* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mesopotamia Sumerian Achievements
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
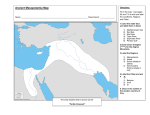
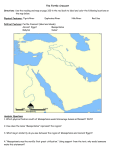
10/18/2014 Kids InfoBits - Document - Mesopotamia Mesopotamia Mesopotamia. Kids InfoBits Presents 2011. Word Count: 483. Full Text: COPYRIGHT 2011 Gale, Cengage Learning Title: Mesopotamia Source: Mesopotamia. Kids InfoBits Presents Detroit: Gale, 2011. Document Type: Topic overview Bookmark: Bookmark this Document Full Text: COPYRIGHT 2011 Gale, Cengage Learning Full Text: A Sumerian wheel. INTERFOTO/Alamy. Mesopotamia is the ancient region located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. In Greek Mesopotamia means “land between rivers.” It was a large, fertile plain in the shape of a new moon. The area is often called the Fertile Crescent. Mesopotamia is also called the cradle of civilization, because many of the first-known cities of the world were built there. These include Ur, Babylon, and Nineveh. Today this region is the country of Iraq. Archaeologists from around the world go there to study the ruins of the Sumerian, Babylonian, and Assyrian civilizations. Sumerian Achievements The Sumerians were the first people to settle in Mesopotamia. In the beginning, they were farmers. They grew barley and wheat and even invented the plow to till their fields. Because the land was dry, they drew water from the Tigris and Euphrates rivers to irrigate their farms. Around 3000 BCE the Sumerians began to form large city-states along the rivers. (A city-state is an independent state consisting of a city and its surrounding territory.) Each city-state had its own ziggurat (temple) and god that protected the inhabitants of the city. http://go.galegroup.com/ps/retrieve.do?sgHitCountType=None&sort=RELEVANCE-SORT&docType=Topic+overview&prodId=ITKE&tabID=T001&sear… 1/2 10/18/2014 Kids InfoBits - Document - Mesopotamia They had a unique government structure with a king, or priest-king, and a large assembly of officials that made sure the laws were obeyed. The Sumerians invented many things, such as the harp, the wheel, and the sailboat. Their greatest achievement was cuneiform writing. They used a stylus (pointed stick) to mark wedge-shaped symbols on wet clay tablets. The Rise of Babylon Eventually the separate Sumerian city-states were united and called Babylon, or Babylonia. King Hammurabi established laws called the Code of Hammurabi. The laws were written down and placed in public places so everyone would know what they were. The laws applied equally to everyone in the kingdom. The Babylonians were great builders. King Nebuchadrezzar II built the Hanging Gardens of Babylon. It was an engineering marvel, with garden terraces and waterfalls tumbling from one level to the next. It is one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.. Assyrian Warriors About 1,000 years after the Sumerians settled in Mesopotamia, the Assyrian civilization arose north of the Tigris River. Several hundred years after the death of King Hammurabi, the Assyrians conquered Babylon. They were a warrior nation and built a strong empire. Their capital city was Nineveh, to the north of Babylon. The walls of Nineveh stretched more than 3 miles (4.8 kilometers) along the Tigris River. Within the walls, the city was filled with beautiful buildings decorated with fine sculptures some of which remain today. The earliest known library was built by an Assyrian emperor, and more than 20,000 clay tablets have been found among the ruins. In spite of their strong armies, the Assyrians did not hold on to their empire. Babylonia was eventually conquered by a desert tribe known as the Chaldeans. Later all of Mesopotamia was conquered by the Persian Empire. Source Citation (MLA 7th Edition) "Mesopotamia." Mesopotamia. Detroit: Gale, 2011. Kids InfoBits Presents. Kids InfoBits. Web. 18 Oct. 2014. Document URL http://go.galegroup.com/ps/i.do? id=GALE%7CLPCBBN935837917&v=2.1&u=west89013tgps&it=r&p=ITKE&sw=w&asid=17b9f173a343cc875d2d621562186a0d Gale Document Number: GALE|LPCBBN935837917 http://go.galegroup.com/ps/retrieve.do?sgHitCountType=None&sort=RELEVANCE-SORT&docType=Topic+overview&prodId=ITKE&tabID=T001&sear… 2/2