* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Disease-causing agents such as viruses, bacteria, and protists are
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
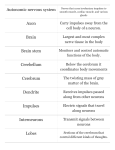
Name ______________________________________________ Date ____________________ Period ________ Unit 2 Exam Multiple Choice: Choose the letter of the response that best answers the question or completes the statement. 1. Disease-causing agents such as viruses, bacteria, and protists are known as a. Antibodies b. Antigens c. Pathogens d. Toxins 2. This type of pathogen infects the host by hijacking the cells. It can not live outside of the host’s cells. a. Bacteria b. Virus c. Protist d. Fungus 3. How are infectious diseases spread? a. through coughing, sneezing, or physical contact b. through contaminated water and food c. by infected animals d. all of the above 4. The mode of disease transmission that can be prevented by washing your hands or covering your mouth when you cough or sneeze is called a. Infected animals b. Physical contact c. Contaminated food/water d. None of the above 5. The body’s most important nonspecific defense system against pathogens is a. Tears b. Mucus c. Saliva d. Skin 6. Your skin is constantly exposed to bacteria and viruses from the air, water, food, and surfaces you come into contact with. The principle (main) reason you are not constantly affected by these pathogens is because a. Phagocytes immediately find them and digest them. b. Antibodies immediately destroy them on contact. c. Your body is immune to all of them already. d. The skin and secretions from your body trap and prevent them from entering the body. 7. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body’s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting phagocytes escape from the body. b. A cut prevents the inflammatory response from occurring. c. A cut provides an entryway into the body for pathogens. d. A cut disables humoral immunity. 8. A nonspecific defense reaction to tissue damage caused by injury or infection is known as a. The inflammatory response b. Active immunity c. Cell-mediate immunity d. Passive immunity 9. The body’s nonspecific defenses against invading pathogens include a. Antibiotics b. Mucus, sweat, and tears c. Antibodies d. White blood cells 10. A substance that triggers an immune response (like an incorrect ID) is a(an) a. Antibody b. Antigen c. B cell d. Pathogen 11. What is the function of white blood cells (phagocytes)? a. They engulf and destroy bacteria. b. The produce antibodies. c. They form a barrier against pathogens. d. They bind to antigens and develop into plasma cells. 12. Physician Edward Jenner injected a boy with fluid from the mild disease cowpox, in hopes that the boy would become immune to the more serious disease smallpox. Later, he injected the same boy with fluid from a smallpox infection, but the boy did not get sick; the experiment was a success. The injection of a weakened pathogen to produce immunity is known as a. An allergic reaction b. A vaccination c. A transplant d. Passive immunity 13. How does vaccination protect the body against disease? a. It suppresses the action of antigens. b. In prevents pathogens from entering the body. c. It stimulates the production of killer T cells. d. It helps your body learn how to fight off a pathogen, before it is exposed to the real one. 14. The following are players in your specific immune system: a. Antibodies, plasma cells, and white blood cells. b. Antibodies, fever, and memory B cells. c. Inflammation, fever, and antibodies. d. Secretions, inflammation, and skin. 15. The HIV virus is especially dangerous to humans because a. It is always transmitted through intravenous drug use. b. It attacks and destroys cells of the immune system. c. It destroys antibodies. d. It does not respond to antibiotics. 16. People with AIDS often die from the common cold or pneumonia. Based upon that information, the most probable explanation for this is that a. Pathogens that cause the common cold and pneumonia have recently become more lethal. b. The common cold and pneumonia are highly contagious and easily contracted. c. AIDS destroys you nonspecific defenses, allowing pathogens for those illnesses to enter your body. d. A person with AIDS has a shortage of white blood cells and helper T cells which would normally fight such pathogens. 17. Which of the following lists the levels of cell organization from least to most complex? a. Organs, cells, organ systems, tissues b. Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems c. Tissues, organs, organ systems, cells d. Cells, organs, organ systems, tissues 18. The way the body maintains homeostasis is often compared to a. A violent thunderstorm that startles people and increases heartbeat. b. A heating system that turns a furnace on and off to control a room’s temperature. c. The monthly cycle that releases an egg from an ovary. d. The period of human development that takes about nine months to be completed. 19. Which process enables the body to maintain a stable temperature? a. Circulation b. Negative feedback c. Respiration d. Positive feedback 20. Which of the following is NOT a part of the circulatory system? a. Heart b. Lungs c. Blood vessels d. Blood 21. The function of the circulatory system is to a. Provide oxygen and remove excess carbon dioxide from the body. b. Bring nutrients and hormones to cells. c. Transport cell waste for removal. d. All of the above. 