* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Week 2 - Humble ISD
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
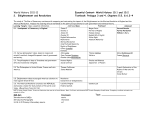
World History FORTH SIX WEEKS CALENDAR: January 3 - February 24, 2012 DATE Week 1 1/2 1/3 1/4/5 1/6 Week 2 1/9 1/10 1/11/12 1/13 Week 3 1/16 1/17 1/18/19 1/20 Week 4 1/23 1/24 1/25/26 1/27 Week 5 1/30 1/31 2/1/2 2/3 Week 6 2/6 2/7 2/8 - 2/9 2/10 Week 7 2/13 2/14 2/15/16 2/17 DAILY TOPICS for LECTURE/DISCUSSION CLASS/HOMEWORK Inservice Conclusion Unit 4 Connecting Hemispheres 1450-1750 Scientific Revolution Intro Scientific Revolution - New ideas in astronomy, medicine, thinking, philosophy Intro Unit 5 1750- 1914 Age of Revolutions Enlightenment Background (Locke & Newton forerunners of Enlightment) Enlightenment in politics, religion, economy Voltaire, Montesquieu, Rousseau, Blackstone Enlightenment in politics, religion, economy Voltaire, Montesquieu, Rousseau, Blackstone Flex Day American Revolution MLK Day American Revolution Assessment #1 – Scientific Revolution/Enlightenment/American Revolution Intro French Revolution French Revolution – National Assembly Primary source analysis Groups Study for test French Revolution – Legislative Assembly French Revolution – National Convention/Reign of Terror French Revolution – Thermidorian Reaction/Directory Rise of Napoleon Demise of Napoleon; Congress of Vienna Congress of Vienna Assessment #2 French Revolution Industrial Revolution – Why England? Spread of Industrial Revolution onto continent Human/social impact of Industrial Revolution Economic theories coming out or Industrial Revolution Classical Economics, Utopian Socialism, Communism Efforts of Reform – politically, economically, socially Second Industrial Revolution; New Ideas in Science, Philosophy Assessment #3 w/CBA Industrial Revolution Revolutions, War, Unification– Europe American Civil War Study for test TEKS for Fourth Six Weeks AD 1450 to AD 1750: Identify major causes and describe the major effects of the following events: the Enlightenment’s impact on political ideas Explain the impact of the Ottoman Empire on Eastern Europe and global trade Explain Ming China’s impact on global trade Identify the origin and diffusion of major new ideas in mathematics, science, and technology that occurred from 1450 to 1750, specifically the impact of the printing press Describe the origins of the Scientific Revolution in 16th- century Europe and explain its impact on scientific thinking worldwide Identify the contributions of significant scientists such as, Copernicus, Galileo, Isaac Newton, and Robert Boyle. Compare the causes, characteristics, and consequences of major political revolutions since the 17th century, including the American and French emphasizing the role of the Enlightenment, the Glorious Revolution, and religion Identify the impact of political ideas contained in the English Bill of Rights Identify the influence of ideas such as separation of powers, checks and balances, liberty, equality, democracy, popular sovereignty, human rights, constitutionalism, and nationalism on political revolutions Identify the historical origins and characteristics of the free enterprise system including the contributions of Adam Smith Explain the political philosophies of John Locke, Thomas Hobbes, Voltaire, Charles de Montesquieu, Jean Jacques Rousseau AD 1750-1914 Compare the causes, characteristics, and consequences of the American and French Revolutions, emphasizing the role of the Enlightenment, and religion Identify the impact of political and legal ideas contained in the following significant historic documents: including, the Declaration of Independence, the U.S. Constitution, and the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen Explain the impact of Napoleon Bonaparte and the Napoleonic Wars on Europe and Latin America Trace the influence of the American and French revolutions on Latin America, including the role of Simón Bolivar Explain how 17th and 18th century European scientific advancements led to the Industrial Revolution Explain how the Industrial Revolution led to political, economic, and social changes in Europe Explain role of textile manufacturing and steam technology in initiating the Industrial Revolution and the role of the factory system and transportation technology in advancing the Industrial Revolution Identify important changes in human life caused by the Industrial Revolution Summarize the role of economics in driving political changes as related to the Industrial Revolution Identify the historical origins and characteristics of communism (scientific socialism), including the influences of Karl Marx Identify the historical origins