* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11 Homework - Digilent Learn site
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Equalization (audio) wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
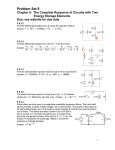
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Homework Chapter 11 Homework: 11.1 For the circuit below, the input voltage Vin(t) = 3cos(2t-20) – 2cos(3t+30) + cos(4t). Determine: a. The steady-state response of the voltage v(t). b. The steady-state response of the current iR(t). (Hint: take advantage of your results from part a) 1Ω iR(t) + + - Vin(t) v(t) 1 F 2 2Ω - 11.2 For the circuit of problem 1, sketch the magnitude and phase response of the voltage v(t). Label your sketch at ω = 0, ω →∞ and the circuit’s cutoff frequency. Does the circuit behave as a lowpass or high-pass filter? Why? 11.3 For the circuit below, the input is the voltage Vin(t). If the output is the current i(t), sketch a straight-line approximation to the Bode plot for the circuit. Label your sketch to include the DC gain and the cutoff frequency of the circuit. i(t) 2Ω 1H + Vin(t) + - 1Ω v(t) - © 2012 Digilent, Inc. 1 Real Analog – Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Homework 11.4 For the circuit below, the input is the voltage u(t) and the output is the current y(t). Sketch a straight-line approximation to the Bode plot. Label your sketch to include the DC gain and the cutoff frequency of the circuit. y(t) u(t) 2Ω + - 1H 11.5 For the circuit of problem 11.4, sketch a straight-line approximation to the Bode plot for the circuit if the output is the voltage v(t). Label your sketch to include the DC gain and the cutoff frequency of the circuit. 11.6 For the circuit shown, the input is the voltage source u(t) and the output is the current through the inductor, y(t). a. Determine the frequency response of the circuit. b. Sketch the magnitude response of the circuit. Label your sketch to show the DC gain and the cutoff frequency of the circuit. c. Does the circuit behave as a high pass or low pass filter? Explain. y(t) 4H u(t) + - 2W © 2012 Digilent, Inc. 4W 2 Real Analog – Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Homework 11.7 For the circuit of problem 1, the input is the voltage source u(t). If the output is the voltage across the inductor, a. Determine the frequency response of the circuit. b. Sketch the magnitude response of the circuit. Label your sketch to show the DC gain and the cutoff frequency of the circuit. c. Does the circuit behave as a high pass or low pass filter? Explain. 11.8 For the circuit shown, the input is the current source u(t) and the output is the current through the inductor, y(t). a. Determine the frequency response of the circuit. b. Sketch the magnitude response and phase response of the circuit. Label your sketch to show the DC gain and the cutoff frequency of the circuit. c. Does the circuit behave as a high pass or low pass filter? Explain. y(t) 2H 2W u(t) 2W 11.9 For the circuit shown, the input is the current source u(t) and the output is the voltage across the 6W resistor, y(t). a. Determine the frequency response of the circuit. b. Does the frequency response you calculated above agree with your expectations as to the circuit’s response at high () and low (0) frequencies? Why or why not? 2W + u(t) 6W y(t) 1 F 4 - © 2012 Digilent, Inc. 3