* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit-4: small signal analysis of amplifiers
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Sound reinforcement system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
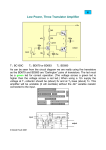
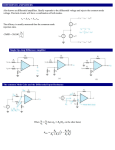
UNIT-4: SMALL SIGNAL ANALYSIS OF AMPLIFIERS 1. Graphically how h-parameters of a BJT are determined? Explain with neat diagram. Also derive expression for input impedance and voltage gain for a BJT amplifier. (10 Marks)(June 2013) At mid or high frequencies, the reactance of the capacitor will be sufficiently small to permit a short- circuit approximation for the element. The voltage Vi will then be related to Vs by At fLS, the voltage Vi will be 70.7% of the value determined by Eq. assuming that Cs is the only capacitive element controlling the low-frequency response.For the network of Fig when we analyze the effects of Cs we must make the assumption that CE and CC are performing their designed function or the analysis becomes too unwieldy, that is, that the magnitude of the reactances of CE and CC permits employing a short-circuit equivalent in comparison to the magnitude of the other series impedances. Using this hypothesis, the ac equivalent network for the input section of Fig. will appear as shown in Fig. The value of Ri for Eq.is determined 2. Give the hybrid equivalent model for the circuit shown, in Fig.Q4(b). Find input impedance, voltage gain, current gain and output impedance. The h-parameters are hie = 1.5k, hje = 100, hre = 110–4, hoe = 25m A/V. (10 Marks)(June 2013) 3. Explain the classification of amplifiers based on their operation. (8 Marks)(Dec 2013) Class A amplifier The power amplifier is said to be class A amplifier if the Q point and the input signal are selected such that the output signal is obtained for a full cycle. For this class, position of the Q point is approx. at the midpoint of the load line. For all the values of the input signal the transistor remains in the active region and never enters into cut off region. When an ac input signal is applied the collector voltage varies sinusoidal hence the collector current also varies. The collector current flows for 360 full cycle of the input signal. Class B amplifier The power amplifier is said to be class B amplifier if the Q point and the input signal are selected such that the output signal is obtained for only one half cycle for a full input cycle. For this operation, the Q point is shifted on X axis, transistor is biased to cut-off. Due to the selection, of Q point on the X axis the transistor remains in the active region only form positive half cycle of the input signal. Hence this half cycle is reproduced at the output. But in a negative half cycle of the input signal the transistor enters into a cut off region and no signal is produced at the output. Class C amplifier The power amplifier is said to be Class AB amplifier, if the Q point and the input signal are selected such that the output signal is obtained for more than 180 but less than 360 for a full input cycle. 4. Draw the DC load line and AC load line for a VDB amplifier. (6 Marks)(Dec 2013) 5. With the circuit diagram explain push pull power amplifier and list the advantages and disadvantages of push pull amplifier. (6 Marks)(Dec 2013) With respect to the center tap, for a positive half cycle of the input signal, the point A shown on the secondary of the driver transformer will be positive. While the point B will be negative, thus the voltages in the two halves of the secondary transformer will be equal with opposite polarity. Hence the input signals applied to base of the transistors Q1 & Q2 will be 180 out of phase. The transistor Q1 conducts for the positive half cycle of the input producing the positive half cycle across the load. While the transistor Q2 conducts for negative half cycle of the input, thus across the load, we get a full cycle for a full input cycle. 6. Derive expression for Ai, Zi, Av, Yo, Ap for a transistor amplifier using h-parameter model (10 Marks) (June 2014) 7. Explain the need for cascading amplifier and with the block diagram, explain two stage cascaded amplifier. (10 Marks)(June 2014) Soln; Need for cascading amplifiers Block diagram of the amplifier Explanation of two stages. 8. Draw the generalized h-parameter model of a transistor based amplifier and derive the expression for Current gain, Input Impedance, Voltage Gain & Output admittance. (8 Marks)(Dec 2014) Ans. The derivation and the figure for the h-parameter model is as shown below… 9. With a neat diagram, Explain the operation of Darlington Amplifier. (6 Marks)(Dec 2014) Ans. 10. What are cascade amplifiers? What are the advantages offered by the amplifier. (6 Marks)(Dec 2014). 11. Explain the need for cascading amplifier and with the block diagram, explain two stage cascaded amplifier. (10 Marks)(June 2015) The voltage gain produced by a signal stage amplifier may not be sufficient for a particular application. In some other cases, the input impedance may be low when the requirement is just opposite or the output impedance may not be of correct magnitude to suit a particular application. In such cases two or more amplifier stages are connected in "cascade". Two stage cascaded amplifier Fig (a) shows the block diagram of two stage cascaded amplifier, these stages are connected such that the output of the first stage is connected to the input of the second stage. As shown in the fig (a) Vi1 is the input of the first stage and V02 is the output of the second stage therefore V02/Vi1 is the overall voltage gain of two stage amplifier and it can be given as So that, we can say the voltage gain of multistage amplifier is the product of voltage gains of the individual stages. 12. Obtain the expression for current gain, input impedance voltage gain, output impedance Power gain of a transistor amplifier using complete h – parameter model. (10 Marks)(June 2015) The figure (a) shows basic amplifier circuit. From the figure (a) we can notice that from a transistor amplifier only it is necessary to connect an external load and signal source, along with proper biasing. Fig (b) represents a transitory in any one of the three possible configurations. We can replace transistor circuit shown in figure (a) with its small signal hybrid model as show in figure (b). Current Gain (Ai) :-For transistor amplifier Ai is defined as the ratio of output to input currents it is given by Current Gain (AIS) :- It is the current gain taking into account the source resistance, RS if the model is driver the current source instead of voltage source, it’s given by. Input impedance (zi):- A show in figure (a) Ri is the input resistance looking into the amplifier Input terminals (1, 11) It is given by. From this equation we can note that input impedance is a function of the load impedance. Voltage Gain (AV): Voltage gain (Avs) :- It is voltage gain including the source. It is given by Output Admissance Yo: It is the ratio of output current I2 to the output voltage V2. It is given by From this equation we can note that output Admissance is function of the source resistance.