* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Transformations Animations
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
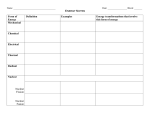
Student Study Guide: Energy Rules! Name: ____________________________________________ Class / Period: ___________________ Instructions: Enter the term, its definition, or an example as indicated. Energy: ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________ energy – the energy of an object or substance in movement; sometimes just called kinetic energy example(s): _______________________________________________________ ___________________ energy – the energy an object has due to place or position, such as its height above the Earth; a form of potential energy example(s): _______________________________________________________ ___________________ energy – the energy of electrons (negatively charged particles) moving or “flowing” within a substance example(s): _______________________________________________________ ___________________ energy – electromagnetic energy that travels in waves; also called radiant energy example(s): _______________________________________________________ ___________________ energy – the internal energy of a substance due to random vibration and movement of its atoms and molecules; also called thermal energy example(s): _______________________________________________________ ___________________ energy – energy that moves through substances (like air) by compression waves; sound example(s): _______________________________________________________ ___________________ energy – energy stored in the chemical bonds between atoms and molecules example(s): _______________________________________________________ ___________________ energy – energy stored in the nucleus of an atom; the energy that holds an atom together; sometimes called atomic energy example(s): _______________________________________________________ Laws of Thermodynamics: ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ Energy Transformations 52 ENERGY IN OUR LIVES MODULE FOR GRADES 6 TO 8 Student Study Guide: Energy Rules! TEACHER ANSWER KEY Name: ____________________________________________ Class / Period: ___________________ Instructions: Enter the term, its definition, or an example as indicated. Energy: the capacity to do work or create change ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ motion ___________________ energy – the energy of an object or substance in movement; sometimes just called kinetic energy a person dancing, car in motion, a thrown ball, flowing water, etc. example(s): _______________________________________________________ gravitational ___________________ energy – the energy an object has due to place or position, such as its height above the Earth; a form of potential energy a rock on the edge of a cliff, water behind a dam, etc. example(s): _______________________________________________________ electric ___________________ energy – the energy of electrons (negatively charged particles) moving or “flowing” within a substance electricity in power lines or home wiring, electricity from a battery example(s): _______________________________________________________ light ___________________ energy – electromagnetic energy that travels in waves; also called radiant energy sunlight, the light of a lamp or of a TV or computer monitor, etc. example(s): _______________________________________________________ heat ___________________ energy – the internal energy of a substance due to random vibration and movement of its atoms and molecules; also called thermal energy heat from the burner of a stove, charcoal grill, forest fire, etc. example(s): _______________________________________________________ sound ___________________ energy – energy that moves through substances (like air) by compression waves; sound any kind of sound - from a human, machine, animal, Discman, etc. example(s): _______________________________________________________ chemical ___________________ energy – energy stored in the chemical bonds between atoms and molecules energy plants store by photosynthesis, any food we eat, coal, oil example(s): _______________________________________________________ nuclear ___________________ energy – energy stored in the nucleus of an atom; the energy that holds an atom together; sometimes called atomic energy uranium at a nuclear power plant; plutonium in a nuclear bomb example(s): _______________________________________________________ Laws of Thermodynamics: The total amount of energy in the universe is constant. Energy can be neither ________________________________________________________________________________________ created nor destroyed, but it can be changed from one form to another. ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ Energy Transformations ENERGY IN OUR LIVES MODULE FOR GRADES 6 TO 8 53 Student Worksheet: Energy Transformations Animations Name: Class / Period: Instructions: Go online to http://www.poweringourfuture.com/students and select Energy Transformations. View each energy transformation and fill in the blanks below with the kinds of energy involved. 1. In a portable stereo, ________________ energy is changed to ________________ energy. 2. When you burn wood in a campfire, ________________ energy is converted to ________________ and light energy. 3. In a computer monitor, ________________ energy is transformed into ________________ energy and sound energy. 4. Through the process of photosynthesis, ________________ energy from the sun is changed to stored ________________ energy. 5. If you place a ball at the edge of a hill, and it rolls downhill, ________________ energy is changed to ________________ energy. 6. In a flashlight, the ________________ energy in batteries is changed to electric energy and then to ________________ energy. 7. In a fan, ________________ energy is changed to ________________ energy. 8. When water held behind a dam is released, ________________ energy is converted first to ________________ energy. 9. At a hydropower facility, the ________________ energy of flowing water can be used to spin a turbine and power a generator, creating ________________ energy. 10. In a photovoltaic panel, the ________________ energy of the sun is converted directly into ________________ energy. 11. In a car, the ________________ energy in gasoline is burned to create heat energy, which is converted to ________________ energy. 12. In a propane-powered chili roaster, ________________ energy is burned to create ________________ energy. 13. In a modern wind turbine, ________________ energy is converted to ________________ energy. 14. A stove uses electric energy or ________________ energy to create ________________ energy. 15. When we run, the ________________ energy stored in our muscles is converted to ________________ energy. Energy Transformations 54 ENERGY IN OUR LIVES MODULE FOR GRADES 6 TO 8 Student Worksheet: Energy Transformations Animations Name: TEACHER ANSWER KEY Class / Period: Instructions: Go online to http://www.poweringourfuture.com/students and select Energy Transformations. View each energy transformation and fill in the blanks below with the kinds of energy involved. 1. electric sound In a portable stereo, ________________ energy is changed to ________________ energy. 2. chemical When you burn wood in a campfire, ________________ energy is converted to heat ________________ and light energy. 3. electric light In a computer monitor, ________________ energy is transformed into ________________ energy and sound energy. 4. light Through the process of photosynthesis, ________________ energy from the sun is changed to chemical stored ________________ energy. 5. gravitational energy is If you place a ball at the edge of a hill, and it rolls downhill, ________________ (potental) motion (kinetic) changed to ________________ energy. 6. chemical In a flashlight, the ________________ energy in batteries is changed to electric energy and light then to ________________ energy. 7. electric motion (kinetic) energy. In a fan, ________________ energy is changed to ________________ 8. gravitational energy is converted first to When water held behind a dam is released, ________________ (potental) motion (kinetic) energy. ________________ 9. motion (kinetic) energy of flowing water can be used to spin a At a hydropower facility, the ________________ electric turbine and power a generator, creating ________________ energy. 10. light In a photovoltaic panel, the ________________ energy of the sun is converted directly into electric ________________ energy. 11. chemical In a car, the ________________ energy in gasoline is burned to create heat energy, which is motion (kinetic) converted to ________________ energy. 12. chemical In a propane-powered chili roaster, ________________ energy is burned to create heat ________________ energy. 13. electric motion (kinetic) energy is converted to ________________ In a modern wind turbine, ________________ energy. 14. heat chemical A stove uses electric energy or ________________ energy to create ________________ energy. 15. chemical When we run, the ________________ energy stored in our muscles is converted to motion (kinetic) energy. ________________ Energy Transformations ENERGY IN OUR LIVES MODULE FOR GRADES 6 TO 8 55 Forms of Energy O v e r h e a d Tr a n s p a r e n c y (involves motion of some type) light (radiant) energy KINETIC ENERGY LESSON THREE 3 heat (thermal) energy sound energy electric energy POTENTIAL / STORED ENERGY motion (kinetic) energy gravitational (potential) energy chemical energy nuclear energy Energy Transformations 56 ENERGY IN OUR LIVES MODULE FOR GRADES 6 TO 8 LESSON THREE 3 Energy Transformations ENERGY IN OUR LIVES MODULE FOR GRADES 6 TO 8 57