* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics WGSB – part 3
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
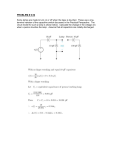
A level Physics Induction task 2 Electricity Name ___________________________________ Please complete all the questions attached and hand in to your Physics teacher on your first lesson in September. Wilmington Grammar School For Boys 1 1. A small solar cell has an area of 50 cm3 (0.005 m2). It is used to power a small electric motor. (a) This circuit is set up outside in bright sunlight. The reading on the voltmeter is 3 V. A solar cell (i) V M When the circuit is switched on for 200 s, the motor is supplied with 12 J of energy. Calculate the current in the solar cell. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... (3) (ii) Calculate the rate, in J/s, at which energy is supplied to the motor. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) The rate at which energy is supplied to the solar cell is much greater than the rate at which energy is supplied to the motor. Explain why. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... (2) Wilmington Grammar School For Boys 2 (b) A student suggests that solar cells could be used to power an electric shower. (i) The electric water heater in a shower needs to be supplied with energy at a rate of 7000 J/s. Calculate the area of solar cells that would be required to do this. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Give two reasons why this suggestion is not a good idea in practice. 1 ................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 2 ................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 10 marks) 2. The diagram shows a way of connecting 40 Christmas tree light bulbs to the mains electricity supply. 40 light bulbs series circuit (a) (i) When in use, the voltage across each light bulb is 6 V. What must be the voltage of the mains supply? ............................................................................................................................. (1) Wilmington Grammar School For Boys 3 (ii) The resistance of the filament in each light bulb is 10 ohms. Calculate the current in a filament when it has a voltage of 6 V across it. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. (3) (iii) What is the current in the circuit when the 40 light bulbs are lit? ............................................................................................................................. (1) (b) (i) Describe the energy changes that take place in the light bulbs when connected to the mains supply. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. (2) (ii) The Christmas tree lights are left on for 12 hours a day for the 12 days of Christmas. Calculate the total energy used by the Christmas tree lights during this period if they consume a total power of 144 W. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. (3) (iii) Calculate the cost of having the Christmas tree lights on for this period if the cost of 3.6 MJ of energy is 9 p. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. (2) (Total 12 marks) Wilmington Grammar School For Boys 4 3. (a) The diagram shows a simplified model of the inside of a metallic electrical conductor. The end A of the conductor is connected to the positive terminal of a battery and the end B to the negative terminal. (i) What name is given to the negatively charged carriers in a metallic conductor? ............................................................................................................................ (1) (ii) Draw an arrow on the diagram to show the direction in which the negatively charged carriers move when the metallic conductor is connected to the battery. Explain why they move in the direction you have shown. ............................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................ (2) (iii) What name is given to the flow of the negatively charged carriers through the conductor? ............................................................................................................................ (1) (b) In an experiment using a conductor, the current in it is 0.5 A when a 12 V supply is connected across it. (i) The supply is connected for 5 minutes. Calculate the number of coulombs of charge that pass through the conductor in this time. ............................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................ (3) Wilmington Grammar School For Boys 5 (ii) How many joules of energy are given to each coulomb passing through the conductor? ............................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................ (1) (iii) Calculate the total energy transferred in the conductor during the time the supply is connected. ............................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................ ......................................................................................................................... J (2) (Total 10 marks) 4. A technician wishes to find the resistance of a lamp for an overhead projector. He measures the current and voltage in an electrical circuit which includes the lamp. The electrical symbol for the lamp is (a) Draw a circuit diagram to show how he finds the resistance of the lamp. Label any devices used in your circuit. (2) (b) The lamp in an overhead projector is protected by a thermistor. The graph shows how the resistance of the thermistor changes with temperature. Wilmington Grammar School For Boys 6 2000 Resistance in ohms 1000 0 0 20 40 60 80 Temperature in ºC The thermistor and the lamp are connected in series. (i) Describe how the thermistor protects the lamp when the projector is first switched on. ....................................…….................................................................………. ....................................…….................................................................………. ....................................…….................................................................………. ....................................…….................................................................………. (2) (ii) What happens as the projector lamp warms up? ....................................…….................................................................………. ....................................…….................................................................………. ....................................…….................................................................………. ....................................…….................................................................………. (2) (iii) What is the resistance of the thermistor at 20 °C? ....................................……......................…. (1) (iv) The resistance of the lamp is 300 at 20 °C. In a series circuit: Total Resistance R = R1 + R2 Wilmington Grammar School For Boys 7 Calculate the current in the circuit at 20 °C when the projector is operated at 240 volts. ....................................…….................................................................………. ....................................…….................................................................………. ....................................…….................................................................………. ....................................…….................................................................………. ....................................…….................................................................………. ....................................…….................................................................………. (3) (Total 10 marks) 5. The current in a wire was measured at different voltages. The table shows the results. (a) Current in amperes (A) 0.20 0.35 0.55 0.70 0.85 Voltage in volts (V) 0.8 1.4 2.2 2.8 3.4 Use the data to draw a graph of current against voltage. 1.0 Current in A 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 1 2 3 4 Voltage in V (3) Wilmington Grammar School For Boys 8 (b) Describe how the current in the wire changes when the voltage is increased. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Calculate the resistance of the wire when the current is 0.6 A. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 8 marks) 6. (a) The diagram shows a diode connected in series with a resistor and an a.c. supply. (i) The graph on the left shows how voltage across the diode changes with time. voltage current 0 0 time time Draw a graph that shows how the current in the diode changes with time. Use the grid on the right. (2) Wilmington Grammar School For Boys 9 (ii) The connections to the diode are now reversed. Draw a graph that shows how the current in the diode changes with time. Use the grid below. current 0 time (1) (b) The graph below shows how the current in a diode depends on the voltage across it. current in A +3.0 +2.0 +1.0 0 –1.0 –0.8 –0.6 –0.4 –0.2 –1.0 +0.2 +0.4 +0.6 +0.8 +1.0 voltage in V –2.0 –3.0 (i) What current passes in the diode when the voltage across it is +0.7 V? ..................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Calculate the resistance of the diode when the voltage across it is +0.7 V. ..................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................... (3) Wilmington Grammar School For Boys 10 (iii) Describe how the resistance of the diode changes as the voltage across it is increased from 0 V to +0.8 V. ..................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 9 marks) Wilmington Grammar School For Boys 11