* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
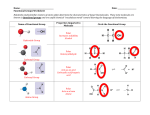
Physical Properties of Organic Compounds PROPERTIES TYPES Alkanes Aliphatic Aromatic Alkenes Aliphatic Aromatic Arenes Benzene Halogen Derivatives Haloalkanes Haloarenes Arenes CH3 EXAMPLE NOMENCLATURE H3C CH3 CnH2n+2 ~e H2C CnH2n Cyclo~e in Mr = More e = more id-id *Branching bp Branched isomer has lower surface area than straight-chain isomer = lower id-id interactions. – BOILING POINT Higher bp than corr. aliphatic alkanes CH3Cl CnH2n CnH2n–2 Presence of cis and trans isomer es with es with g C CH2 g C Similar bp as alkane with same number of C *bp may be slightly higher for cis isomers as the dipole moment do not cancel out = pdpd interactions Higher bp MELTING POINT SOLUBILITY (POLAR SOLVENTS) SOLUBILITY (NON POLAR SOLVENTS) DENSITY Higher bp than corr. aliphatic alkenes (WRT WATER) Variable Higher bp than 6C alkane (69°C) and 6C alkene (63.5°C). Comparable bp with cyclohexane (81°) and cyclohexene (83°C). 5.5°C Higher mp than corr. aliphatic alkanes es with g C Trans–isomers pack better into a regular lattice i.e. higher bp than cis-isomers. Higher mp than corr. aliphatic alkenes Insoluble Insoluble Soluble (CCl4) Soluble Less Dense Less Dense C6H6 Phenyl~ 80°C es with g C M.P affected by how close the molecules can pack together Branchg may mp Though less efficient id-id forces, isomer able to pack into regular arrays (Denser than aliphatic alkanes) Cl Higher mp than 6C alkane (– 95°C) and 6C alkene (–138°C). Comparable mp with cyclohexane (6.5°). Has higher mp than cyclohexene (–104°C) Dependent on e– cloud size (molecular weight) CnH2n+1X Higher bp than corr. alkanes due to larger Mr. (for some also due to presence of pd-pd) Bp es -with size of X. Effect of id-id forces outweigh polarity of bond i.e weaker pd-pd -with more subsn of X Dependent on molecular weight and shape. For isomers, 1,4usually has the highest mp compared to 1,2and 1,3-. More symmetrical molecular fits better into crystal lattice. Insoluble Soluble (acts as solvent) C6H5X Higher mp than corr. alkanes due to larger Mr. Comparable bp to corr. alkyl halides i.e higher bp than corr. alkanes Comparable mp to corr. akyl halides i.e higher bp than corr. alkanes Insoluble (unable to form H bondg with water) Soluble Less Dense Less Dense (Denser than aliphatic alkenes) Less Dense Less Dense Denser nh05 Physical Properties of Organic Compounds PROPERTIES TYPES Hydroxy Compounds Alcohols Phenols Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes Ketones OH EXAMPLE NOMENCLATURE BOILING POINT MELTING POINT SOLUBILITY (POLAR SOLVENTS) SOLUBILITY (NON POLAR SOLVENTS) DENSITY (WRT WATER) H CnH2n+1OH CnH2n+2O Much higher than correspong alkanes.IMF H bondg. Lower alc are liquids at room temp till 12C Factors *Length of Alkyl Chain (id-id) *Branching R C CH3OH C6H5OH 182°C Higher than hexanol (156.5°C) O O C O R R ~al/formyl~ ~one/oxo~ Polar compds. Higher bp than non-polar compds of similar M r. Lower bp than acid and alc. because no H bonding Much higher than correspong alkanes. 41°C Higher than hexanol (–52°C) Lower alc are soluble. Solubility as C due to h.phobic nature Partially soluble in rt due to H bg but has big h.phobic ring. Solubility is enhanced by heating or addition of alkali. Carboxylic Acid & Derivatives Carboxylic A. A. Derivatives Polar compds. Higher mp than nonpolar compds of similar Mr. Lower mp than acid and alc. because no H bonding RCOOH H3C ~oic acid Cl ~yl chloride Higher bp due to H bonding in polar compd. Stronger than alcohol because OH is more polarized (presence of e– carbonyl groups) Higher mp due to H bonding in polar compd. Branching & packing affects mp too. Lower aldehydes and ketones are soluble in water, ability to form H bonding with water C ethanoyl chloride Lower acids are soluble in water Nitrogen Compounds Amines Amides O R N R R C N R R R ~amine/ 1°: ~oic acid ~amide 2°: alkyl on N as sub. amino~ Acid chlorides: Lower bp wrt to carboxylic acid because of its inability to form H bonding. Acid amides: Has –NH2 group and posses IM H bonding. Higher bp. Acid chlorides: Polar, no H Bg Acid amides: Polar, H Bg Acid derivat.s: depend on size Amides & Acid Chloride: soluble Polar compds (ex 3°) can H Bondg. Higher mp than nonpolar compds of similar Mr but lower than alc and carboxylic acid. High bp due to H bondg, usually higher than corr carboxylic acids. (1° or 2°) Higher mp than non-polar compds of similar Mr but lower than alc and carboxylic acid. High mp due to H bondg, usually higher than corr carboxylic acids. Lower amines are soluble due to H Bondg Lower amides are soluble due to H Bondg Soluble (solubility decreases with increasing C for all these compounds) Similar Similar Similar Similar nh05