* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Patterns of Evolution
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
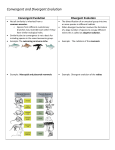
Do Now: Open your books to page 308-309. Read through section and answer the following questions: What is the relationship between allele frequencies and a gene pool? Why aren’t mutations in nonreproductive cells sources of genetic variation? Write down the following statements in your notes. Important to Understand: The frequency of a phenotype depends on the frequency of the genotype that codes for the trait. Genetic variation is the basis for the evolution of populations Phenotypic Variation Hitchhiker’s Thumb Tongue Rolling Ability What would happen to the genetic variation of the population if, for example, all of the tongue-rolling students left the class or if 10 hitchhiker-thumbed students were added to the class? Looking at the picture answer the following questions: What traits of penguins are adaptive to the Antarctic environment? What factors would result in changes to the genetic variation of penguins in a colony? Remember: Only those penguins that successfully reproduce and raise, live, healthy chicks will pass on their genes and the phenotypes that they code for. INDIVIDUALS DO NOT EVOLVE; POPULATIONS DO! Patterns of Evolution Chapter 11 Species adapt to their environment in several ways. The speed and pattern of evolution depend on the changes occurring in the environment. The 3 main patterns of evolution are: Coevolution Convergent evolution Divergent evolution Coevolution Coevolution is the process of change in 2 or more species that are dependent on each other. An evolutionary change in one organism may also be followed by a change in another organism. Examples: Birds and flowers Bees and flowers Coevolution Example Hummingbirds and the flowers they pollinate. The longer the beak of the hummingbird, the more food it will get. The farther away the food in the flower, the better the flower gets pollinated. Convergent Evolution What does Convergent mean? to bring together Convergent evolution is when organisms with different ancestry have similar phenotypes This occurs because of the environment the organisms live in causes similar characteristics to be fit, therefore leading to similar characteristics being passed on. Structures are usually analogous to one another Convergent Evolution Examples Sharks and dolphins Sharks are fish, while dolphins are mammals. However, both sharks and dolphins are similar in their body structures: fins, smooth body, etc. Divergent Evolution What does divergent mean? To move apart Divergent Evolution occurs when organisms that are similar become different. Usually caused by different habitats Can result in new species formation Examples of Divergent Evolution Polar bears and brown bears Polar bears and brown bears have common ancestors The differing environments selected different fitness characteristics Adaptive Radiation is a type of divergent evolution Adaptive radiation occurs when a number of different species evolve from a single common ancestor. Ex: Galapagos Finches – Each evolved from the same mainland species, but because the islands had different food, their beaks shapes changed over time. Artificial Selection Artificial Selection is the breeding of organisms for certain traits. It is a type of divergent evolution, but sped up. In artificial selection, nature provided the variation, and humans selected those variations that they found useful. Ex: Peas Peas have 2 variations yellow and green (recessive). All peas we eat are green because farmers bred the green peas to produce a pure strain. Artificial Selection cont’d Ex: Domesticated dogs All dogs are the same species Canis familiaris but they have been bred by humans for certain characteristics.