* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download College of Business Administration
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
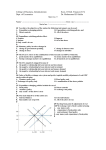
College of Business Administration Dept. of Economics Econ. Of Intl. Finance (315) Dr. Mohammed El-Sakka Quiz no. 5 Name \ -------------------------------------------------------------Univ. no.\-------------------Serial no. \ -----------------------1. The IS curve is negatively inclined because: a. the higher is the rate of interest the smaller is the quantity of money demanded for speculative purposes b. higher rates of interest lead to greater capital flows *c. at lower interest rates the levels of investment and national income are higher d. at lower interest rates the level of national income is lower 2. If the BP curve is above the point of intersection of the IS and LM curves, the nation will: *a. have a balance of payments deficit at that level of income b. have a balance of payments surplus at that level of income c. be in recession d. face inflation 3. To correct unemployment from a condition of external balance, a nation will usually have to use: a. expansionary fiscal policy only b. easy monetary policy only c. expansionary fiscal policy and easy monetary policy *d. expansionary fiscal policy and tight monetary policy 4. In a world of perfectly elastic international capital flows and fixed exchange rates: a. fiscal policy is completely ineffective *b. monetary policy is completely ineffective c. both fiscal and monetary policies are completely ineffective d. both fiscal and monetary policies are effective 5. To correct unemployment and a balance of payments deficits with flexible exchange rates and imperfect capital mobility: a. both fiscal and monetary policies are required b. fiscal policy is required c. monetary policy is required *d. either monetary or fiscal policy is required 6. Direct controls refer to: a. tariffs, quotas, and other quantitative restrictions on the flow of international trade b. restrictions on international capital flows c. multiple exchange rates *d. all of the above 7. Expenditure changing policies include the use of a. fiscal policy b. Direct controls c. monetary policy d. exchange rate policy e. only a and c of the above is true e 8. The main objectives of the nation are: a. Internal balance b. External balance b. Reasonable rate of growth d. All of the above is true D Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Q7 Q8 1. Starting from point E, adjustment of real GDP in the above graph is achieved by using: a. tight money and contractionary F. policy b. easy money and contractionary F policy c. expansionary fiscal policy only e. tight money and expansionary fiscal policy d 2. At point E, given MPM =.25, there is a. deficit of 75 b. deficit of 500 c. deficit of 15 d. none of the above d 3. If capital flows are less elastic with respect to interest rates, the new interest rate would be: a. 7% b. 4% c. 10% d. none of the above c 4. If MPM is .15, at point E there is a: a. BOP surplus of 45 b. BOP deficit of 45 c. BOP deficit of 75 d. BOP surplus of 75 c 5. Starting from point E, adjustment of real GDP in the above graph is achieved by using: b. tight money and expansionary F. policy b. easy money and expansionary F. policy c. expansionary F. policy and tight money d. contractionary F. iscal policy b 6. If the BP line perfectly elastic and exchange rate is fixed, adjustment of real GDP could be achieved by: a. easy money only b. expansionary fiscal policy only c. contractionary fiscal policy d. easy money and expansionary fiscal policy b 7. If the BP line perfectly elastic and exchange rate is flexible, adjustment of real GDP could be achieved by: a. easy money only b. expansionary fiscal policy only d. contractionary fiscal policy d. easy money and expansionary fiscal policy a Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6



![[MT445 | Managerial Economics] Unit 9 Assignment Student Name](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001525631_1-1df9e774a609c391fbbc15f39b8b3660-150x150.png)