* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the circulatory system
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
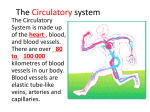
Circulatory System Recall: Cellular respiration: the process of a cell converting glucose into energy. Oxygen is an important reactant required for this process: C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + energy Circulatory System: MAIN FUNCTIONS 1. Transport substances around the body a. oxygen (needed for cellular respiration) and carbon dioxide b. nutrients (e.g. from intestines) and wastes (e.g. to kidneys) c. hormones d. infection-fighting white blood cells and chemicals from immune system 2. Regulate body temperature COMPONENTS: 1. Heart 2. Blood vessels 3. Blood 1. Heart : made up of cardiac muscle, nerve, and connective tissues pumps blood through the body tissues and inner surface covered by epithelial tissues to protect heart from damage and allow blood to flow freely. 2. Blood has 2 main components a. Plasma (55%) b. Blood cells (45%) – red (transport oxygen) – more 43% - white (infection-fighting) – 1% - platelets (help in blood clotting) – 1% 3. Blood Vessels: a. Arteries: carry blood away from heart. Have thick walls b. Veins: carry blood towards the heart. Walls are not as thick. c. Capillaries: link arteries and veins together tiny blood vessels. Very thin walls allow substances to diffuse between the blood and other body fluids and tissues. Overall: oxygen diffuses through capillaries from the lung into the bloodstream heart pumps oxygenated blood through arteries into the capillaries where the oxygen (and other important substances) diffuse through the capillaries to the surrounding tissues. blood then absorbs carbon dioxide and other substances through the capillaries and travel back to the heart and eventually diffuses back into the lungs which then realease it into the air. Heart Diseases: Coronary artery diseases: artery can become blocked by deposits of fat, cholesterol, etc Blood (with oxygen) cannot get to heart muscle – heart can stop pumping (heart attack) Cause can be genetic or poor diet, exercise, or habits COMPONENTS: 1. Heart : discuss later 2. Blood has 2 main components c. Plasma (55%) d. Blood cells (45%) – red (transport oxygen) – more 43% - white (infection-fighting) – 1% - platelets (help in blood clotting) – 1% 3. Blood Vessels: a. Arteries: carry blood away from heart. Have thick walls b. Veins: carry blood towards the heart. Walls are not as thick. c. Capillaries: link arteries and veins together tiny blood vessels. Very thin walls allow substances to diffuse between the blood and other body fluids and tissues. Overall: oxygen diffuses through capillaries from the lung into the bloodstream heart pumps oxygenated blood through arteries into the capillaries where the oxygen (and other important substances) diffuse through the capillaries to the surrounding tissues. blood then absorbs carbon dioxide and other substances through the capillaries and travels back to the heart through veins and which pumps it to capillaries in lungs and CO2 diffuses back into the lungs which then release it into the air. The Mammalian Heart Heart consists of 2 parallel pumps separated by a septum Left atrium and right atrium contract and send blood to ventricles Left and right ventricles contract and send blood to lungs and body Left side receives oxygenated blood from lungs and pumps it to cells of body Right side receives deoxygenated blood and pumps it to lungs Valves prevent back flow into the heart when it pumps The Circulatory System (Section 3.4) 1. State what other systems the circulatory system interacts with when it transports a) oxygen and carbon dioxideb) waste substances2. Blood is considered a _______________________ tissue. 3. Why are the walls of arteries thicker than veins? 4. Why do the walls of the capillaries need to be very thin? Heart 5. Heart tissue is made up of all 4 tissue types. a) What is unique about cardiac muscle? b) What are 3 purposes of the epithelial tissue in the heart? Coronary Artery Disease 6. a) What happens to the blood vessels in this disease b) What factors affect plaque build-up? c) What are the symptoms of this disease? d) How can it be diagnosed? e) What is a heart attack? Other: 7. Answer pg. 87 #1-9 The Mammalian Heart Heart consists of 2 parallel pumps separated by a septum Left atrium and right atrium contract and send blood to ventricles Left and right ventricles contract and send blood to lungs and body Left side receives oxygenated blood from lungs and pumps it to cells of body Right side receives deoxygenated blood and pumps it to lungs Valves prevent back flow into the heart when it pumps Overheads: digestive track, circulatory diagrams and notes Heart? Photocopy: circulatory handout + diagrams SNC2D: -take up homework on digestive system (5 min) -make note on digestive system (10 min) -have them copy the table on pg. 76 down -when done have them do – diffusion activity - tissue exercise – talk about diffusion -talk about cellular respiration? - videos on mitosis/cancer? Wed: circulatory system Thurs: videos on mitosis/cancer Finish heart? SNC2DG: Take up homework Have them read 3.4 and do handout Take notes + discuss diagrams Maybe video? Wed: video? Talk about the heart? Start respiratory system?