR Synchronous replication RPO N/A 0 Synchronous replication RTO N/A <4 hours Asynchronous replication RPO >10 seconds 15 minutes to 24 hours Asynchronous replication RTO <4 hours <4 hours Max. number of managed sites Local site: 32 Remote site: 32 Local site: 32 Remote site: 32 Max. number of disk arrays High-end: 2 Medium-range: 8 Low-end: 32 High-end: 2 Medium-range: 8 Low-end: 32 Max. number of protection groups 64 64 Max. number of VMs protected by a protection group UltraVR technical specifications Max. number of protected VMs 500 500 3000 3000 Max. number of protection policies 64 64 Max. number of time schedules of a protection policy 3 3 Max. number of recovery plans 64 64 Max. number of recovery plans that can be concurrently executed 10 10 Item Overall indicators 52 Remarks 1000 VMs 1000 VMs FusionSphere 5.1 Features 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 1 Computing Virtualization 2 Storage Virtualization 3 Network Virtualization 4 Migration and Availability 5 Backup and Disaster Recovery 6 Installation and Deployment 7 Security 8 Compatibility and Interconnectivity 9 Cloud Management 10 Virtual Data Center Services 53 Installation Procedure Install FusionSphere. Install FusionCompute. Install FusionManager. Install VSAM if required. Configure alarm reporting. Connect and configure resources. Connect resources. Configure resource pools. Prepare templates. Create VDCs. Create networks and VMs. Create VPCs and networks. VDC administrator 54 Provision VMs. System administrator Physical Device Networking 192.168.100.200 Internet VLAN 100 Management NIC 1 Management NIC 2 Service NIC 1 Service NIC 2 BMC BMC network FusionCompute Management network FusionCompute Service network Storage network Storage link Storage network 55 Service Deployment Plan FusionManager FusionManager Zone 1 FusionCompute Zone 2 ... Connect resources Create zones. Zone Cluster 1 Cluster 2 Cluster N Connect the hypervisor. FusionManager Availability zone 1 Availability zone 2 Zone Resource cluster 1 Create availability zones. 56 Resource cluster 2 Associate resource clusters with zones. Professional Support Tool – Rainbow Server where the migration tool is running Cloud data center based on Huawei virtualization platform Network Restart VM Source server FusionSphere Agent Replicate data Source disk Destination disk Online and offline service migration Snapshot Partition Create bootloader. Modify registry format (driver and boot configuration) Traditional physical data center or third-party virtual data center Supports smooth application migration to the cloud based on service methodology and the state-of-the-art migration tool, reducing migration risks and improving migration efficiency. 57 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 1 Computing Virtualization 2 Storage Virtualization 3 Network Virtualization 4 Migration and Availability 5 Backup and Disaster Recovery 6 Installation and Deployment 7 Security 8 Compatibility and Interconnectivity 9 Cloud Management 10 Virtual Data Center Services 58 Complete User Data Deletion Virtual disk Virtual disk 1. Rent 1. Rent 2. Use User A User A 3. Release 3. Release Permanently delete data on the virtual disk. The virtual disk is formatted, but data is not deleted. 4. Rent Risks 4. Rent User B 2. Use 5. Use software to obtain the data. Secure User B Others: Delete data by formatting virtual disks, and the data can be restored using software. There are high risks of information leakage. 59 Huawei: The physical bits of the released virtual disks are overwritten by 0. Data on the disks cannot be restored, and there are no security risks. System Tailoring and Hardening OS tailoring • • OS component tailoring: Remove OS components that may cause security risks to decrease potential security vulnerabilities, and the software package size is reduced to about 370 MB. Kernel tailoring: Remove 14 kernel modules that may cause security risks, including the bluetooth and WiMAX. System hardening • SRay • • 60 System security hardening: Harden ports and access to the system and comply with the industry security standards. Protect system integrity using AIDE, an invasion detection tool. Implement security hardening based on industry best practices. The hardened CNA nodes scores over 80 after being scanned by security scanner, CIS-CAT. Antivirus Virtualization SVM GVM GVM √ GVM Implementation • √ Interface for memory sharing FusionSphere Antivirus management server Technical features & benefits • Host 1 • • Antivirus application deployment Unified policy configuration Scan SVM GVM GVM √ GVM √ Interface for memory sharing FusionSphere FusionSphere provides an open API for antivirus virtualization, and antivirus software vendors provide virtual antivirus solutions based on