* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EXPERIMENT 8: MOSFET – Common
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
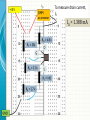
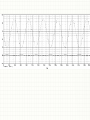
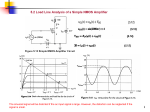
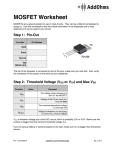
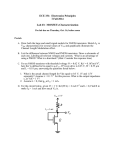
EXPERIMENT 8 MOSFET – Common-Source Amplifier 2N7000 - NMOS Drain (D) Gate (G) Source (S) NMOS CIRCUIT SYMBOL MOSFETs vs BJTs BJTs • Three different currents in the device: IC, IB and IE • Consume a lot of power • Large size device MOSFETs • Mostly widely used today • Low power • Very small device (nm) • Simple manufacturing process • Only 1 current, ID • Common Source is similar to Common Emitter (BJT) • The voltage/current gain is negative value PART A MOSFET DC ANALYSIS • Construct the circuit of Fig. 8.1 but DO NOT CONNECT the capacitor yet and record the measured values of the resistors. • Using the DMM, measure the values of VGS, VDS and ID. G D S VDS VGS = 2.17 V VDS = 5.42 V To measure drain current, ID ID = 1.388 mA • Using the threshold voltage, VTN = 2.1 V, please confirm that the transistor is in saturation. (VDS > VDSsat and VDSsat = VGS - VTN) • VDSsat = VGS – VTN = 2.17 – 2.1 = 0.07 V • So is your measured VDS > VDS sat? • From the measured value of ID, deduce the value of the conduction parameter Kn using the drain current in saturation formula I D K n VGS VTN 2 Kn = 1.388 mA / (2.17 – 2.1)2 Kn = 0.283 A/V2 PART B COMMON SOURCE AMPLIFIER (AC ANALYSIS) • By using the same circuit configuration – connecting the capacitor this time, • Set the function generator to 100 mV amplitude, 20 kHz sinusoidal wave. Connect it to vin. • Connect Channel 1 of the oscilloscope to vin and Channel 2 of the oscilloscope to vout. • Measure the peak-to-peak value for both input and output voltages on Channel 2 of the oscilloscope. • Calculate the value of the gain, vo / vin vo / vin ≈ - (34 to 37)