* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gerunds Infinitives and Participles Fill in Blank Notes
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish verbs wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Finnish verb conjugation wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Danish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
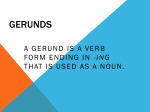
Notes: Gerunds and Infinitives GERUNDS ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ The base form of a verb + __________ When a noun looks like a verb with -ing, it is called a gerund. Can be the ___________ of a sentence: Jogging is good exercise. To jog is good exercise. Can be the _________________: I like reading books. I like to read books. Can be the _______________________, for example: We are talking about swimming in English class. We discussed quitting smoking for good. If you want to use an action word in a place that requires a noun, you can usually use a verb with an -ing ending. For example: Fishing is fun. _________________ is difficult. That is ballet _______________. In these sentences, fishing, hiking, and dancing look like verbs, but they are not verbs. They are nouns. When a noun looks like a verb with -ing, it is called a gerund. Notes: Gerunds and Infinitives INFINITIVES ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ The base form of a verb + _________ For example: To sleep To wash To love Infinitives and infinitive phrases can be both subjects and objects in sentences. ____________ To study hard will increase your chances of getting into college. _____________: Kathy wants to study with her friends. Gerunds and infinitives can use the same verb. However, the way the verb is used in each part of speech can change the meaning of the sentence. Notes: Gerunds and Infinitives Example Gerund Meaning Louise stopped drinking soda. Infinitive Louise stopped to drink soda. Though there are always exceptions to the following, here are two suggestions that will help you distinguish the difference between infinitives and gerunds: Suggestion #1 Infinitives are more often used to answer WHY-questions. Look at the following conversation: Louise: I stopped. Harry: Why? Louise: I stopped to drink water. Gerunds are usually not used to answer why-questions. Gerunds are nouns. Gerunds directly receive actions (when in the object position) just like other nouns. I stopped the car. (object-noun) I stopped the thief. (object-noun) I stopped arguing. (object-gerund=noun) Notes: Gerunds and Infinitives Suggestion #2 Infinitives in the subject position are often used for general or habitual actions. Here are some examples: To live a happy life is everyone’s deepest desire. To err is human, to forgive, divine. (Shakespeare) To fix a car requires a lot more than a screwdriver. NOTE: All of these sentences can use gerunds (living a happy life is everyone’s deepest desire). When the action happened in the past, a gerund is usually used. Past Action Monika has studied German. Gerund Studying German was easy for her. This action happened in the past. Therefore, use a gerund. Using an infinitive to refer to a past action is not as common and natural as using a gerund. Notes: Gerunds and Infinitives Practice: Identify each of the following as a gerund or infinitive. I forget locking the door. I forgot to lock the door. I stopped drinking soda. I stopped to drink soda. A PARTICIPLE is a word formed as a verb that can be used as an adjective. There are two main types of participles: 1. Present Participle-ends in –ing 2. Past Participle-ends in –ed, -en Verb Past Participle Present Participle rise the risen sun the rising sun boil the boiled water the boiling water break the broken news the breaking news cook the cooked ham the cooking ham **Note: Each of these are used to describe (adjective) not as an action (verb). Notes: Gerunds and Infinitives Participle End in: -ed, -en, -ing Acts like: adjective Gerund Ends in: -ing Acts like: noun Infinitive To + a verb Acts like: noun, adjective, adverb Step 1: _________________________________(Who/what is the sentence is about?). Step 2: ______________________________________ (What did the subject do?). Step 3: Are there any other words in the sentences that have verb endings (-ed, -en, -ing). NO YES Is it describing a noun? YES Participle You’re through! (no verbals) NO Does it end in –ing & act like a noun? (ie. Subject or object) YES Gerund NO Is “to” directly in front of it? YES Infinitive