* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
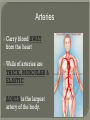
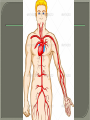
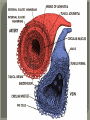
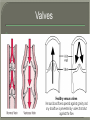
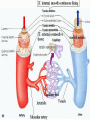
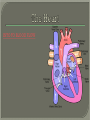
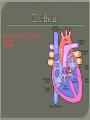
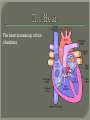
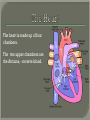
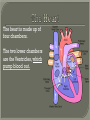
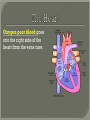
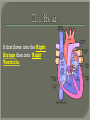
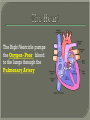
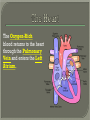
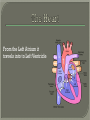
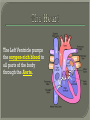
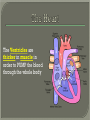
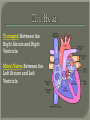
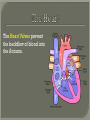
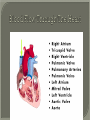
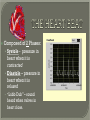
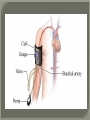
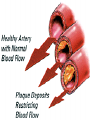
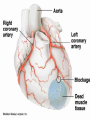
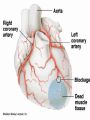
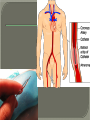
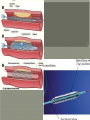
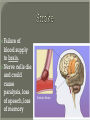
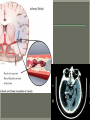
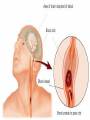
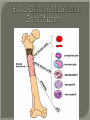
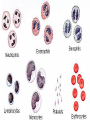
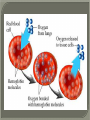
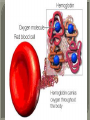
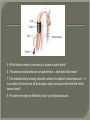
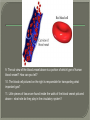
We always Start with a Song: The circulatory system helps transport fluids throughout the body which helps it obtain oxygen, nutrients and to remove wastes Supplies cells with oxygen and nutrients Carries hormones Maintains body temperature Protects the body from infection Helps in removing waste products Has ability to clot Main Parts: Arteries /Veins /Capillaries Heart Blood Lymph Vessels Arteries Carry blood AWAY from the heart Walls of arteries are THICK, MUSCULAR & ELASTIC AORTA is the largest artery of the body. Veins Carry blood TOWARD HEART from body tissues and organs Walls are THIN & only SLIGHTLY ELASTIC. Contain The One-Way VALVES Vena Cava is the largest vein of the body. Valves Found in VEINS Keep blood flowing toward the heart Also found in the heart to keep blood flowing through the chambers Valves Capillaries Connect arteries to veins One cell layer thick - so narrow that RBC pass through Gas exchange occurs by DIFFUSION Made up of : Lymph Vessels Lymph Nodes Thymus as blood circulates, some fluid leaks into the surrounding tissues lymph vessels collect the fluid and returns it to the circulatory system into large veins by neck found along lymph vessels trap bacteria and other disease-causing organisms become enlarged when there is an infection Every minute your heart beats 70 – 80 times Every minute your heart pumps 5 liters of blood INTO TO BLOOD FLOW Happy Days – PUMP YOUR BLOOD The heart is made up of four chambers. The heart is made up of four chambers. The two upper chambers are the Atriums, - receive blood. The heart is made up of four chambers. The two lower chambers are the Ventricles, which pump blood out. Oxygen poor blood goes into the right side of the heart from the vena cava It first flows into the Right Atrium then into Right Ventricle. The Right Ventricle pumps the Oxygen- Poor blood to the lungs through the Pulmonary Artery The Oxygen-Rich blood returns to the heart through the Pulmonary Vein and enters the Left Atrium. From the Left Atrium it travels into to Left Ventricle The Left Ventricle pumps the oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the body through the Aorta. The Ventricles are thicker in muscle in order to PUMP the blood through the whole body Tricuspid: Between the Right Atrium and Right Ventricle Mitral Valve: Between the Left Atrium and Left Ventricle The Heart Valves prevent the backflow of blood into the Atriums. Heartbeat – cardiac muscle cells are capable of contracting independently but they respond to the specific electrical impulses The Sinoatrial node (S-A node) is a group of cells located in the wall of the right atrium This node is known as the pacemaker of the heart The S-A node causes the atria to contract The AV node – atrioventricular node – near the right atria and right ventricle that coordinates the contraction of the ventricles When the SA node contracts it