and characteristics of utopian socialism William Blackstone Simon Bolivar Napoleon Bonaparte Marie Curie Required Historical Personalities Thomas Edison Albert Einstein Thomas Jefferson Louis Pasteur Queen Victoria Adam Smith James Watt William Wilberforce World History FIFTH SIX WEEKS CALENDAR: February 20 – April 13, 2012 DATE Week 1 2/20 2/21 2/22/23 2/24 Week 2 2/27 2/28 2/29 – 3/1 3/2 Week 3 3/5 3/6 3/7 3/8 3/9 DAILY TOPICS for LECTURE/DISCUSSION CLASS/HOMEWORK Student Holiday American Civil War Assessment #1 Revolutions and War Lecture: Events of the late 19th Century and the Ism’s Flex Day Causes of “New “ Imperialism; Imperialism in Africa Imperialism in India and Southwest Asia Imperialism in Latin America Imperialism in China ELA TAKS – March 7 Imperialism in Japan Assessment #2 Imperialism ELA TAKS Intro to Unit 6 – 20th Century to Present Long-term causes of World War I Study for test Spring Break March 12-16, 2011 Week 4 3/19 3/20 3/21/22 3/23 Week 5 3/26 3/27 3/28/29 3/30 Week 6 4/2 4/3 4/4/5 4/6 Week 7 4/9 4/10 4/11/12 4/13 Immediate Causes of World War I; Stalemate Total War: Life in the Trenches & on the Homefront 1917: Turning Point in the War – Russian Revolution; U.S. enters War Armistice – Treaty of Versailles STAAR Testing – English I & III Consequences of Treaty Assessment #3 World War I Europe: Uneasy Peace – 1920 - 1930 Cultural and Intellectual Trends of the 1930’s 1920’s – 1930’s Africa, Asia and Latin America Flex Day Assessment #4; CBA #5 Good Friday Student Holiday Path to World War II Major Events of World War II – Europe, including Holocaust Major Events of World War II -- Asia Study for test Study for test TEKS for Fifth Six Weeks AD 1750-1914 Identify the major political, economic, and social motivations that influenced European imperialism in the late 19th century Explain the roles of military technology, transportation technology, communication technology, and medical advancements in initiating and advancing 19th century imperialism Explain the major characteristics and impact of European imperialism in the late 19th century Describe the specific changing roles of women, children, and families from 1750 to 1914 Identify significant examples of art and architecture that demonstrate an artistic ideal or visual principle from 1750 to 1914 Identify the origin and diffusion of major new ideas in mathematics, science, and technology that occurred from 1750 to 1914 AD 1914 to the present Identify major causes and describe the major effects of the following events the world wars and their impact on political, economic, and social systems Identify the importance of imperialism, nationalism, militarism, and the alliance system in causing World War I Identify major characteristics of World War I, including total war, trench warfare, modern military technology, and high casualty rates Explain the political impact of Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points and the political and economic impact of the Treaty of Versailles, including changes in boundaries and the mandate system Identify examples of politically motivated mass murders in Armenia Identify the causes of the February (March) and October (November) revolutions of 1917 in Russia, their effects on the outcome of World War I, and the Bolshevik establishment of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. Identify the historical origins and characteristics of fascism Describe the emergence and characteristics of totalitarianism Summarize the international, political, and economic causes of the global depression Explain the responses of governments in the United States, Germany, and the Soviet Union to the global depression Explain the significance of the League of Nations Explain the roles of various world leaders, including Benito Mussolini, Adolf Hitler, Hideki Tojo, Joseph Stalin, Franklin D. Roosevelt, and Winston Churchill , prior to and during World War II Explain the major causes and events of World War II, including the German invasions of Poland and the Soviet Union, the Holocaust, Japanese imperialism, the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Normandy landings, and the dropping of the atomic bombs Identify the Holocaust Summarize how the outcome of World War II contributed to the development of the Cold War Explain the effects of major new military technologies on World War I and World War II Required Historical Personalities: Winston Churchill Adolf Hitler Benito Mussolini Franklin D. Roosevelt Joseph Stalin Hideki Tojo Woodrow Wilson Mao Zedong World History SIXTH SIX WEEKS CALENDAR: April 16 – May 31, 2012 DATE Week 1 4/16 4/17 4/18/19 4/20 Week 2 4/23 – 4/27 Week 3 4/30 5/1 5/2/3 5/4 Week 