* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Matter Classification
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
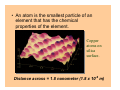
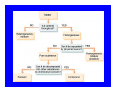
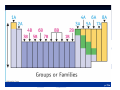
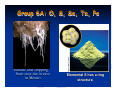
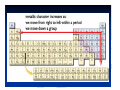
Matter and Energy Description Conservation Laws Periodic Table Energy Revised 5/11/07 Previous Material • Accuracy & precision • Significant Figures • SI Units Length Mass Temperature Mole • Conversions within Metric English-Metric • Medical Dose Units Simple Definitions • Matter – anything which has mass and occupies space • Energy – the ability to do work • An atom is the smallest particle of an element that has the chemical properties of the element. Copper atoms on silica surface. Distance across = 1.8 nanometer (1.8 x 10-9 m) Conservation • Conservation of Matter - matter is neither created nor destroyed must account for all matter during a reaction • Conservation of Energy - energy is neither created nor destroyed, changed from one form to another must account for all energy Three States of Matter • Solid – defined shape and volume • Liquid – adopt shape of container and defined volume • Gas – adopt shape and volume of container (pages 55 – 57, table 2.7, textbook) Matter Classification Description of Matter Matter Heterogenous (mixtures) Homogenous Pure Substances Elements Compounds Solutions Matter Classification Element Pure substance that cannot be decomposed any further by ordinary means About 115 elements listed on Periodic Table metals, non-metals, metalloids, atomic number, atomic symbol Long Form-Periodic Table Periodic Table Dmitri Mendeleev developed the modern periodic table. Argued that element properties are periodic functions of their atomic weights. We now know that element properties are periodic functions of their ATOMIC NUMBERS. p.79a p.79b Regions of the Periodic Table Group 1A: Alkali Metals Li, Na, K, Rb , Cs Rb, Cutting sodium metal Group 2A: Alkaline Earth Metals Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra Magnesium Magnesium oxide Group 7A: Halogens F, Cl Cl,, Br, I, At Group 8A: Noble Gases He, Ne Ne,, Ar Ar,, Kr, Xe Xe,, Rn Group 6A: O, S, Se, Te, Po Sulfuric acid dripping from snot-tite in cave in Mexico Elemental S has a ring structure. Transition Elements Lanthanides and actinides Iron in air gives iron(III) oxide Forms of the Elements Most are monoatomic – a single atom is the element, examples: Zn (s), Al (s), Cs (s) Some are Diatomic – two atoms bound together form the element (not single atom shown of Periodic Table) H2 (g); N2 (g); O2 (g); F2 (g); Cl2 (g); Br2 (l); I2 (s); Periodic Trends Properties of elements that may be predicted by relative position on Periodic Table Metal Character Atomic Size Ionization Energy Electronegativity See: Pages 99-101, textbook Atomic Size Compound Pure substance composed of two or more elements bonded together in a definite ratio by weight. Identified by a unique set of physical and chemical properties. H2O and H2O2 Na2CrO4 and Na2Cr2O7 Compounds Same three component elements – Na, Cr, but different weight ratios Na2CrO4 Na2Cr2O7 Comparison of Physical Properties Water and Hydrogen Peroxide Water Hydrogen peroxide Melting point °C 0.0 -2 Boiling point °C 100 158 Density, g/mL 1.0 1.46 Terms for Matter • • • • • • Heterogeneous Homogeneous Mixture Solution Physical process Chemical process • • • • • • Element Compound Atom Period Family Metal Classification of Energy (pages 40 –41, textbook) Description of Energy Energy Potential Kinetic (position or stored) (motion) Forms of Energy Energy Heat Light Electricity ENERGY is the capacity to do work or transfer heat. HEAT is the form of energy that flows between 2 objects because of their difference in temperature. Other forms of energy — •light •electrical •kinetic and potential Gravitational Potential Energy: E = mgh h = height g = * 9.82 m/s2 m = mass * On Earth Potential Energy Potential energy is stored energy and the energy of position––There are several forms of potential energy. Chemical Energy is energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. It is the energy that holds these particles together. Biomass, petroleum, natural gas, and propane are examples of stored chemical energy. Stored Mechanical Energy is energy stored in objects by the application of a force. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands are examples of stored mechanical energy. Nuclear Energy is energy stored in the nucleus of an atom––the energy that holds the nucleus together. The energy can be released when the nuclei are combined or split apart. Nuclear power plants split the nuclei of uranium atoms in a process called fission. The sun combines the nuclei of hydrogen atoms in a process called fusion. Scientists are working on creating fusion energy on earth, so that someday there might be fusion power plants. Gravitational Energy is the energy of position or place. A rock resting at the top of a hill contains gravitational potential energy. Hydropower, such as water in a reservoir behind a dam, is an example of gravitational potential energy. Kinetic Energy E = 1/2 mv2 E = energy (Joules) m = mass (kilograms) v = speed (meters/sec.) Marion Jones Sprints to Victory in the 200 meter. Kinetic Energy Kinetic energy is motion––of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, substances, and objects. Electrical Energy is the movement of electrical charges. Electrical charges moving through a wire is called electricity. Radiant Energy is electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. Radiant energy includes visible light, x-rays, gamma rays and radio waves. Light is one type of radiant energy. Thermal Energy, or heat, is the internal energy in substances––the vibration and movement of the atoms and molecules within substances. Geothermal energy is an example of thermal energy. Motion Energy is the movement of objects and substances from one place to another. Wind is an example of motion energy. Terms for Energy • • • • • Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Heat Light • • • • Temperature Specific Heat calorie, cal Wave length