* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Theoretical Genetics Practice Problems The allele for hemoglobin in
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
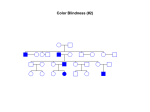
Theoretical Genetics Practice Problems 1. The allele for hemoglobin in sickle cell anemia (HbS) is only different by one base pair from the allele for normal hemoglobin (HbA). To produce the sickle cell allele, at some point in human history a mutation occurred in a gamete and the DNA sequence GAG became GTG because of a base substitution mutation. This caused glutamic acid to be replaced by valine in the protein sequence. This causes the hemoglobin molecule to be misshapen, and therefore the entire erythrocyte to be sickle-shaped. If a person is homozygous for the trait, they do not have sickle cell anemia. If the person is homozygous for sickle cells, they have sickle cell anemia and are likely to die at an early age. If, however, a person is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait, they have both sickled and normal cells, and so can survive normally. The heterozygote is also resistant to malaria and less likely to die from it. Given this information, find out what the possible offspring there are when both parents are heterozygous. Use this information to help you explain why sickle cell trait continues to be present in the gene pool in some areas of the world, despite how terrible sickle cell anemia is for people who have it. 2. A woman with type AB blood is caring for her elderly parents. As she is coordinating their treatment with the doctor, she finds out her father has type A blood and her mother has type O blood. From this information, she thinks she may be adopted. Use Punnett squares to help you decide why she might come to this conclusion. Also, are there any more explanations for what she has found? 3. Color blindness is a sex-linked trait. A woman is pregnant with a son. Her husband is colorblind and so is her father, but none of her mother’s relatives ever have been. What are the chances that her son will be colorblind? Use Punnett squares to help you fully explain your answer.