22. Which body system works with the circulatory system to regulate oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the body? a. Respiratory system b. Nervous system c. Excretory system d. Digestive system 23. Which body system works with the circulatory system to transport waste from cells, to the bladder for removal from the body? a. Respiratory system b. Endocrine system c. Excretory system d. Integumentary system 24. Which system works with the circulatory system to transport nutrients form the intestines, to the other cells in the body? a. Nervous system b. Endocrine system c. Excretory system d. Digestive system 25. The endocrine system a. Affects only the reproductive system. b. Releases hormones into the blood stream. c. Competes with the nervous system. d. Removes waste from the body. 28. When fat cells start to fill up with storage reserves a. Leptin concentration decreases, causing the appetite center in the brain to start the hunger stimulus. b. Leptin is released and binds to the appetite center of the brain, turning off appetite. c. Leptin is unable to bind to the appetite center of the hypothalamus continuing the hunger stimulus. d. Too much leptin is release, giving the feeling of being over-full. 29. People who are obese often lack a. The will power to stop eating. b. The hormone leptin. c. The appetite center of the hypothalamus. d. Receptors for leptin to bind to. 30. Obesity is often due to a. Genetics b. Life-style choices c. Environment d. All of the above 31. What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous system? a. Receptor b. Neuron c. Organ d. Tissue Use the picture below to answer questions 32 and 33. A 26. The region of the brain that recognizes hunger is the a. Brain stem. b. Medulla oblongata. c. Hypothalamus. d. Thalamus. 27. The hormone that controls appetite is a. Leptin b. Pepsin c. Adrenaline d. Estrogen H C F G D E B 32. What is the name of the structure labeled C? a. Axon b. Dendrite c. Myelin Sheath d. Cell Body 33. What is the function of the structure labeled D? a. To transmit impulses from one neuron to the next. b. To regulate neuron activity. c. To insulate the neuron in order to be able to transmit impulses. d. None of the above. 34. The messages that travel through the nervous system are called impulses. What type of signals are those impulses? a. Gravitational b. Electrical c. Light d. Magnetic 35. The function of a motor neuron is to a. Carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord, to the muscles and glands. b. Carry impulses from the muscles and glands to the brain and spinal cord. c. Transmit impulses within the brain only. d. Pick up information from the environment and relay it to the brain. 36. Grabbing and quickly dropping a object that is very hot is a behavior known as a. An instinct. b. Imprinting. c. A reflex. d. Conditioning. _________________________________________ Use the following diagram to answer question 37. _________________________________________ Sensory Neuron Sensory Receptor Motor Neuron Muscle Cell 37. Which of the following is the correct pathway in a reflex arc? a. Muscle cell, sensory receptor, motor neuron, interneuron. b. Sensory receptor, sensory neuron, motor neuron, muscle cell. c. Motor neuron, interneuron, muscle cell, sensory receptor. d. Sensory receptor, muscle cell, motor neuron, sensory neuron. 38. The function of the sensory division of the nervous system is to a. Transmit impulses from the central nervous system, to the muscles or glands. b. Transmit impulses from sense organs (eyes, ears, nose, mouth, skin) to the central nervous system. c. Transmit impulses within the brain only. d. Transmit impulses between the brain and spinal cord. 39. Two functions in the body that would be controlled by the autonomous nervous system would be a. Moving the arms and legs. b. Breathing and walking. c. Regulating the heart and digestive system. d. Running. 40. What is the function of neurotransmitters? a. To transmit nerve impulses through dendrites. b. To stimulate the production of epinephrine. c. To transmit nerve impulses across synapses. d. None of the above. Name ______________________________________________ Date ____________________ Period ________ Unit 1: Reproving of Mastery Multiple Choice: Choose the letter of the response that best answers the question or completes the statement. 41. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells a. are much smaller. b. have permeable membranes. c. have a higher rate of reproduction. d. have a nucleus 42. All cells of green plants have a. Cell membranes but no cell walls. b. Cell walls but no cell membranes. c. Cell walls and cell membranes. d. Cell walls or cell membranes. 46. All of the following processes require the cell to use energy EXCEPT a. Endocytosis b. Exocytosis c. Active transport d. Osmosis Directions: Use the information given below to answer question 7. Cellular respiration: 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy Photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 A B C E D G F 43. What is the function of the structure labeled C? a. It stores water, salts, proteins, etc. for the cell. b. It produces most of the energy the cell needs. c. It controls most cell processes and contains genetic information. d. It produces proteins. 44. Studies of two different types of cell show that Cell A has fewer mitochondria than Cell B. A biologists would most likely infer that Cell A a. Does not require energy. b. Has an energy requirement equal to those of Cell B. c. Requires less energy than Cell B. d. Requires more energy than Cell B. 45. Which of the following in NOT a macromolecule? a. Salt b. Protein c. Carbohydrate d. Nucleic acid 47. Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between cellular respiration and photosynthesis? a. The products of each provide the reactants needed for the other. b. The products of both reactions are the same. c. The reactants for one process are the same as the reactants for the other. d. There is no relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. 48. Enzymes are ___________________ that catalyze chemical reactions within cells. a. Vitamins b. Proteins c. Nucleic acids d. Carbohydrates 49. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions in cells because they a. Increase the activation energy of the reaction. b. Increase the amount of energy stored in the products. c. Decrease the activation energy of the reaction. d. Decrease the amount of energy stored in the products. 50. The cell structure responsible for the movement of substances into and out of the cell is the a. Cell wall. b. Cell membrane. c. Ribosome. d. Nucleus.