* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Circuits
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Fuse (electrical) wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
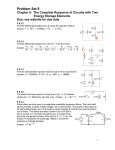
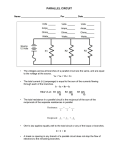
Electric Circuits Series and Parallel Circuits Circuit Diagrams • An electric circuit is a complete path through which charge can flow • Circuit diagrams use symbols to represent parts of a circuit • Circuit diagrams show a source of electrical energy, and devices run by electrical energy Circuit Diagrams • A circuit diagram will show one or more paths for the charge to flow • Switches are where the circuit can be open • An open circuit occurs if a switch is open then the circuit is not a complete loop and the current stops • A closed circuit is when the switch is closed and the circuit is complete Series Circuit • A series circuit has only one path that the charge can flow • If one element in a series circuit stops working then the whole circuit will not work • Each bulb in a series circuit adds resistance and makes all of the bulbs dimmer Parallel Circuit • A parallel circuit is when two or more paths through which the charge can flow • If one element stops working then the charge can flow along another path • This is common in houses Power and Energy • The rate at which electrical energy is converted to another form of energy is electric power • The unit is joule per second or watt (W) • Power is often in kilowatts (kW) • Power = current x voltage or P = I x V • P(watts) = I (amps) x V (volts) Example • An electric oven is connected to a 240 volt line and it uses 34 amps of current. What is the power used by the oven? • Current = I = 34 amps Voltage = V = 240 volts Power = I x V • Power = 34 amps x 240 volts Power = 8160 watts Electrical Safety • There are several things needed to make a house safe such as correct wiring, fuses, circuit breakers, insulation, and grounded plugs • In the US most houses have an average of 120 volts and each device increases the current • If too many devices are used it may cause a fire Home Safety • A fuse prevents current overload in a circuit • A wire in the fuse will melt if there is too much current • This is how we “blow a fuse” • Most houses now use circuit breakers • A circuit breaker is a switch that will open when a current is too high