sends the impulse to the AV node The impulse then travels to a bundle of fibers called the Purkinje fibers which helps contract the heart. Nodes in Heart Label The Heart Composed of 2 Phases: • Systole - pressure in heart when it is contracted • Diastole – pressure in heart when it is relaxed • “Lubb Dub” – sound heard when valves in heart close. Pressure of blood against walls of arteries Guide to Blood Pressure: • Normal BP = 120/80 or less Referred to as HYPERTENSION BP> 140/90 Can strain heart and result in heart attack or Stroke Causes: • Stress • Smoking*** • Hereditary (genetic) • High sodium (salt) diet • Obesity A LEAKAGE of blood in heart caused by damaged valve. Narrowing of arteries due to growing plaques of cholesterol Blood can not pass through Could lead to heart attack Blood supply cut off to heart – cells die, and the heart stops working. Symptoms: • Severe pain and pressure in chest • Sweating • Shortness of breath • Pain in left arm Angioplasty – microscopic balloon fed into blocked artery with a catheter - presses plaque against arterial walls to resume blood flow Failure of blood supply to brain. Nerve cells die and could cause paralysis, loss of speech, loss of memory Carries materials throughout the body: • Oxygen and carbon dioxide • Nutrients • Cell wastes • Enzymes • Hormones maintains body temperature maintains constant pH protection against microorganisms liquid part of blood clear or straw-colored 90% water makes up ~ 50% of blood volume Nutrients Wastes Enzymes, hormones, proteins, antibodies aka: erythrocytes life span = 120 days most numerous of the blood cells biconcave disc No nuclei or mitochondria: Function is to carry oxygen on hemoglobin (Hb) Hb is a protein containing iron that binds to oxygen CO binds more strongly to Hb than O2 body cells die from lack of oxygen aka: leukocytes function is to identify and destroy foreign particles in the body 1. phagocytes: engulf & destroy bacteria by phagocytosis 2. lymphocytes: some produce antibodies to destroy foreign substances (antigens) cell fragments involved in blood clotting contain no nuclei – formed from bits of cytoplasm from large cells in bone marrow damaged cells release an enzyme that makes platelets sticky a series of enzyme reactions occurs to make a protein called thrombin thrombin helps make strands of fibrin fibrin is a protein that forms a mesh around broken blood vessel and traps RBCs and platelets to form a clot As water evaporates from clot, a dryer scab forms. Disorder characterized by too few RBC or not enough Irons and hemoglobin. Symptoms: Pale, feeling easily Treatment: eating faint, tiring iron-rich food (spinach, broccoli, red meat), and taking vitamin B12 injections Cancer of the blood or bone marrow uncontrollable abnormal cell division usually of the WBC. Unable Can to fight off infections be controlled or even cured with drugs. Genetic bleeding disorders in which it takes a long time for the blood to clot. Hemorrhage Usually – Unable to Stop Bleeding treated by replacing the missing clotting factors. 1. Which of the 4 blood components pictured above is responsible for transporting nutrients, hormones, enzymes and salts? 2. Which blood cell is most numerous in the human blood? 3. A protein molecule that is attached to RBC is responsible for the blood’s red color – what is this protein molecule? 4. What role does hemoglobin play in human transport? 5. Which blood vessel is most easy to locate a pulse within? 6. This persons blood pressure is hypertensive…what does that mean? 7. The brachial artery is being utilized to obtain this patient’s blood pressure – it is an artery that branches off what major artery leaving the left ventricle of the human heart? 8. Provide three ways to effectively lower your blood pressure. 9. The cut view of the blood vessel above is a portion of which type of human blood vessel? How can you tell? 10. The blood cell pictured on the right is responsible for transporting what important gas? 11. Little pieces of tissue are found inside the walls of the blood vessel pictured above – what role do they play in the circulatory system? 12. The small cell fragments pictured at the left are responsible for clotting blood. What are these cell fragments called? 13. Where are all of the blood cells pictured at the left produced? 14. What is the role of a white blood cell? What would having a high WBC indicate to a doctor?