the API. √ • • • • Leverages the next-generation DPI technology. Uses the industry-leading agent-free mode. Leverages the state-of-the-art antivirus engine. Displays overall system security conditions in an easy-to-understand way. Provides high reliability. Provides comprehensive virus log collection and analysis functions. Provides accurate and efficient file monitoring. Host 2 Interface Interface provided by antivirus service provider for functional modules 61 Internal interface for Huawei virtualization software modules Open APIs provided by the Huawei virtualization platform Network Isolation Management Management VM VM User VM Management VLAN User VM User VM User VLAN 1 User VM User VM User VLAN 2 User VM User VLAN 3 Virtual switch Storage VLAN SAN storage Switch Technical features • • • The management plane, storage plane, and service plane are isolated from one another. User VMs in different groups are isolated from one another using VLANs. The firewall is used to ensure access security of users and administrators. 62 Cloud data center Administrator Firewall User Account Security Management VRM cluster 1 Forbidden operation VM VM VM VM VM VM FusionCompute Administrator of cluster 1 Forbidden operation Management network Firewall VRM cluster 2 VM VM VM VM VM VM FusionCompute Administrator of cluster 2 Technical features • • • Support role-based management for operations, such as creating VMs and volumes, and domain-based management for logical clusters. Support lifecycle management of accounts and roles. Support password complexity management, such as password length and validity period configuration. 63 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 1 Computing Virtualization 2 Storage Virtualization 3 Network Virtualization 4 Migration and Availability 5 Backup and Disaster Recovery 6 Installation and Deployment 7 Security 8 Compatibility and Interconnectivity 9 Cloud Management 10 Virtual Data Center Services 64 Compatible with Mainstream Hardware and OSs VM OS x86 server Dozens of OSs 9 mainstream vendors and 115 server models Network Storage Application 12 mainstream vendors and 89 storage device models 65 18 switch models Compatible with a Wide Range of Huawei Hardware Devices Storage 5300/5500 V3 5600/5800 V3 OceanStor 9000 N8500 Big data storage system SAN Server RH2288 RH5885 Rack server E9000 8-processor server E9000 FusionCube High-performance server Appliance Network S57XX Access switch 66 CE12804 CE12808 CE12812 Cloud Engine core switch Open APIs FusionSphere open APIs • VM management API • VM snapshot management API • VPC management API • Virtual storage API • Virtual network API • Virtual firewall management API 67 SNMP Northbound Interface Provides the SNMP northbound interface for alarm and performance data reporting and for interconnection with the existing SNMP network management system. 68 Open eSDK for Integration FusionSphere Cloud Operating (Business Center) Product and Service Catalog Management User Management Resale Management Retailer Management Order Management Billing Management Service SLA • VM management Resource Management (VRM) Resource Service Management (Resource Center) Global Resource Service Cloud management • Image/snapshot management Self-Service Resource Management • Virtual storage management FusionSphere API FusionSphere • Virtual firewall management Resource Pool Management (FusionManager) Automation & Orchestration Cloud Basic O&M Application Automation & Orchestration VDC Automation & Orchestration Resource Scheduling Template and Image Management Physical Device Automation (server/storage/network devices) FusionCompute Installation and Deployment Performance Authentication Topology Service catalog Alarm uStorage FusionNetwork Elastic Computing API Elastic Storage API Elastic Network API Computing Resource Scheduling (HA/FT/DR) Storage Resource Scheduling Network Resource Scheduling Distributed Software-Defined Storage SDN Controller Bare Metal Huawei Server UVP/ KVM ThirdParty VMM Storage Third-Party Server Huawei Device Third-Party Storage Device HDD/SSD vSwitch Huawei Switch and DC Gateway 69 VSA Third-Party Switch and DC Gateway • Virtual network management eSDK: REST JAVA API Python API • Resource monitoring Automation plug-ins • Platform capability plug-in • Pre-integrated workflow plug-in eSDK Application Scenarios and Benefits Application Scenario State Grid project: The resource orchestration center invokes open APIs of FusionSphere to obtain virtual resources. 1. Apply for VMs and handle applications. 2. Disassembly and assembly from services to resources. 