* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
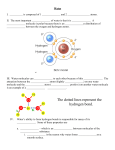
CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE (Chapters 2-3) 1. The characteristics of all living things are determined by their similar chemical makeup. 90 chemical elements occur in nature & 25 of these are essential to life. Living things are 96% carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, & nitrogen. 2. Elements are composed of atoms: a) the center is called the nucleus & contains positively charged particles called protons & particles that have no electrical charge called neutrons b) electrons are negatively charged particles – they are located on energy levels outside the nucleus c) atoms contain equal numbers of electrons & protons – this gives them no electrical charge 3. A compound is a substance composed of atoms of 2 or more different elements. (H2O, CH4, NaCl, CaCl2) This happens because atoms become more stable when their outermost energy level is full. (2 8 18) 4. Atoms combine with other atoms & are held together by chemical bonds. a) covalent bond - sharing of electrons (water H2O & sugar C6H12O6 & methane CH4 & ammonia NH4) – this is a very strong bond (handcuff chains) & is common in living things (sugars, fats, proteins, & water) b) ionic bond - gaining or losing electrons – these atoms have electrical charge & are called ions (salt NaCl & sodium fluoride NaFl) – this is a weak bond (magnets) – ions are most often part of biological processes (transmission of nerve impulses, muscle contraction, plant roots absorbing minerals) 5. Water is essential to life - it makes up 70% - 95% of most living things. It transports materials within living things & most life processes occur only when molecules are dissolved in water. 6. Water is an inorganic compound because it contains no carbon. A molecule of water consists of 1 atom of oxygen & 2 atoms of hydrogen held together at an angle by a covalent bond. 7. The hydrogen side of a water molecule is positively charged & the oxygen side is negatively charged. This uneven distribution of electrical charge makes water a polar compound. 8. Water molecules are attracted to each other. The positively charged hydrogen atoms of 1 water molecule attract the negatively charged oxygen atoms of another water molecule. This attraction of opposite charges forms a weak bond called a hydrogen bond. 9. The properties of water are a result of the polarity of water molecules & the weak hydrogen bonding with other water molecules. a) easily dissolves other compounds (salt, sugar, oxygen) b) moves upward by capillarity (plants, blood, meniscus, capillary tube) because molecules stick to other substances by adhesion c) expands when it freezes (pond ice floats, cracks rocks to form soil) d) resists change in temperature & helps maintain environmental conditions (protection of aquatic species, our body temp. & air temp.) e) droplets hold together like a magnet – this is called cohesion – it maintains surface tension (insects/pond) & buoyancy (jellyfish) 10. Organic compounds contain carbon & are made by living things. They are covalently bonded to other carbon atoms & to hydrogen, oxygen, & nitrogen to form these 4 compounds: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, & nucleic acids. 11. Carbohydrates: a) sugars & starches are used by cells to store & release energy b) carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen molecules that form a ring-like structure (CHO = 1:2:1 ratio) c) monosaccharides are simple sugars - glucose & fructose d) disaccharides are 2 sugars linked together - glucose + fructose = sucrose e) polysaccharides are many monosaccharide subunits - these complex carbohydrates include: starch (plant food storage in seeds & roots), glycogen (mammals store in liver), chitin (exoskeletons of insects, spiders, shrimp, etc.) & cellulose (plant cell walls) 12. Lipids: a) store energy & are a major part of membranes surrounding all living cells b) lipids are made up of fatty acids attached to glycerol molecules c) these large non-polar molecules do not dissolve in water – these long molecules contain only carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen - there are always twice as many hydrogen atoms as oxygen atoms (H:O = 2:1) d) commonly called fats (animal body fat, waterproof wax on leaves) & oils e) other lipids include steroids found in hormones, cholesterol, & animal/plant venom 13. Proteins: a) many small molecules bond together to form large complex proteins called polymers - composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, & nitrogen b) examples in nature include: 1) make up tissues & organs – muscles 2) enzymes carry out the chemical reactions in cells – all of these reactions are referred to as metabolism 3) antibodies destroy germs 4) pigments that give hair, eyes, & flowers their colors c) 20 amino acids are the basic building blocks of 1000’s of different types of protein molecules - these amino acids are held together by peptide bonds & form a chain called a polypeptide d) the structure of an amino acid can be recognized by the presence of a NH2 group & a COOH group 14. nucleic acids: a) very large complex molecules that store important information for cell characteristics & processes b) examples are DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid & RNA – ribonucleic acid c) nucleic acids are composed of 1000’s of subunits called nucleotides d) 1 nucleotide = a phosphate group + a 5-carbon sugar + a nitrogen base 15. pH is the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. This results from dissociation when a water molecule breaks apart into 2 ions of opposite charge: H2O H+ (hydrogen ions) = OH- (hydroxide ions) a) more H+ result in acids forming – this creates an acidic solution b) more OH- result in bases forming – this creates an alkaline/basic solution 16. Acids & bases are measured with a pH scale ranging from 0-14: 0---1---2---3---4---5---6---7---8---9---10---11---12---13--14 acidic neutral basic a) acid solutions have a pH of 0 to 6.9 – sour taste & are highly corrosive b) base solutions have a pH of 7.1 to 14 – bitter taste & feel slippery 17. Enzymes (also called catalysts) are protein molecules that change the rate of chemical reactions in cells to breakdown or create molecules. This process is similar to a lock & key mechanism: a) an area on the enzyme’s surface called the active sites attaches to a specific molecule called the substrate (hydrogen peroxide or sucrose) b) the enzyme weakens the chemical bonds – this results in the hydrolysis or breakdown of the substrate into smaller molecules called products (water & oxygen or glucose & fructose) c) after the reaction, enzymes are released unchanged & they can repeat the reaction again & again d) enzymes may fail to work if their environment is changed in some way – for example, a change in temperature or pH can cause a change in the shape of the enzyme or substrate & the reaction can’t occur