* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Guide for Body Systems and Cells Test
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
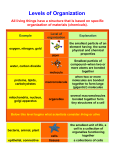
Review Guide for Body Systems and Cells Test 7.12 B Student Expectation The student is expected to identify the main functions of the systems of the human organism, including the circulatory, respiratory, skeletal, muscular, digestive, excretory, reproductive, integumentary, nervous, and endocrine systems. Key Concepts Key Concept 1: The circulatory system circulates blood through the body, supplies cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes waste products. Key Concept 2: The respiratory system supplies blood with oxygen in the lungs and removes carbon dioxide. Key Concept 3: The skeletal system holds organs in place, provides a structural support for the body and its muscles, stores minerals and contains materials to make new blood cells. Key Concept 4: The muscular system allows the body to move when attached to bone, and allows movement in internal organs such as the heart and intestines. Key Concept 5: The digestive system converts food into simpler substances for the body to absorb as nutrients. Breakdown of food also provides energy for all body functions. Key Concept 6: The excretory system filters water and fluids from the blood while also collecting waste urine. Key Concept 7: The reproductive system allows humans to continue as a species by fertilizing a female ovum with a male sperm through sexual reproduction. Key Concept 8: The reproductive system allows humans to continue as a species by fertilizing a female ovum with a male sperm through sexual reproduction. Key Concept 9: The integumentary system continuously receives communication with the external environment (temperature, humidity, etc.) and protects the body’s deeper tissues. It excretes waste, helps rid the body of heat and synthesizes vitamin D. Key Concept 10: The nervous and endocrine systems work together and are the body’s two systems for control and communication. The nervous system sends immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. The endocrine system sends signals in the form of hormones to the body but more slowly than the nervous system. The endocrine system controls growth, reproduction and metabolism. Key Concept 11: The immune system responds to pathogens and provides defenses to the body’s systems from disease. 7.12 C Student Expectation The student is expected to recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. Key Concepts Key Concept 1: Groups of cells, the smallest living units of a plant or animal, form tissues. Tissues with similar structures and functions form organs. Key Concept 2: Organ systems are the result of various organs working together. Key Concept 3: Organisms are the sum of all levels of organization operating together. 7.12 D Student Expectation The student is expected to differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole. Key Concepts Key Concept 1: Eukaryotic plant and animal cells contain organelles that perform specific tasks for the cell’s metabolism and growth. Key Concept 2: Both plant and animal cells contain cell membranes, a nucleus that contains the chromosomes, mitochondrion (creates energy), and cytoplasm (structure and metabolism). Key Concept 3: In addition to the organelles also found in animal cells, plant cells contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis, a large central vacuole (chemical storage) and a cell wall (protection and structure). 7.12 EF Student Expectation The student is expected to compare the functions of a cell to the functions of organisms such as waste removal AND recognize that according to cell theory all organisms are composed of cells and cells carry on similar functions such as extracting energy from food to sustain life. Key Concepts Key Concept 1: Each organelle has a different and specific job that the others rely on for the total survival of the cell, like the waste removal role of the lysosome. Key Concept 2: The function of each organelle’s essential task can be compared with the functions of organisms to obtain energy, such as the “power factories” of mitochondria and the “storage facilities” of endoplasmic reticulum. Key Concept 3: Cells make up all living organisms, unicellular or multicellular, and have similarities in structure cells and all cells need genetic and environmental information in order to and function. The cell theory states that new cells come from old survive. Key Concept 4: Cells use a series of chemical reactions to break down nutrients in food to create energy and produce waste through a process called metabolism. Key Concept 5: Cellular respiration is the process of breaking down carbohydrates, fats and proteins to release energy that can be delivered to each cell of the organism. Plant cells use photosynthesis to convert sunlight into oxygen and energy for consumption by other organisms. ****Complete and study concept maps ****Complete and study Post-Assessment questions on StemScopes for the above units. YOU WILL SEE THEM AGAIN!!!!!!! ****Be sure you know the functions of each cell organelle, each body system and be able to compare the functions of the systems to the cell organelles.