* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download knee joint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
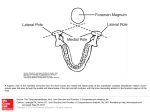
KNEE JOINT •One of the largest and complex joint. •Formed by lateral femorotibial, medial femorotibial and femoropatellar articulations. •Articular surfaces: •Condyles of femur •Condyles of tibia •Patella •LIGAMENTS: •Fibrous capsule: •It is thin and absent anteriorly where it is replaced by the tendon of quadriceps, patella and ligament patellae. •Fibrous capsule (external fibrous layer) Synovial membrane (Internal layer) •Fibrous layer →Make the intrinsic ligaments. •Attached → superior on femur (Proximal to articular area). •Posterior → Covers condyles + intercondylar fossa. •Inferior → margins of tibial plateau. •Coronary ligament and short lateral ligament are the parts of the fibrous capsule: •Fibrous capsule is being strengthened by –Medial and lateral patellar reticula (Anterior) –Iliotibial tract (Lateral) –Sartorius and semimembranous (Medial) –Oblique popliteal ligament (Posterior) •Opening → Leads to supra patellar bursa –Exit for popliteus tendon. •Synovial membrane → All the surface bounding the articular cavity (Joint cavity) Patella and menisci are covered. •Patellar ligament → (anterior ligament of knee joint). Also receives aponeurotic expansions of vastus medialis, vastus lateralis and deep fascia (Medial and lateral pattelar retinacula). •Medial collateral (Tibial collateral ligament → Medial epicondyle of femur to condyle of femur → superior part of medial surface of tibia. •Lateral collateral (Fibular collateral ligament of head of fibula. Lateral epicondyle → lateral surface •Oblique popliteal ligament → Expansion of semimembranosus from medial tibial condyle to lateral femoral condyle. •Arcuate popliteal ligament → Posterior aspect of fibula → spreads to knee joint. •Intra capsular ligament: •Cruciate → Crossing each other •Out side the synovial cavity •Below the capsule •Anterior cruciate ligament: •Anterior intercondylar area of tibia •To posterior surface of medial side of lateral condyle and tibia. Prevents → Posterior displacement of femur. •Posterior cruciate ligament: •Posterior intercondylar area prevents → anterior displacement of femur attached on anterior part of lateral surface of medial condyle •Menisci → Fibro cartilaginous plates deepens the articular surface and play a role in shock absorption. •Coronary ligament portions of joint capsule between the meniscal margins and tibial condyles. •Transverse Ligament → Between the anterior edges of menisci •Anastomosis around knee joint: •Femoral / Sciatic / obturator nerve •Locking and unlocking of knee joint •Flexion → Biceps, Semimembranosus, Semitendinosus, Gracilis, Sartorius, Popliteaus, Gastrocnemius •Extension → Quadriceps femoris, tensor fascia lata. •Medial rotation → Popliteus, semis (Membranosus and tendosus) sartorius gracillis. •Lateral rotation → Biceps femoris •Articular surfaces are not congruent (Tibial condyles are small) •Leg may be abnormally abducted and adducted (Rickets etc). •Osteoarthritis, aspiration of fluid. •Arthroscopy •Injury to mensci, ligaments etc.