* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Work of Gregor Mendel - OG
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
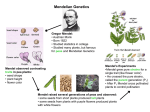
Name _________________________________________________ Period____________ The Work of Gregor Mendel – 1. What is genetics? 2. Who was the founder of the field of genetics? 3. What were his three main professions? Gregor Mendel and His Peas – 4. How did Mendel become interested in plants and how did this help him with his work as a scientist? 5. Name the 7 traits (characteristics) of the pea plant that Mendel studied and the 2 contrasting traits for each: Characteristic a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Contrasting Traits 6. How did Mendel end up with a stock of plants that were all identical to their parent plant? 7. What does “true breeding” mean? 8. What is the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination? 9. Why did Mendel want to cross-pollinate his pure strains of pea plants? 10. How did Mendel prevent self-pollination when he wanted to cross-pollinate certain pea plants? 11. What is a hybrid? 12. What did Mendel call the original pair of plants in a genetic cross? What did Mendel call the offspring of that generation? 13. What is the difference between a gene and an allele? Give an example 14. Mendel came up with the Principle of Dominance. What does this principle tell us about what traits we see (or don’t see) in any given organism? 15. Take a look at Figure 11-3 and write the results in the table below. The first is done for you as an example. Characteristic P Cross F1 Generation _______ x _______ 1. Seed shape Round x Wrinkled Round 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Mendel’s Results & Conclusions16. When Mendel crossed a pure green pod plant with a pure yellow pod plant, what were the results? 17. What happens when a trait controlled by a recessive allele is paired with a dominant allele? 18. What do capital letters refer to, and what do lower case letters refer to? 19. Mendel crossed a tall plant (Tt) with another tall plant (Tt) and ended up with 75% tall plants and 25% short plants. Why didn’t he end up with 100% tall plants? 20. Match the vocabulary term from the right to its correct description on the left 1. ____ Sex cells A. Parental 2. ____ Different forms of a gene B. Fertilization 3. ____ Heritable characteristics C. Alleles 4. ____ Offspring of crosses between parents of differing traits D. Gametes E. Traits 5. ____ Process in which 2 reproductive cells join and a new cell develops F. Genes 6. ____ Factors passed from parent to offspring H. Hybrid G. First filial I. Segregation 7. ____ P generation 8. ____ F1 generation 9. ____ Alleles separate during gamete formation