3. Obtain resources. The resource orchestration system uses SDK or APIs of resource pools. Cloud resource management portal Resource orchestration center IT infrastructure supplier Open cloud management capability: provides multi-API aggregation and multi-language adaption, and hides version differences to open cloud management and resource virtualization capabilities. Process automation: supports ISV quick orchestration of the resource allocation procedure based on automation plug-ins provided by the Resource Center. Open eSDK Open Cloud Management Capability Cloud management SDK: Automation plug-in SDK: – – – – – – – Platform capability plug-in – Pre-integrated workflow plug-in VM management Image/snapshot management Virtual storage management Virtual firewall management Virtual network management Resource monitoring Note: Plug-ins are used in the Resource Center. 70 Technical features Benefits Centralized O&M: Third-party business operation/O&M system interconnects with the cloud platform to obtain virtual resources. Streamlined process: Virtual resources can be automatically allocated based on virtual resource management service requirements. FusionSphere 5.1 Features 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 1 Computing Virtualization 2 Storage Virtualization 3 Network Virtualization 4 Migration and Availability 5 Backup and Disaster Recovery 6 Installation and Deployment 7 Security 8 Compatibility and Interconnectivity 9 Cloud Management 10 Virtual Data Center Services 71 Huawei FusionManager 5.1 Key Features Feature Description Multi-Tenant VDC Consists of a collection of resources for customer organizations or for specific use and is the basis to vApp and network resource allocation. Application Template Enables the system to create applications using VM images and software components. VPC Provides comprehensive VPC services to meet complicated service networking requirements. Resource SLA Allows users to define resource SLA, and the system attaches tags to resource pools based on the user-defined SLA and allocates VM resources based on the SLA. Multi-Data Center Management Enables FusionManager to manage both the local data center and the data centers in other regions. Third-Party Virtualization Platform Management Can manage VMware vSphere virtualization platforms. 72 FusionManager – Cloud Management System 1 Centralized Management 2 Automatic Management 3 Enables template-based, automatic application deployment Enables on-demand scheduling of resources required by applications. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis 73 Centrally manages hardware devices, virtualization platforms, and applications. Uniformly manages virtualization platforms, as well as hardware and software from different vendors. Manages multiple data centers and enables rights- and domain-based management. Centrally manages hardware and software systems. Provides comprehensive resource, topology, alarm, and log management and monitoring functions. Centralized Management of Hardware and Software from Multiple Vendors x86 servers from multiple vendors vSphere, FusionCompute, XenServer Huawei FusionCube Physical servers Virtualization platform SUSE Linux Red Hat Linux CentOS Windows7 and Windows 8 Windows Server 2008 Huawei EMC NetApp IBM Hyper-converged infrastructure OS Microsoft Exchange Microsoft SharePoint Application Huawei FusionManager Storage Network Database Oracle7+ Microsoft SQL Server 7+ Security Huawei… Cisco, Huawei, Juniper... FusionManager centrally manages computing, storage, network, and security resource, VMs, OSs, databases, middleware, and applications. 74 Unified Management of Multiple Data Centers Unified management across regions • FusionManager can manage both resources in a local data center and those across different data centers. • FusionManager can use a uniform management procedure and model to centrally manages multiple data centers across regions. • An organization can use resources at different data centers across regions. DC 1 DC N Local FusionManager Rights- and domain-based management FusionManager supports rights- and domain-based DC 2 Local FusionManager DC 4 management for administrators to prevent unauthorized management operations. DC 3 Local FusionManager Ultra-large management scope FusionManager can centrally manage up to 16 data centers, and each data center can accommodate up to 1024 physical hosts. 75 Rights- and Domain-based Management User System administrator Default username: admin Service administrator Administrator 1 Administrator 2 Authorization Administrator Operator Auditor User Orgmanager Self-defined role 1 Service administrator 1 Authorization Default domain: default Domain 1 76 Organization 1 Organization 2 Organization 3 Domain 2 Role Service administrator 2 Domain Organization FusionManager – Cloud Management System 1 Centralized Management 2 Automatic Management 3 Enables template-based, automatic application deployment Enables on-demand scheduling of resources required by applications. