* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab 5 – Bias point of a MOSFET Amplifier
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
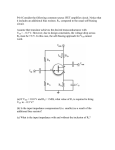
Lab 5 – Bias point of a MOSFET Amplifier Consider the enhancement-type n-channel MOSFET amplifier shown in Fig.1. The MOSFET has a threshold voltage VT = +2V, K = 0.5µnCoxW/L = 1 mA/V2, and a channel-length modulation factor λ=0.01 V−1. 1. Assuming a fixed bias of VGS=+5V, trace the MOSFET output characteristics iD vs. vDS for the ideal case of negligible channel-length modulation (λ=0) and for the real case with channel-length modulation λ=0.01 V−1. 2. Comment on the effect that the location of the DC operating point has if the drain resistance RD is increased from 1.33 KΩ to 1.78KΩ. Draw the load line for both value of RD and derive both analytically and graphically the two operating points Q1=(VGS1, VDS1, ID1) and Q2(VGS2,VDS2,ID2). Q1 is the operating point corresponding to RD=1.33 KΩ and Q2 is the operating point corresponding to RD=1.78KΩ. [Hint.: use SPICE .OP to verify the correctness of your computations] 3. Further comment on the effect that the location of the DC operating point has on the behavior of the amplifier, by considering the application of a 1 V peak-to-peak triangular waveform input signal of 1KHz frequency in series with the 5V DC bias voltage applied at the gate of the transistor. Make sure to: 1) include the SPICE deck, any plot necessary to illustrate your findings, and any relevant section of SPICE’s output file, 2) Hand calculate the operating point (VGS, VDS, ID), the transconductance gm, the output resistance ro and the voltage amplification Av of the circuit, and 3) compare theoretical and SPICE results. gm = ∂i D ∂vGS OP g o = g ds = ∂i D ∂v DS OP AV = ∂v DS ∂vGS OP = v ds v gs Page 1 of 2 OP Page 2 of 2