4 5/7 5/8 5/9/10 5/11 Week 5 5/14 5/15 5/16/17 5/18 Week 6 5/21 5/22 5/23/24 5/25 Week 7 5/28 5/29 5/30 5/31 DAILY TOPICS for LECTURE/DISCUSSION CLASS/HOMEWORK End of War and its Aftermath (Cold War) Study for test Assessment #1 World War II TAKS Review TAKS Review TAKS Week Topics for the week: Cold War – Major events, including Korean War, Vietnam, arms race Development of communism in China Collapse of communism in Soviet Union and Eastern Europe Independence movements in Africa, Middle East, and South Asia Arab-Israeli Conflicts; Development of radical Islamic fundamentalism Flex Day Assessment #2; CBA #6 Review STAAR Window 5/7-5/18; 5/19 STAAR Make-up Review Review Review Review Study for test Enrichment Activities to count as Assessment #3 Enrichment Enrichment Enrichment Review for finals Review for finals Review for finals Final exams Holiday Final exams Final exams Final exams TEKS for Sixth Six Weeks AD 1914 to the present Explain the significance of the League of Nations Explain the roles of various world leaders, including Benito Mussolini, Adolf Hitler, Hideki Tojo, Joseph Stalin, Franklin D. Roosevelt, and Winston Churchill , prior to and during World War II Explain the major causes and events of World War II, including the German invasions of Poland and the Soviet Union, the Holocaust, Japanese imperialism, the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Normandy landings, and the dropping of the atomic bombs Identify the Holocaust Summarize how the outcome of World War II contributed to the development of the Cold War Explain the effects of major new military technologies on the Cold War Identify major causes and describe the major effects of the following events: communist revolutions and their impact on the Cold War independence movements globalization Summarize the factors that contributed to communism in China, including Mao Zedong’s role in its rise, and how it differed from Soviet communism Identify the following major events of the Cold War, including the Korean War, the Vietnam War, and the arms race Explain the roles of modern world leaders, including Ronald Reagan, Mikhail Gorbachev, Lech Walesa, and Pope John Paul II , in the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union Summarize the rise of independence movements in Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia. and reasons for ongoing conflicts Explain how Arab rejection of the State of Israel has led to ongoing conflict Summarize the development and impact of radical Islamic fundamentalism on events in the second half of the 20th century , including Palestinian terrorism and the growth of al Qaeda Explain the U.S. response to terrorism from September 11, 2001, to the present Summarize the economic and social impact of 20th century globalization Explain why communist command economies collapsed in competition with free-market economies at the end of the 20th century Formulate generalizations on how economic freedom improved the human condition , based on students’ knowledge of the benefits of free enterprise in Europe’s Commercial Revolution, the Industrial Revolution, and 20th century free-market economies compared to communist command communities Explain the significance the United Nations Identify examples of politically motivated mass murders in Cambodia, China, Latin America, and the Soviet Union Identify examples of genocide, including genocide in the Balkans, and Rwanda , and Darfur Identify examples of individuals who led resistance to political oppression such as Nelson Mandela, Mohandas Gandhi, Natan Sharansky, Las Madres de la Plaza de Mayo, and Chinese student protestors in Tiananmen Square Assess the degree to which American ideals have advanced human rights and democratic ideas throughout the world Describe the specific changing roles of women, children, and families from 1914 to the present Identify significant examples of art and architecture that demonstrate an artistic ideal or visual principle from 1914 to the present Identify the origin and diffusion of major new ideas in mathematics, science, and technology that occurred from 1914 to the present Describe the political, economic, and cultural major influences of women such as Mother Teresa, Indira Gandhi, Margaret Thatcher, and Golda Meir Explain the roles of telecommunication technology, computer technology, transportation technology, and medical advancements in developing the modern global economy and society Required Historical Personalities: Winston Churchill Indira Gandhi Mohandas Gandhi Mikhail Gorbachev Nelson Mandela Golda Meir Mother Teresa Pope John Paul II Ronald Reagan Oscar Romero Natan Sharansky Margaret Thatcher Lech Walesa Mao Zedong