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis 77 Centrally manages hardware devices, virtualization platforms, and applications. Uniformly manages virtualization platforms, as well as hardware and software from different vendors. Manages multiple data centers and enables rights- and domain-based management. Centrally manages hardware and software systems. Provides comprehensive resource, topology, alarm, and log management and monitoring functions. Graphical, Automatic, Template-based Application Deployment Technical features 1. Supports commonly-used vApp template design by dragging and dropping required objects on the center pane. 2. Supports automatic resource application, service deployment, and resource reclamation based on vApp templates. VM VM CNA VM VM CNA • Convenient vApp template design: You can design a vApp template by dragging and dropping required objects on the center pane, greatly reducing the complexity of service design. • Automatic service deployment/resource reclamation: One-click service deployment allows quick deployment of enterprise IT services and resource reclamation. • Policy-based elastic resource capacity expansion and reduction: Flexible policies are designed to enable automatic resource capacity expansion and reduction, adapting to everchanging service requirements in a prompt manner. 3. Supports service cluster capacity expansion and reduction based on userdefined policies. VM VM CNA VDC resource pool VM VM CNA VM CNA VDC resource pool 78 VM Resource SLA VM VM Technical features VM • Gold SLA Silver SLA Copper SLA • • Gold resource pool Silver resource pool Bronze resource pool Administrators can customize resource SLA tags that define service performance, reliability, and other required service indicators. The system automatically attaches the SLA tags to different resource pools based on customers' customization. When users create VMs, they can select resource SLA tags. The system then will automatically allocate resources to the VMs from the resource pools that meet the needs of the SLA tags. Benefits • Resource pools can be managed using tags, simplifying resource management. • Users can customize the tag names, which makes management convenient. 79 Elastic Scaling of Application Resources 0% 0% 0% 60% Utilization: 20% App C 50% 100% App B 50% 100% 50% 100% App A Utilization: 60% 20% Utilization: 60% 20% Provides an elastic scaling mechanism for application resources, which avoids a waste of resources and improves resource utilization. 80 FusionManager – Cloud Management System 1 Centralized Management 2 Automatic Management 3 Enables template-based, automatic application deployment Enables on-demand scheduling of resources required by applications. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis 81 Centrally manages hardware devices, virtualization platforms, and applications. Uniformly manages virtualization platforms, as well as hardware and software from different vendors. Manages multiple data centers and enables rightsand domain-based management. Centrally manages hardware and software systems. Provides comprehensive resource, topology, alarm, and log management and monitoring functions. Centralized, Scalable Infrastructure O&M 1 Automatically detects connected devices to improve O&M efficiency. 2 Hides device peculiarities and provides user-friendly GUI, which simplifies O&M. 3 Allows system dashboards to be customized and faults to be detected directly without the need to analyze huge amounts of data. 82 Top Fault Statistics for Quick Fault Locating 1 Top N faults and descriptions are clearly displayed on the management portal. 2 Faults can be detected in a quick manner once occurring, and main services can be recovered in a timely manner. 83 Comprehensive Performance Analysis 1 Monitors performance changes of key services. 2 Automatically analyzes and displays Top N statistics. 84 Capacity Analysis 1 Clearly displays resource usage data. 2 Detects potential resource bottlenecks before services are adversely affected. 85 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 1 Computing Virtualization 2 Storage virtualization 3 Network virtualization 4 Migration and Availability 5 Backup and Disaster Recovery 6 Installation and Deployment 7 Security 8 Compatibility and Interconnectivity 9 Cloud Management 10 Virtual Data Center Services 86 Self-Service Capability Self-O&M Self-service Service application • Service change • Service maintenance Service approval O&M management Service release Users can perform the following operations on their own: • • • • • Self-service 87 Query the resource usage, capacity, used resources, and available resources in a VDC. Query the number of obtained resources in a VDC by resource type. Apply for more VDC resource quotas. Manage VDC users. Manage VDC service catalogs. Configure VDC network environments. Approve service applications from service users. Service Catalog Service catalog A service catalog contains the following content: • Service name, description, and icon • Service parameters that can be customized when users apply for services • Service parameters that can be configured when administrators approve service applications • Parameters for locking a service • Service approval policies 88 Template Service App OS Application template (VM template+Software package+Network connection+Scaling group) ISO image App RAM OS CPU Disk VM logical template VM template Software package Provides comprehensive template services to facilitate VM and application creation. 89 Multi-Tenant VDC Resource Pool Application service WEB ERP Email VPC A Organization 1 Organization management Resource cluster 1 Organization 3 VPC B VDC 1 VDC 2 Zone A Computing resource pool V M Resource management Organization 2 V M Resource cluster 2 Physical resource pool P M V M VDC 3 P M VDC 5 VDC 6 VDC 7 Resource cluster 3 Zone B P M VDC 10 Resource cluster 6 Computing resource pool Network resource pool VM VM VM Network resource pool VM Huawei FusionCompute Equipment room Subrack Cabinet Slot 90 VM VM Storage resource pool Storage resource pool Device management VDC 9 VDC 8 Equipment room Subrack Cabinet Slot VMware vSphere Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) VDC V M V M V M V V M M V M V V M M VPC 2 Department A Employees on business trip VPC 1 Internet Department B Technical features • • • • Isolated environment: The VPC provides isolated VM and network environments to meet isolation requirements of different departments. Comprehensive services: Each VPC can provide independent virtual firewall, elastic IP address, virtual LB, security group, super VLAN, IPsec VPN, and NAT gateway services. (Some of these functions can be provided by VSA.) Flexible networking: The VPC provides multiple networking modes, such as direct networks, routed networks, and internal networks. The VPC provides resource usage information that can be used in a billing system. 91 VLAN Aggregation (Super VLAN) Technical features • Internet connection between VPCs can be configured on the same super VLAN, in which sub-VLANs are created to implement layer 2 isolation. • In the same VPC, the Super VLAN technology allows different internal subVLANs to share an IP address segment. Benefits • Reduces the number of private and public IP addresses required. 92 Integrated CE128XX Series Agile Switches Virtual Private Network Solution Comparison Software Gateway Firewall–based Gateway Switch-based Gateway Solution overview Uses softwarebased firewalls to provide virtual firewall and router functions. Virtual firewalls and routers are created on hardware firewalls. Virtual firewalls are created on hardware firewalls, and virtual routers are created on switches. Gateway performance Medium Medium High Firewall performance Medium Medium High Reliability Low High High Dependence on device selection None Medium High 93 Solution Virtual firewalls and routers are created on different hardware devices, increasing throughput of VPC networks. Advantages Separate deployment and optimal performance Limitations Requires the hardware firewall virtualization function. Requires CE128XX series agile switches. Contents 1 FusionSphere 5.1 Overview 2 FusionSphere 5.1 Features 3 Product Support 94 Product Support Click the following link to obtain product datasheets, success stories, and software: http://e.huawei.com/en/products/cloud-computing-dc/cloud-computing 95 Product Support Visit http://support.huawei.com/enterprise and choose > IT > FusionCloud > FusionSphere > FusionSphere to obtain after-sales support documentation involving installation, test acceptance, maintenance, and troubleshooting. 96 Product Support Visit http://support.huawei.com/ecommunity/bbs/ and choose IT Forum > FusionCloud to visit the Huawei cloud computing technical forum. 97 HUAWEI ENTERPRISE ICT SOLUTIONS A BETTER WAY Copyright © 2015 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. The information in this document may contain predictive statements including, without limitation, statements regarding the future financial and operating results, future product portfolio, new technology, etc. There are a number of factors that could cause actual results and developments to differ materially from those expressed or implied in the predictive statements. Therefore, such information is provided for reference purpose only and constitutes neither an offer nor an acceptance. Huawei may change the information at any time without notice.